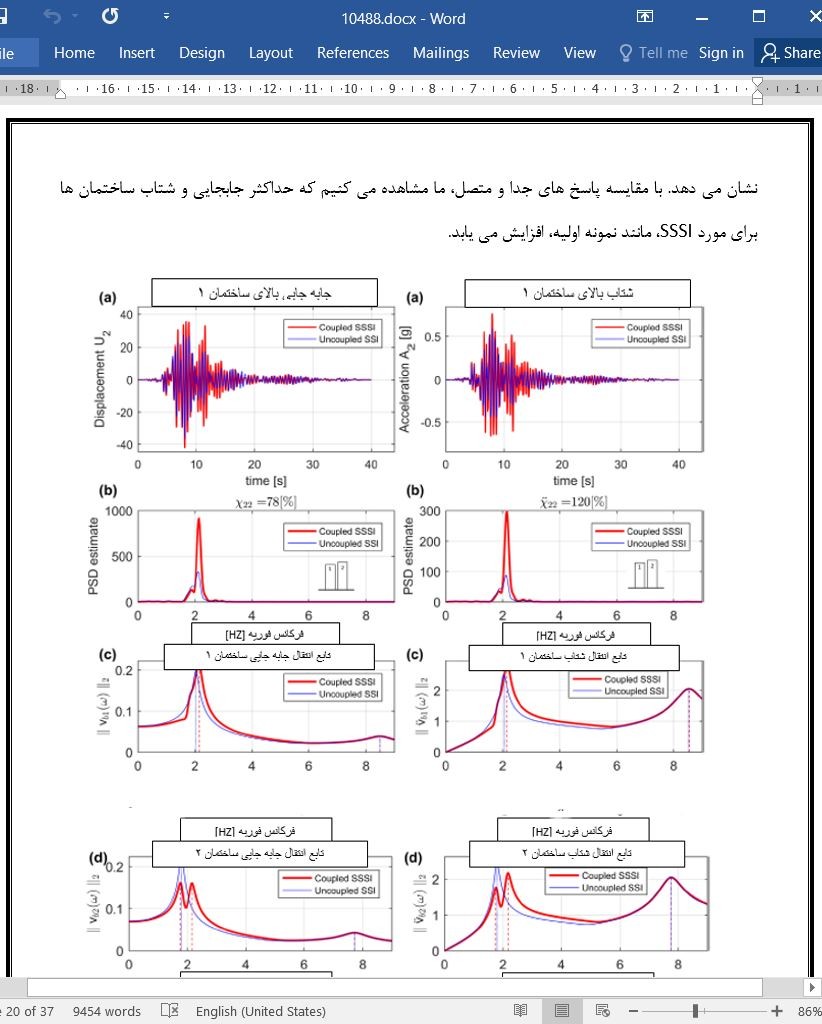
اندرکنش سازه - خاک - سازه لرزه ای با مودهای بالاتر بین ساختمان های مجاور در طی زلزله
چکیده
اين مقاله اثر اندرکنش سازه- خاک - سازه (SSSI) بين دو ساختمان تحت تحریک لرزه ای را با توجه به پارامترهاي مختلف ساختمان ها، فاصله بين ساختمان ها و نوع خاك بررسي می کند. یک مدل ساده شده قابل تعمیم با درجه کاهش یافته، که امکان اندرکنش مود بالاتر بین سازه ها را فراهم می کند، پیشنهاد شده است. این امر باعث اکتشاف تعامل بین ساختمان ها با تفاوت بسیار زیاد در ارتفاع می شود. یک پایگاه داده از سوابق حرکات شدید زمین با مشخصات میدان دور، میدان نزدیک بدون پالس و میدان نزدیک پالس گونه استفاده شده است. بیش از 3 میلیون مورد حرکت سیستم/زمین در این مطالعه پارامتری گسترده مورد آنالیز قرار گرفته است. نتایج نشان می دهد که این مدل گسترده، تعاملات قابل توجهی در واکنش های جابجایی برای مواردی مانند یک ساختمان کوچک نزدیک به یک ساختمان بسیار بلندتر را در بر می گیرد.
1. مقدمه
در طی یک زلزله، سازه های کشوری با خاک اطراف زیر پایه های خود تعامل دارند. این سازه ها به طور معمول (به صورت دینامیکی) به عنوان سازه های تک یعنی بدون توجه به سازه های مجاور خود، مورد آنالیز قرار می گیرند. این پدیده به عنوان اندرکنش سازه خاک (SSI) شناخته شده و اهمیت توجه به اثرات مفید و یا مضر ساختاری آن بیش از 40 سال مورد توجه بوده است. با این وجود، وجود تراکم بالای ساختمان ها در شهرهای بزرگ به ناچار منجر به ایجاد تعامل لرزه ای ساختمان های مجاور از طریق خاک زیرین می شود. این مسئله بیشتر به عنوان اندرکنش سازه- خاک - سازه (SSSI) شناخته شده و در سال های اخیر توجه بیشتری به آن شده است. آثار پیشگام Luco و Contesse [1]، Kobori و همکاران [2]، Lee و Wesley [3]، Murakami و Luco [4]، Wong و Trifunac [5]، Lysmer و همکاران [6]، و Roesset و Gonzales [7] بر پیچیدگی مسئله تاکید کرده و اهمیت توجه به اتصال پویا میان چند سازه را بررسی کرده اند. برخی مطالعات تجربی اولیه در مقیاس واقعی یا کوچک ارائه شده توسط Mattiesen و MacCalden [8]، و Koroby و همکاران [9] نیز اثرات SSSI را در بر گرفته اند.
Abstract
This paper evaluates the effect of Structure-Soil-Structure Interaction (SSSI) between two buildings under seismic excitation given different parameters of the buildings, inter-building spacing, and soil type. An extended simplified reduced-order model, that enables higher mode interaction between structures, is proposed. This enables the exploration of the interaction between buildings with a very large difference in height. A database of strong ground motions records with Far-Field, Near-Field Without Pulse and Near-Field Pulse-Like characteristics are employed. Over 3 million system/ground motion cases are analysed in this extensive parametric study. The results suggest that the extended model captures significant interactions, in displacement responses, for the cases of a small building closely flanked by a much taller one.
1. Introduction
During an earthquake, civil structures interact with the surrounding soil beneath their foundations. These structures are typically analysed (dynamically) as singleton structures, i.e. without any consideration of their neighbouring structures. This phenomenon is widely known as Soil-Structure Interaction (SSI), and the importance of including its beneficial or adverse structural effects has been the focus of attention for more than 40 years. Nevertheless, the existence of a high density of buildings in large cities inevitably results in the possibility of seismic interaction of adjacent buildings through the underlying soil. This problem is better known as Structure-Soil-Structure Interaction (SSSI) and has received more attention in recent years. The pioneering works of Luco and Contesse [1], Kobori et al. [2], Lee and Wesley [3], Murakami and Luco [4], Wong and Trifunac [5], Lysmer et al. [6], and Roesset and Gonzales [7] have emphasized the complexity of the problem and have investigated the importance of considering the dynamic coupling between several structures. Some early experimental studies at real or small scaled conducted by Mattiesen and MacCalden [8], and Koroby et al. [9] have also captured the SSSI effects.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
1.1: اهداف
2. یک مدل نظری با درجه کاهش یافته برای SSSI
2.1. معادلات غیر بعدی حرکت
2.2 کاهش تعداد پارامترهای سیستم
2.3 تعیین معیارهای عملکرد سیستم
3. آنالیز
3.1 انتخاب حرکت زمین
3.2 پاسخ سیستم برای مجموعه ای از پارامترها
3.3. تغییر در توان با تغییر در نسبت ابعاد ε و نسبت ارتفاع s
3.4. تغییر در توان با توجه به تغییر در نوع خاک و فاصله میان ساختمان z
4. نتیجه گیری
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
1.1. Aims
2. A theoretical reduced order model for SSSI
2.1. Non-dimensional equations of motion
2.2. Reducing the number of system parameters
2.3. Defining system performance measures
3. Analyses
3.1. Ground motion selection
3.2. Response of the system for a set of parameters
3.3. Change in power with variation in aspect ratio ε and height ratio s
3.4. Change in power due to variation in soil type and inter/building spacing z
4. Conclusion
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه