دانلود مقاله امنیت انتقال داده های مبتنی بر SDN برای اینترنت اشیا
چکیده
رشد بالقوه دستگاه های متصل به شبکه منجر به توسعه کاربردهای اینترنت اشیا (IoT) جدید و سرویس های آنلاین شده است، که ممکن است نیازمندی های پویا و متنوعی در کیفیت دریافتی داشته باشند. اگرچه، رویکرد شبکه نرم-افزار محور (SDN) نوظهور می تواند به طور پویا در محیط IoT برای رسیدن به سطح های کیفیت متفاوت برای وظایف IoT مختلف در سناریوهای بی سیم نامتجانس استفاده شود، رابط های باز در SDN می توانند حملات شبکه ای جدیدی را ارائه کنند، که ممکن است باعث بد کار کردن IoT مبتنی بر SDN شوند. این چالش ها در استفاده ایمن از SDN برای سیستم های IoT قرار دارند. برای نشان دادن این چالش، ما یک مدل امنیتی انتقال داده مبتنی بر SDN، محافظ تجهیزات (M-G) را طراحی می کنیم. هدف M-G کاهش نهفتگی شبکه و مدیریت مناسب جریان داده برای تضمین کارکرد ایمن شبکه می باشد. ابتدا، براساس سیاست های امنیتی متفاوت، تجهیزات مربوط به سیاست های امنیت محور در مناسب ترین مکان با استفاده از انتزاع جریان داده و یک الگوریتم ابتکاری قرار می گیرند. بعد، برای جلوگیری از هات اسپات شدن تجهیزات، یک الگوریتم هرس برنامه خطی صحیح آفلاین (ILP) در M-G برای درگیر نمودن قیدهای حجم سوییچ ارائه می شود. به علاوه، یک فرمول بندی برنامه خطی آنلاین برای کنترل توازن بار وارد می شود. در نهایت، مکانیزم های امنیتی برای کنترل حملات مختلف ارائه می شوند. و مسیریابی شبکه به طور انعطاف-پذیر از طریق پروتکل مدیری جریان داده حل می شود، که از طریق ترکیب تونل ها و تگ ها فرمول بندی می شوند. نتایج تجربی نشان می دهند که این مدل می تواند عملکرد امنیتی و مدیریت جریان داده را به طور موثر در سیستم IoT مبتنی بر SDN بهبود ببخشد.
1- مقدمه
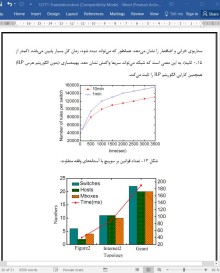
تکامل پیوسته سرویس های جدید و رشد اطلاعات در گردش در اینترنت، منجر به پیدایش ایده ها، مفاهیم و پاردایم-هایی مانند اینترنت اشیا شده است. اما، زیرساخت شبکه سنتی، که به سیاست های شبکه و پروتکل های پیکربندی سطح بالا نیاز دارد، غیرموثر هستند و محدودیت های قابل توجهی برای پشتیبانی از سطح بالای مقیاس پذیری، میزان بالای ترافیک و تحرک دارند. شبکه نرم افزارمحور (SDN) شبکه بسته سنتی را به سطح داده، سطح کنترل و سطح کاربرد تقسیم می کند، که کنترل و مدیریت متمرکز کل شبکه را ممکن می سازد. با این اصل طراحی جدید، شبکه می تواند انعطاف پذیر رفتار کند و می تواند به آسانی با نیازهای سازمان های مختلف سازگار شود. به علاوه، معماری متمرکز به جمع آوری اطلاعات مهم از شبکه و استفاده کردن از آن برای بهبود و سازگاری با سیاست های شبکه به طور پویا اجازه می دهد. بنابراین، به صورت نشان داده شده در شکل 1، یک معماری IoT مبتنی بر SDN جریان محور و قابل برنامه ریزی مطلوب می باشد. اگرچه، رابط های باز در SDN طراحی کاربردهای امنیتی در IoT بزرگ و پیچیده را ساده کرده اند، نسبت به حملات شبکه ای جدید نیز آسیب پذیر هستند و این آسیب پذیری امنیت را در معماری IoT مبتنی بر SDN کاهش می دهد. در IoT، جریان داده باید از چندین فرآیند قبل از اینکه تمام وظایف مورد نیاز اتمام یابند بگذرد. بنابراین، کنترل مناسب جریان های داده در هر دستگاه، برای پایدار کردن و ایمن کردن کارکرد شبکه مهم می باشد. مطالعات اخیر درباره استفاده از تجهیزات و SDN به سه دسته شامل تجهیزات تحقق یافته نرم-افزاری، مسائل زنجیره ای سرویس و یکپارچه سازی تجهیزات سنتی در شبکه های SDN تقسیم می شوند.
اولین چالش پویایی جریان داده در IoT می باشد. تعداد کاربران و حجم جریان داده در IoT با زمان تغییر می کند. اما، بیشتر تکنیک های کنترل داده موجود یک شبکه پایدار را فرض می کنند. بنابراین، چنین تکنیک هایی نمی توانند به طور فعال امنیت شبکه را در نظر بگیرند. اگر یک تعداد زیاد جریان داده به طور همزمان برسند، شبکه IoT کل ممکن است از کار بیفتد. بنابراین، هنگام توسعه راهکارهای کنترل جریان داده، در نظر گرفتن پویایی های جریان های داده می تواند امنیت و پایداری کل شبکه را بهبود ببخشد.
دومین چالش استقرار تجهیزات در IoT می باشد. در شبکه های سنتی تجهیزات در موقعیت خاصی قرار می گرفت. و مطالعات اخیر محدودیت ها را شکسته اند و کار مشارکتی تجهیزات تحت کنترل سطح کنترل را ممکن ساخته اند. اما، نهفتگی شبکه یک اندازه گیری مهم عملکرد کلی شبکه IoT می باشد. به علاوه، سیاست های امنیتی مختلف ممکن است تقاضاهای مختلفی در ترتیب دنباله های تجهیزات داشته باشند. بنابراین استقرار تجهیزات در مکان هایی با کمترین نهفتگی شبکه، یک نقطه عطف جدید استقرار تجهیزات شده است.
7- نتیجه گیری
قراردهی تجهیزات، قیدهای ظرفیت تجهیزات و جدول جریان سوییچ های SDN چالش های کلیدی هنگام ترکیب تجهیزات و SDN با هم می باشند. هدف این مطالعه استفاده از تجهیرات در IoT مبتنی بر SDN برای مدیرتی جریان داده و بهبود پایداری و امنیت شبکه بود. به این منظور، M-G، یک مدل امنیت انتقال داده مبتنی بر SDN در IoT براساس تجهیزات ارائه شد. M-G در جهت بهبود حصول پذیری کاربردهای امنیت IoT مبتنی بر SDN پاسخ فعال به تهدیدهای شبکه تلاش کرد. ما اول قراردهی های تجهیزات را نشان دادیم. مکان های مناسب با استفاده از یک الگوریتم انتخاب قراردهی انتخاب می شوند، که نفهتگی شبکه را کاهش می دهند. بعد، ما توازن شبکه را در نظر گرفتیم. در اینجا، یک الگوریتم هرس ILP و یک فرمول بندی LP برای توازن بارها در سراسر تجهیزات و سوییچ ها مستقر می شوند. در نهایت، ما مدیریت جریان داده را بررسی کردیم. مکانیزم های امنیتی می توانند در برابر چندین حمله دفاع کنند. با استفاده از پروتکل مدیریت جریان داده ارائه شده، وضعیت یک بسته مشاهده می شود و مسیر به طور مناسب تعیین می شود. نتایج تجربی ما نشان می دهند که مدل M-G و پروتکل های مدیریت متناظر جریان داده را در تجهیزات به طور مناسب مدیریت می کنند و می توانند امنیت و پایداری کل شبکه IoT را بهبود ببخشند.
Abstract
The exponential growth of devices connected to the network has resulted in the development of new Internet of Things (IoT) applications and online services, which may have diverse and dynamic requirements on received quality. Although, the emerging software-defined networking (SDN) approach can be leveraged for the IoT environment, to dynamically achieve differentiated quality levels for different IoT tasks in very heterogeneous wireless networking scenarios, the open interfaces in SDN introduces new network attacks, which may make SDN-based IoT malfunctioned. The challenges lies in securely using SDN for IoT systems. To address this challenge, we design a SDN-based data transfer security model middlebox-guard (M-G). M-G aims at reducing network latency, and properly manage dataflow to ensure the network run safely. First, according to different security policies, middleboxes related to the defined secure policies, are placed at the most appropriate locations, using dataflow abstraction and a heuristic algorithm. Next, to avoid any middlebox becoming a hotspot, an offline integer linear program (ILP) pruning algorithm is proposed in M-G, to tackle switch volume constraints. In addition, an online linear program (LP) formulation is come up to handle load balance. Finally, secure mechanisms are proposed to handle different attacks. And network routing is solved flexibly, through dataflow management protocol, which are formulated via combining tunnels and tags. Experimental results demonstrate that this model can improve security performance and manage dataflow effectively in SDN-based IoT system.
I. INTRODUCTION
THE continued evolution of new services and the growth of the information circulating the Internet, has led to the origin of ideas, concepts and paradigms such as the Internet of Things (IoT)[1]. However, traditional network infrastructure, which need high-level network policies and configuring protocols, are inefficient and have significant limitations to support the high level of scalability, high amount of traffic and mobility. Software-Defined Networking(SDN)[2] decouples the traditional closed network into data plane, control plane and application plane, which enables logically centralized control and management of the whole network. With this new design principle, the network could behave more flexibly and can easily adapt to the needs of different organizations. Besides, the centralized architecture allows important information to be collected from the network and in turn used to improve and adapt their policies dynamically. Thus, as shown in Figure 1, a programmable, flexible, flow-centric SDN-based IoT architecture is favorable. Although, open interfaces in SDN have simplified the design of secure applications in large and complex IoT, they are vulnerable to new network attacks [3]- [4], and this vulnerability inevitably reduces security in SDNbased IoT architecture. In IoT, the dataflow has to go through several processes before all required tasks are finished. Thus, proper handling of data flows in each device, is important for stable and secure network operation. Recent studies about the use of middleboxe and SDN[5]-[9] fall into three categories, including software realized middlebox, service chaining problems and integrating traditional middlebox into SDN networks.
The first challenge is the dynamic of dataflow in IoT.The number of users and dataflow volume in IoT vary over time. However, most existing dataflow control techniques assume a stable network. Therefore, such techniques can not actively consider network security. If a large number of data streams arrive simultaneously, the entire IoT network may become paralyzed. Thus, when developing dataflow control strategies, considering dataflow streams dynamics can improve the security and stability of the entire network.
The second challenge is the deployment of middleboxes in IoT.In traditional networks, the middlebox is deployed in particular position. And recent studies have broken the restrictions, and enabled the middleboxes work collaboratively under the control of control plane. However, network latency is an important measure of overall IoT network performance. In addition, different security policies may have different demands on the order of middlebox sequences. So deploying the middleboxes at positions with the lowest network latency, becomes a new break point of middlebox deployment.
VII. CONCLUSION
Middlebox placement, the middlebox and flow table capacity constraints of SDN switches are key challenges when combining middlebox and SDN together. The goal of this study was to use middlebox in SDN-based IoT to manage dataflow, and improve the stability and security of the network. To this end, M-G, a SDN-based data transfer security model in IoT based on middleboxes was proposed. M-G attempts to improve the availability of SDN-based IoT secure applications and actively respond to network threats. We first addressed middlebox placements. Appropriate positions are selected using a placement selection algorithm, which reduces network latency. Next, we considered network balance. Here, an ILP pruning algorithm and an LP formulation are deployed to balance load across middleboxes and switches. Finally, we investigated dataflow management. The secure mechanisms can defend several attacks. By using the proposed dataflow management protocol, the status of a packet is observed and the route is properly determined. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed M-G model and corresponding protocols manage dataflow in middleboxes effectively, and can improve the overall IoT network security and stability.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2- کار مرتبط
3- فرمول بندی مساله
4- چارچوب
5- مکانیزم های امنیتی و پروتکل مدیریت جریان داده
6- آزمایش
7- نتیجه گیری
منابع
Abstract
.1 INTRODUCTION
2. RELATED WORK
.3 PROBLEM FORMALIZATION
4. FRAMEWORK
5. SECURE MECHANISMS AND DATAFLOW MANAGEMENT PROTOCOL
6. EXPERIMENT
7. CONCLUSION
REFERENCES
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه