
اصلاحات اداری و عملکرد سیاست های عمومی محلی
چکیده
هدف – هدف این مقاله توضیح و تفسیر ارتباط بین اصلاحات اداری در پرتغال و تاثیرات آن بر وابستگی دولت-های محلی در مواجهه با منابع بودجه ایالت و مجموعه درآمدهای شهری محلی می باشد، که در بین دیگران به فرم مشارکت جامعه مدنی در سیاست های عمومی محلی شناخته می شود. طرح / روش / رویکرد – این مطالعه با استفاده از رویکرد گراندد تئوری (نظریه پایه یا نظریه زمینه)، شامل استفاده از داده های مربوط به ساختارهای دولت محلی و مشارکان با بخش خصوصی، و با تکیه بر خطوط اصلی (خط مشی) اصلاح اداری عموم برای یک تحلیل اکتشافی انتخاب شده است. داده ها با تجزیه وتحلیل مستندات، شامل اسناد قانونی و مقاله ها در مناطق اختصاصی غیر متمرکزسازی اداری و مشارکت جامعه مدنی در سیاست های عمومی محلی، تکیمل شده است. یافته ها – این مقاله بینش های تجربی درباره نحوه ارتباط افزایش مشارکت جامعه مدنی در سیاست های محلی با وابستگی واتکای کمتر به بودجه های ایالتی و تعداد زیاد ساختارهای مدیریتی محلی فراهم می کند. محدودیت ها / مفاهیم تحقیق – به دلیل انتخاب رویکرد پژوهشی، نتایج قابل تعمیم نمی باشند. مطالعه تطبیقی و مقایسه ای بین چند کشور بینش های جالبی را ایجاد خواهدکرد. مفاهیم اجتماعی – این مقاله مفاهیمی را برای توسعه اقتصادی و اجتماعی سیاست های جدید محلی در زمینه اصلاحات اداری (اجرایی) شامل می شود. اصالت / ارزش – این مقاله چندین همکاری نظری و تجربی در این زمینه پژوهشی، به خصوص درباره تصمیمات مدیران عمومی محلی برای انتقال منابع مالی دربین سیاست فعال توسعه پایدار محلی داشته است.
1. مقدمه
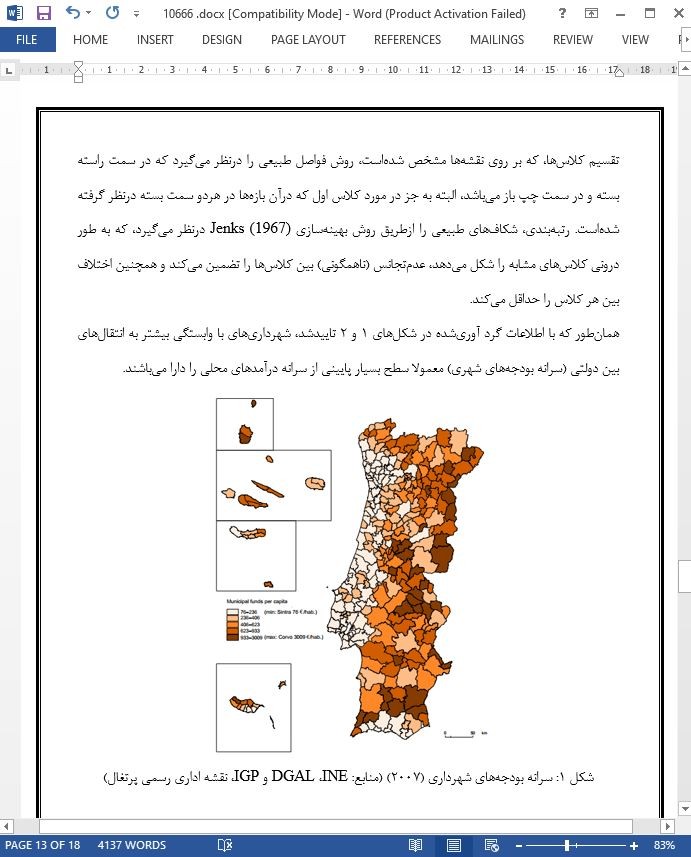
این مطالعه تاثیر اصلاحات اداری و غیر متمرکزسازی سیاست های عمومی را، به خصوص بر وابستگی شهرداری های پرتغال به نقل وانتقالات مالی از بودجه دولت مرکزی (سرمایه های شهرداری) و توانایی جمع آوری درآمدهای شهرداری محلی را تجزیه وتحلیل می کند. این اصلاحات با جابجایی بودجه های شهداری، به دنبال نزدیک کردن نواحی داخلی (محروم ترین مناطق) به نواحی ساحلی کشور (برخوردارترین) می باشد. ارتباط این موضوع از این حقیقت ناشی می شود که، اگرچه اصل همبستگی منجربه سیاست های عمومی می شود که برطبق Hertzog (1991)، Hoffmann-Martinot (1992) و Debbasch (1976) متمایل به جابجایی منابع مالی از نواحی توسعه یافته به محروم ترین نواحی می باشد، اما سطح جمع آوری درآمدهای شهرداری محلی یک شکل از مشارکت جامعه مدنی در سیاست های عمومی محلی است که در پایدارسازی مالی مدیریت عمومی محلی مشارکت می کند. با این حال، این مطالعه نشان می دهد که این تخصیصات مجدد نیز توسعه نواحی متاثر را بهبود نمی بخشد.
5. محدودیت ها و تحقیقات آینده
نتایج این مطالعه برای توسعه سیاست های جدید در حوزه اصلاح عمل ایالت، به خصوص درنظر گرفتن اصلاحات مالی محلی که با منشور اتحادیه خودمختار اروپایی پشتیبانی می شود، مهم می باشد. ما نهادهای عامه محلی را که برطبق متون کارشناسان ملی، یک کمبود در گردآوری درآمدهای محلی ارائه می دهند و تا حد زیادی وابسته به عملکرد هزینه های شهرداری می باشند، بررسی کردیم. تغییرات قانونی اخیر هیچ تاثیری بر این موضوع نداشته است، موقعیتی که باید در تحقیقات آینده تجزیه وتحلیل شود.
Abstract
Purpose – The purpose of this paper is to clarify the relationship between administrative reform in Portugal and the impacts on the dependence of local governments in the face of budgetary resources of state and local municipal revenue collection, which is understood as a form, among others, participation civil society in local public policies. Design/methodology/approach – The study opts for an exploratory analysis using the grounded theory approach, including the use of data relating to local government structures and partnerships with the private sector, based on the main lines of the public administration reform. The data were supplemented by documentary analysis, including legislative documents and papers in specialized area of administrative decentralization and civil society participation in local public policies. Findings – The paper provides empirical insights about how the increased participation of civil society in local public policies is associated with less reliance on state budgets and a greater number of local managerial structures. Research limitations/implications – Due to the chosen research approach, the results cannot be generalized. A comparative study between several countries could bring several interesting insights. Social implications – The paper includes implications for economic and social development of new public policies in the context of administrative reforms. Originality/value – This paper makes several theoretical and empirical contributions on this research field specially about local public manager’s decisions for financial resources transfers within the active policy of sustainable local development.
1. Introduction
This study analyses the administrative reforms impact and the public policies decentralization, particularly on the Portuguese municipalities’ dependence on financial transfers from the central government budget (municipal funds) and the ability to collect local municipal revenue. These reforms have sought to approximate the interior regions (most deprived) to the coastal regions of the country (most favored), by relocation of municipal funds. The relevance of this issue stems from the fact that, although the principle of solidarity led to public policies that tend, according to Hertzog (1991), Hoffmann-Martinot (1992) and Debbasch (1976), to shift financial resources from more developed regions to the most deprived, the collection level of local municipal revenue is a form of civil society participation in local public policies that contributes to the financial sustainability of local public administration. However, this study shows that these reallocations did not improve the development on the affected regions.
5. Limitations and futures research
The results of this study are important for the development of new policies in the scope of reform action of the State, especially regarding local finances reforms supported by the Local Autonomy European Union Charter. We are dealing with public local entities that, according to national expert literature, present a deficit at the collection of local revenues and are largely based on the performance of municipal expenditures. Recent legislative changes had no impact on this issue, a situation that should be analyzed in future research.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. زمینه نظری
2 – 1: اصلاح اداری عامه
2 – 2: غیرمتمرکزسازی و مشارکت
2 – 3: قابلیت پایداری سیاست های عمومی محلی
3. روش شناسی
3 – 1: منابع داده و اطلاعات
3 – 2: پردازش داده ها
4. نتایج اصلی و نتیجه گیری ها
5. محدودیت ها و تحقیقات آینده
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical background
2.1 Public administration reform
2.2 Decentralization and participation
2.3 Sustainability of local public policies
3. Methodology
3.1 Data and information sources
3.2 Data processing
4. Main results and conclusions
5. Limitations and futures research
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
