
شناسایی، نگاشت و مدل سازی مسیرهای فقر در سطح محله
چکیده
تجزیه وتحلیل طولی به ندرت در زمینه جغرافیا برای درک تغییر محله بکار برده می شود، اگرچه مطالعات زیادی تبدیل های مهم در مناطق شهری را استناد قرار داده اند (برای مثال، نوسازی، بینوایی سازی حومه های داخلی و غیره). هدف این مقاله، شناسایی و مدل سازی مسیرهای فقر محله در مونترال در 5 سرشماری سالانه متوالی (1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 و 2006)، با استفاده از مدل سازی رشد کلاس پنهان می باشد. محله ها به هشت گروه، برحسب شناسایی آن ها با مسیرهای پایدار، افزایشی یا کاهشی از فقر تقسیم شده اند. تحلیل رگرسیون لجستیک (منطقی) چندجمله ای نشان می دهد که نسبت ساکنان با سطح پایین آموزش، نرخ بیکاری، نسبت مهاجران اخیر و نسبت اجاره دهندگان اندازه گیری شده در شروع دوره (1986)، پیش بینی کننده های مهمی از مسیرهای فقر هستند که در سراسر دوره مطالعه (1986 – 2006) در نسبت های مهاجران جدید و ساکنان با سطوح پایین آموزش متغیر می باشند.
مقدمه
جهانی سازی، بازسازی اقتصادی، تغییرات جمعیتی، و همچنین تغییرات در سیاست های دولتی، تقسیم های اجتماعی از شهرها (Jargowsky, 2003; Van Kempen & Murie, 2009; Walk, 2001)، به خصوص توزیع فضایی جمعیت های با سطح درآمد کم در مناطق شهری را تغییر داده است. در نتیجه، جغرافیای فقر و محرومیت اجتماعی در حال حاضر توجه فزاینده ای را در آمریکای شمالی و همچنین در اروپا دریافت می کند (Cooke & Marchant, 2006; Heisz & McLeod, 2004; Kearns & Parkinson, 2001; Kitchen & Williams, 2009; Lupton & Power, 2004; Madden, 2003a, 2003b). تا به امروز، بیشتر کارهای تجربی در تغییر محله تبدیل های بین دو نقطه در زمان (Kitchen & Williams, 2009; Mikelbank, 2006; Reibel & Regelson, 2011; Vicino, 2008) را بررسی کرده اند. به استثناء کار اخیر Mikelbank (2011) در منطقه شهری کلیولند – آکرون، مطالعات اندکی مسیرها را با دقت بررسی کرده اند، برای مثال، بسیاری از تحقیقات تغییرات در مشخصات اقتصادی – اجتماعی جمعیت های محله را در بیشتر از دو نقطه زمانی بررسی نکرده اند.
نتیجه گیری
نتایج ما نشان می دهد که تغییرات ریشه ای در جغرافیای فقر یک استثنا در CMA مونترال می باشد. نواحی فقر برطبق شاخصه های اولیه خود تکامل می یابند و در طول زمان به ندرت تغییر می کنند، به جز برای مناطق سرشماری در مسیر نوسازی که درآن تغییرات در سطوح فقر بسیار مشخص می باشد. از سال 1986 به بعد، ما حضور تمرکزهای ضعیف و بسیار ضعیف از جمعیت های با سطح درآمد کم را در حومه های قدیمی تر مشاهده کردیم که با مقادیر LQ بزرگتر 1 نشان داده می شود. این امر نشان می دهد که فرایند نوسازی از قبل در مناطق سرشماری در حال انجام می باشد و درطی دوره مطالعه به اندازه ناچیزی افزایش می یابد (این مناطق سرشماری به وسیله مسیرهای فزاینده فقر مشخص می شوند). اگرچه مناطق سرشماری در مسیرهای F و G با مقادیر LQ کم مشخص می شوند، اما فقر کمتری را در این محله ها نسبت به CMA مونترال نشان می دهند، جمعیت های فقیر در این قلمروها حضور داشتند. همان طور که در مطالعات قبلی استناد شد (Séguin, 1998; Séguin & Germain, 2000)، این امر پدیده ترکیب نسبتا اجتماعی در محله های مونترال را حتی در مناطق ثروتمندتر پشتیبانی می کند.
Abstract
Longitudinal analysis is rarely leveraged in the field of geography to understand neighbourhood change despite many studies documenting important transformations within metropolitan areas (e.g. gentrification, impoverishment of inner suburbs, etc.). This paper aims to identify and model trajectories of neighbourhood poverty in Montreal over five consecutive census years (1986, 1991, 1996, 2001 and 2006), using Latent Class Growth Modelling. Neighbourhoods are classified in eight groups, identifying those with stable, increasing or declining trajectories of poverty. Multinomial logistic regression analysis shows that the proportion of residents with low levels of education, unemployment rate, proportion of recent immigrants and the proportion of renters measured at the beginning of the period (1986) are important predictors of poverty trajectories, as are variations throughout the study period (1986–2006) in the proportions of recent immigrants and of residents with low levels of education.
Introduction
Globalization, economic restructuring, demographic shifts, as well as changes in government policies have modified the social divisions of cities (Jargowsky, 2003; Van Kempen & Murie, 2009; Walk, 2001), notably the spatial distribution of low-income populations within metropolitan areas. As a result, the geography of poverty and social deprivation is now receiving growing attention in North America as well as in Europe (Cooke & Marchant, 2006; Heisz & McLeod, 2004; Kearns & Parkinson, 2001; Kitchen & Williams, 2009; Lupton & Power, 2004; Madden, 2003a, 2003b). To date, most of the empirical work on neighbourhood change has examined transformations between two points in time (Kitchen & Williams, 2009; Mikelbank, 2006; Reibel & Regelson, 2011; Vicino, 2008). With the exception of the recent work of Mikelbank (2011) on the ClevelandeAkron metropolitan area, few studies have analyzed trajectories with precision i.e. they have not investigated changes in the socioeconomic characteristics of neighbourhood populations over more than two points in time.
Conclusion
Our results show that radical changes in the geography of poverty are an exception in the Montreal CMA. Poverty zones evolved according to their initial characteristics and changes were minor over time, except for CTs in the gentrification trajectory where changes in poverty levels were more marked. From 1986 onward, we observed the presence of weak and very weak concentrations of low-income populations in the older suburbs, as indicated by LQ values greater than one. This illustrates that the impoverishment process was already underway in these CTs and that it slightly increased during the period of study (these CTs were characterized by trajectories of increasing poverty). Although census tracts in trajectories F and G were characterized by low LQ values, indicating lower poverty in these neighbourhoods than across the Montreal CMA, poor populations were nonetheless present within these territories. As documented in past studies (Séguin, 1998; Séguin & Germain, 2000), this supports the phenomenon of a relative social mix in Montreal neighbourhoods, even in wealthier areas.
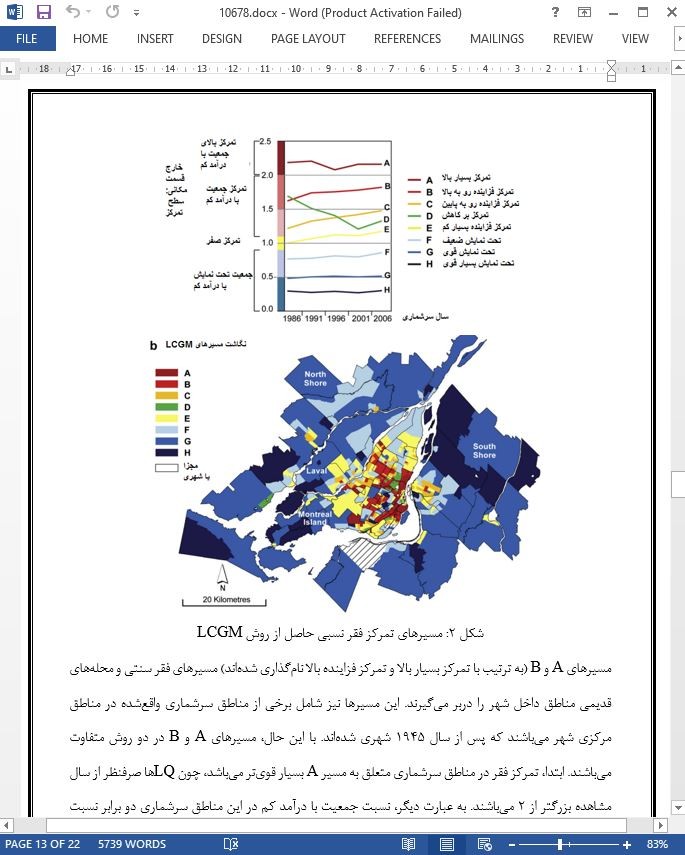
چکیده
مقدمه
پیش زمینه
مطالعه تغییرات در فقر محله
مسیرهای فقر و حضور جمعیت های درخطر
اهداف تحقیق
داده ها و روش ها
شناسایی مسیرهای تمرکز فقر نسبی
مدل سازی مسیرهای با تمرکز نسبی فقر
نتایج
توصیف مسیرهای فقر محله
توصیف مسیرها در فقر محله
نتیجه گیری
Abstract
Introduction
Background
Studying changes in neighbourhood poverty
Poverty trajectories and presence of populations at risk
Research objectives
Data and methods
Identifying trajectories of relative poverty concentration
Modelling trajectories of relative poverty concentration
Results
Describing trajectories of neighbourhood poverty
Explaining trajectories of neighbourhood poverty
Conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
