
تنوع نیروی کار در مدل های مدیریت منابع انسانی استراتژیک
چکیده
هدف: تنوع نیروی کار به عنوان یکی از چالشهای اصلی مدیریت منابع انسانی در سازمانهای مدرن محسوب میشود. علی رغم اهمیت استراتژیک نیروی کار ، اکثر مدلهای ارائه شده در این زمینه تفاوت های فرهنگی میان کارمندان را به حساب نمیآورند و آنها را به عنوان گروهی مشابه و کلی را در نظر میگیرند. هدف این مقاله ارائه مروری اصولی از نوشته های مربوط به تنوع میان کارمندان در مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار یا SHRM هستیم. هدف این تحلیل مفهومی، شناخت محدودیتهای تحقیقات قبلی و مسائل حل نشدهای هستیم که در پیشبرد تحقیقات آتی سهمی دارا است. طرح/روش شناسی/رویکرد: این مقاله برای گسترش این تحلیل مفهومی، نوشتههای پیشین درباره مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار را مبنی بر تمایز میان دورنماهای جهان شمول، تصادفی و ترتیبی مرور می کند. هریک از این رویکردها در تحقیقاتشان به دنبال یافتن راهی هستند که در آن از تنوع نیروی کار و میان فرهنگی بودن سخن به میان رفته باشد. یافتهها: در انتها مقاله نتیجه میگیرد که مدیریت نیروی کار مشابه نیازمند تغییرات جامعی در استراتژیهای نیروی کار است. با این حال، تلاشهای مربوط به تعریف مدل های میان فرهنگی و مبتنی بر تنوع همچنان ناکافی باقی مانده است. محدودیتهای تحقیقات گذشته در زمینه تنوع میان کارمندان در مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار در این مقاله آورده شده است. محدودیتهای تحقیق و کاربرد: با توجه به محدودیتهای اعمال شده در زمینه تنوع میان کارمندان در مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار، این مقاله چهار سوال تحقیق را لازم به طرح میداند. این سوالات عبارتند از: تحلیل عمیقتر درباره مفهوم تنوع، معرفی فرآیند روانشناسی موجود در رابطه میان تنوع و عملکرد، گسترش تنوع در انواع مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار و تعریف دوباره شاخصهای عملکرد برای محاسبه اثرات تنوع. اصالت/ارزش: این مقاله مدلی نظری را برای به تصویر کشاندن موقعیت فعلی صنعت و خطوط تحقیقات آتی در زمینه تنوع، مدیریت میان فرهنگی و مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار ارائه میکند.
1. مقدمه
تغییرات اجتماعی در دو دهه اخیر باعث افزایش اساسی میزان تنوع نیروی کار و میان فرهنگی بودن شده است. با این حال، همانگونه که بنشاپ (2001) اظهار میکند، اکثر مدلهای مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار به طور تلویحی و بدون در نظر گرفتن تفاوتهای فرهنگی میان کارکنان نیروهای کار را گروههایی مشابه و کلی فرض کردهاند. بدین ترتیب، نیاز به گنجاندن تنوع در مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار به عنوان چالش اساسی در تحقیقات آتی مربوط به این زمینه بیش از پیش احساس میشود.
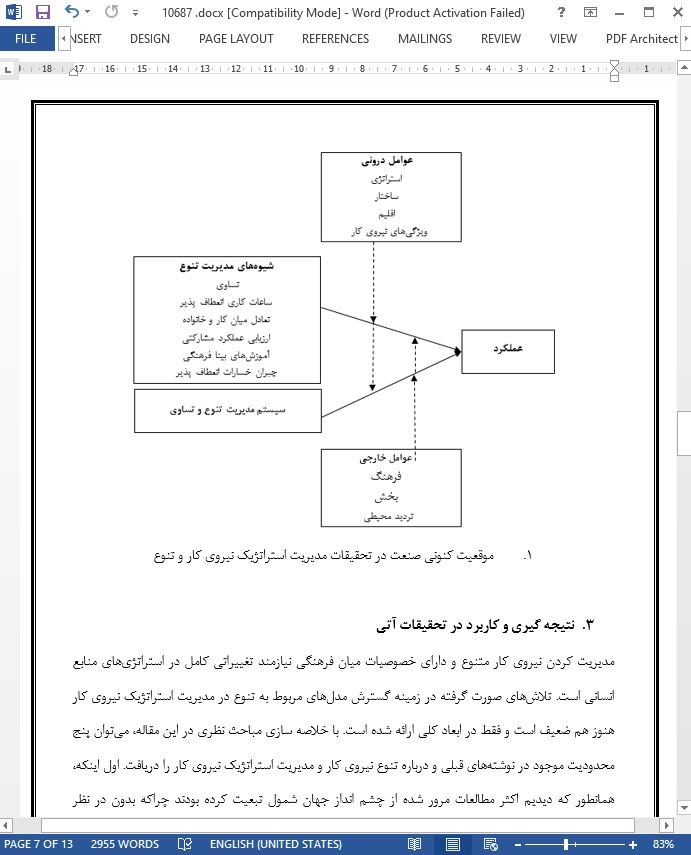
3. نتیجه گیری و کاربرد در تحقیقات آتی
مدیریت کردن نیروی کار متنوع و دارای خصوصیات میان فرهنگی نیازمند تغییراتی کامل در استراتژیهای منابع انسانی است. تلاشهای صورت گرفته در زمینه گسترش مدلهای مربوط به تنوع در مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار هنوز هم ضعیف است و فقط در ابعاد کلی ارائه شده است. با خلاصه سازی مباحث نظری در این مقاله، میتوان پنج محدودیت موجود در نوشتههای قبلی و درباره تنوع نیروی کار و مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار را دریافت. اول اینکه، همانطور که دیدیم اکثر مطالعات مرور شده از چشم انداز جهان شمول تبعیت کرده بودند چراکه بدون در نظر گرفتن تاثیرات متنی و تصادفی، بر شناخت جداگانه برترین شیوه ها تمرکز کرده بودند. همچنین این اهداف جهان شمول باعث شده تا محققان را به سمت گرایشات دیدگاهی رهنمون شود. در واقع اکثر مدلهای مدیریت تنوع به جای توضیح تاثیرات تنوع بر پیشنهاد ابزارهای مدیریت عمومی تمرکز کردهاند. سومین محدودیت موجود، رویکرد «جعبه سیاه» برای تحلیل تاثیرات تنوع است. تاثیرات تنوع به عنوان روابط مستقیم اتفاقی در نظر گرفته میشد، آن هم بدون احتساب عوامل بالقوه واسطه و متعادل کنندهای که قادر به توضیح این واقعیت پیچیده بودند. همچنین ما محدودیت دیگری را در رابطه با مفهوم تنوع دریافتیم. راههای مختلف مفهوم سازی و اندازه گیری تنوع ارائه شده است که در بسیاری از موارد روی دستهای از ویژگیهای متفاوت تاکید شده است. در نهایت، یکی از نتایج مطالعه ما از نوشتهها، کمبود گونه شناسی خاص منابع انسانی است. در واقع، مدلهای ترتیبی بسیار کمی ارائه شده است تا بتواند چگونگی مدیریت همزمان تنوع نیروی کار توسط سیاستها و روشهای مختلف منابع انسانی را توصیف کند.
Abstract
Purpose – Workforce diversity is considered one of the main challenges for human resource management in modern organizations. Despite its strategic importance, the majority of models in this field implicitly consider workforce as a generic and homogeneous category, and do not take into account cultural differences among employees. The aim of this paper is to present a systematic review of the literature on diversity among employees in strategic human resource management (SHRM). The objective of this conceptual analysis is to identify limitations in previous research and unresolved issues that could drive future research in this field. Design/methodology/approach – To develop this conceptual analysis, the paper reviews previous literature on SHRM, drawing on the distinction between the universalistic, contingent and configurational perspectives. Each of these approaches is explored, looking for the way in which they have treated workforce diversity and cross-culturality. Findings – The paper concludes that managing a heterogeneous workforce requires a holistic transformation of human resource strategies. Nevertheless, efforts to define cross-cultural and diversity-oriented models still remain undeveloped. Limitations of previous research in the diversity-SHRM field are indentified in the paper. Research limitations/implications – Drawing on the limitations of the treatment given to diversity in SHRM research, the paper identifies four research questions that still need to be addressed: deeper analysis of the concept of diversity, introduction of psychological processes mediating the diversity-performance relationship, development of diversity oriented SHRM typologies and redefinition of performance indicators to measure the effects of diversity. Originality/value – This paper proposes a theoretical model to illustrate present state of the art and future research lines in the fields of diversity, cross-cultural management and SHRM.
1. Introduction
Social transformations in the last two decades have substantially increased workforce diversity and cross-culturality (Cook and Glass, 2009; Seyman, 2006). Nevertheless, as Benschop (2001) argued, the majority of strategic human resource management (SHRM) models have implicitly assumed that workforces are “generic and homogeneous categories”, without considering cultural differences between employees. In this sense, the need to incorporate diversity in the SHRM debate has been considered one of the main challenges to be addressed in future research on the field (Curtis and Dreachslin, 2008; Shen et al., 2009).
3. Conclusions and implications for future research
Managing a diverse and cross-cultural workforce requires a complete transformation of HR strategies (Shen et al., 2009; Bleijenbergh et al., 2010; Tatli, 2011). Efforts to develop diversity-oriented SHRM models are still weak and presented in only general terms (Kossek and Lobel, 1996). Summarizing the theoretical discussion developed in this paper, we could highlight five limitations of previous literature about SHRM and workforce diversity. First, as we have seen, the majority of the studies reviewed followed a universalistic perspective, as they focused on identifying isolated best practices, without discussing contingent and contextual influences. This universalistic objective also leads them to follow a prescriptive orientation. In fact the majority of diversity management models are focused on recommending generic management tools instead of explaining the effects of diversity. The third limitation identified is the “black box” approach to the analysis of the effects of diversity. The effects of diversity were considered as direct causal relationships, without exploring potential mediating and moderating factors that could help explain this complex reality. Similarly, we have also perceived another limitation regarding the concept of diversity. Different ways of conceptualizing and measuring diversity have been proposed, focusing in many cases on different sets of attributes. Finally, one of the conclusions from our review of the literature is a lack of specific HR typologies. In fact, very few configurational models have been proposed to describe how different HR policies and practices can be synergistically integrated to manage workforce diversity.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2.تنوع نیروی کار در مدلهای مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار
1.2 تنوع در مدلهای جهان شمول
2. 2 تنوع در مدلهای تصادفی
2. 3 تنوع در مدلهای ترتیبی
3 نتیجه گیری و کاربرد در تحقیقات آتی
الف)تحلیلی عمیق تر از مفهوم تنوع
ب) باز کردن «جعبه سیاه» تاثیرات تنوع
ج)تجدید نظر درباره متغیرهای عملکرد برای سنجش تاثیرات تنوع
د)گسترش گونه شناسی مربوط به تنوع مدیریت استراتژیک نیروی کار
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Workforce diversity in SHRM models
2.1 Diversity in universalistic models
2.2 Diversity in contingent models
2.3 Diversity in configurational models
3. Conclusions and implications for future research
(a) Deeper analysis of the concept of diversity
(b) Opening the “black box” of the effects of diversity
(c) Rethink performance variables to measure the effects of diversity
(d) Develop diversity-oriented SHRM typologies
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
