
یک مدل اقتصاد سنجی برای ارزیابی کردن صرف ریسک سهام
چکیده
در این پژوهش، ما روابط بین صرف ریسک سهام و اقتصاد کلان بنیادی و متغیرهای مالی در ایالات متحده را در فاصلهی زمانی 1964 تا 2012 با استفاده از رگرسیون OLS استاندارد و فیلتر هودریک پرسکات ارزیابی میکنیم. در نتیجه، براساس این نتایج و بهکار بردن مدلهای ARIMA، ما تکامل تدریجی صرف ریسک سهام در ایالات متحده را برای فاصلهی زمانی 2013 تا 2016 پیشبینی میکنیم. با توجه به نتایج ما، صرف ریسک سهام در ایالات متحده در این سالها به تدریج افزایش پیدا میکند و یک تکامل تدریجی با استفاده از چشمانداز سیاست پولی FED و همچنین با محدود نمودن شکاف مصرف خصوصی، تعیین شده است.
1- مقدمه
مفهوم صرف ریسک سهام (ERP) یک تئوری مرکزی در مورد حسابداری و مالی مدرن میباشد که پیدایش آن مربوط به تحقیق مارکوویتز (1952) بر روی بازارهای مالی بود. چندین روش مختلف برای ارزیابی کردن ERP وجود دارد (کوهن، 2009)؛ ابتدا، ERP میتواند از طریق CARM تخمین زده شود؛ در حالت دوم با استفاده از بررسی کردن حرفههای سرمایهگذاری ارزیابی میشود؛ در حالت سوم با استفاده از بازدههای واقعی غیراریب، بازدههای مورد انتظار داراییها تخمین زده میشود.
3- نتیجهگیری
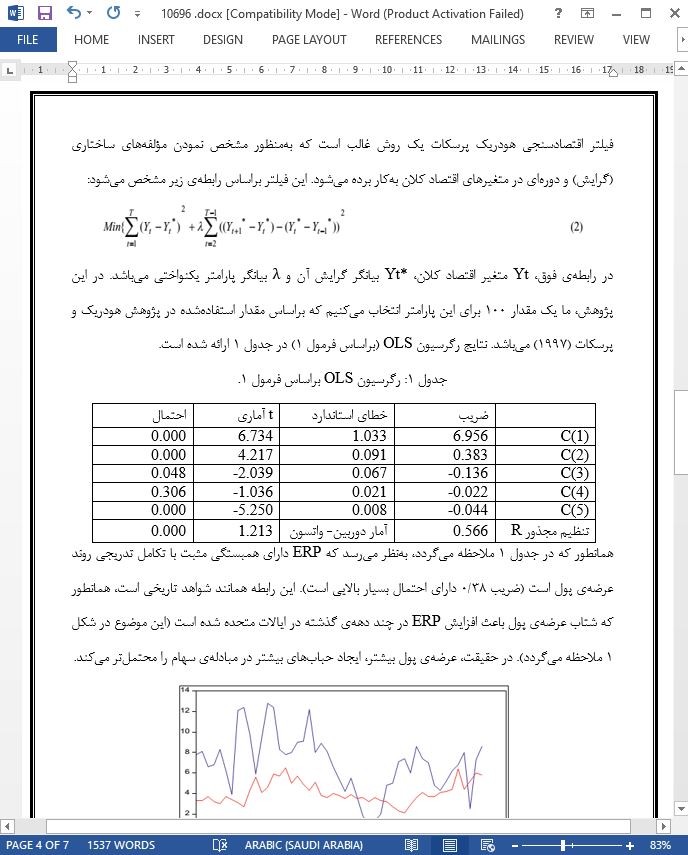
این تحلیل به ما چندین نتیجهگیری جالب با توجه به ERP در ایالات متحده را ارائه میدهد. بهعبارت دیگر، ممکن است ما به ایجاد یک نقطهی بازگشت ERP کمک کنیم (بازگشت از طریق کاهش در طول سالهای گذشته که به تدریج در سالهای بعد افزایش پیدا میکند که این موضوع در شکل 3 ملاحظه میگردد). این تکامل تدریجی بهوسیلهی شتاب عرضهی پول، همچنین با استفاده از راهاندازی مجدد جریانهای سرمایهگذاری در اقتصاد و ادامهی افزایش پول FED (در یک سرعت آهسته) تعیین خواهد شد. بهنظر میرسد که وابستگی بین تمایلات بازارهای مالی و افزایش پول غیرمتعارف FED بسیار بیشتر میشود. در نتیجه ما انتظار نداریم که بازگشت سیاست پولی FED، چشمگیر باشد و در این حالت ممکن است یک شوک برای بازارهای سهام ایجاد شود که یک اثر منفی متوالی برای تکامل تدریجی اقتصاد حقیقی بهوجود میآید.
Abstract
In this paper we estimate the relation between the equity risk premium and the fundamental macroeconomic and financial variables in the United States during the period 1964-2012 by applying the standard OLS regression and the Hodrick-Prescott filter. Consequently, based on these results and applying the ARIMA models we forecast the evolution of the equity risk premium in the United States for the period 2013-2016. According to our results the equity risk premium in the United States is going to gradual increase in the following years, an evolution determined by the FED monetary policy perspectives, but also by the narrowing of the private consumption gap.
1. Introduction
The concept of equity risk premium (ERP) is a central one in modern finance and accounting theory, being related to the research of Markowitz (1952) on financial markets. There are several methods for estimating ERP (Cohen, 2009): firstly, the ERP can be estimated from the CAPM; secondly, by surveying investment professionals; thirdly, by using the actual returns unbiased estimates for the expected returns of assets.
3. Conclusions
This analysis allows us several interesting conclusions regarding the ERP in the United States. On the one hand, we may assist at a turning point of the ERP (inflexion from the decline over the past years to a gradual increase in the following years, as can be noticed in Fig. 3). This evolution would be determined by the acceleration of the money supply, determined either by the re-launch of the investments flows in the economy and by the continuation of the FED monetary expansionism (at a slower pace). It seems that the dependence between the financial markets sentiment and the FED non-conventional monetary expansionism became very high. Consequently, we do not expect the inflexion of the FED monetary policy to be dramatic, as it might determine a shock for the stock markets, with negative consequences for the evolution of the real economy.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2- روش بررسی و دادهها
3- نتیجهگیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and methodology
3. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
