
استفاده ترکیبی از انتشار تک پخشی در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم
چکیده
روش زمان بندی ترکیبی جمع آوری انتشار تک پخشی مشترک (UBA) به منظور حداکثر کردن جمع آوری اطلاعات و به حداقل رساندن تاخیر در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم (WSN) پیشنهاد داده شده است. روش UBA شرایط ذیل را برای حداکثر کردن جمع آوری اطلاعات و به حداقل رساندن تاخیر می پذیرد: (1) نودها در فاصله دور از منطقه مقصد حالت انتشار را می پذیرند که نه تنها می توانند اطلاعات سنجش بیشتری را از همان شکاف زمانی جمع آوری کنند بلکه همچنین می تواند کل تاخیر شبکه را نیز کاهش دهند و (2) نودها در فاصله نزدیک به مقصد از حالت تک پخشی برای جمع آوری اطلاعات سنجش استفاده می کنند که می تواند صرفه جویی قابل توجهی در مصرف انرژی به منظور افزایش طول عمر شبکه ارائه کند. روش UBA دارای مزیت بسیار بزرگی است چرا که می تواند اطلاعات سنجش بیشتری را جمع آوری کند و تاخیر را بدون کوتاه کردن طول عمر شبکه کاهش دهد. نتایج شبیه سازی و تحلیل های نظری به طور آشکار نشان می دهد که روش پیشنهادی می تواند به طور قابل توجهی سبب بهبود اطلاعات سنجش به میزان 25 درصد شود و تاخیر را به میزان 14 تا 18 درصد تحت همان طول عمر شبکه کاهش دهد.
1. مقدمه
کارکرد اصلی شبکه های حسگر بی سیم (WSN) سنجش و جمع آوری اطلاعات اطراف به طور دوره ای از طریق نودهای حسگر تشکیل دهنده شبکه و انباشته کردن آن در نود مقصد برای پردازش بعدی است [1-5]. در چنین کاربردهایی، تمامی نمونه های نود در هر چرخه نمونه قرار دارند. تمامی نودهای حسگر برای هر چرخه نمونه تنها یک بار عملیات نمونه برداری را انجام می دهند [2-5]. انباشتگی داده به وضعیتی اشاره دارد که در آن دو پکت داده در یک نود در روند مسیریابی با یکدیگر برخورد می کنند و به یک پکت داده جدید یکپارچه می شوند [1,6]. مطابق با الزامات لحظه ای شبکه های حسگر بی سیم، انباشتگی داده ها به دو دسته تقسیم می شود: (1) پخش همگرا : این یکی از پرکاربردترین الگوهای جمع آوری داده های لحظه ای در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم است. (2) جمع آوری لحظه ای داده ها: در شبکه جمع آوری لحظه ای داده ها، نود مقصد می بایست حداکثر اطلاعات سنجش ممکن را در طی یک چرخه نمونه از پیش تعریف شده جمع آوری کند [1]. اگر اطلاعات جمع آوری شده توسط نود فاقد هرگونه شکاف زمانی قابل دسترس برای ارسال در این چرخه نمونه را داشته باشد، آنگاه سبب از دست رفتن داده ها می شود. دلیل این است که این نود بخشی از اطلاعات سنجش را در چرخه نمونه بعدی تولید می کند و ارسال اطلاعات سنجش قدیمی بی معنی خواهد بود [1]. پس از بروز این رخداد، هیچ شکی وجود ندارد که اطلاعات سنجشی که توسط نود مقصد جمع آوری شده است به دلیل از دست رفتن داده ها کاهش یابد. به طور کلی، چرخه نمونه یک شبکه لحظه ای بسیار کمتر از یک شبکه غیر لحظه ای است. زمان بندی شکاف زمان شبکه لحظه ای منتظر دریافت تمامی اطلاعات سنجش از سوی فرزندان نود پیش از ارسال آن ها مطابق با روش جمع آوری پخش همگرا نمی ماند.
6. نتیجه گیری و کار آتی
در این مقاله روش زمان بندی جمع آوری انتشار تک پخش مشترک (UBA) ترکیبی برای حداکثر کردن جمع آوری اطلاعات و حداقل کردن تاخیر جمع آوری داده ها در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم چند مسیره پیشنهاد داده شده است. دو مکانیزم اصلی روش UBA شامل پذیرش یک حالت زمان بندی ترکیبی و استفاده از انرژی باقیمانده نودها است که مکانیزم اول استراتژی انتشار را در ناحیه دور از مقصد و استراتژی تک پخش در ناحیه نزدیک به مقصد می پذیرد؛ مکانیزم دوم بهترین استفاده را از انرژی باقیمانده نودها در نودهای غیر هات اسپات برای پیاده سازی استراتژی انتشار می برد. علاوه بر این، الگوریتم توزیع شکاف زمانی برای نودهای فرزند (TASDC) نیز پیشنهاد داده شده است که می تواند شکاف های زمانی بهینه را به نودهای فرزند اختصاص دهد و تاخیر شبکه را به طور موثر کاهش دهد. نتایج ارزیابی حاصل از شبیه سازی و تحلیل های نظری روش پیشنهادی نشان می دهد که روش UBA می تواند اطلاعات سنجیده شده را به میزان 25 درصد بهبود دهد و تاخیر را به میزان 14 تا 18 درصد با همان طول عمر شبکه در مقایسه با روش های EASDC و DAS کاهش دهد. حداکثر کردن جمع آوری اطلاعات و حداقل کردن تاخیر دو مساله حیاتی در جمع آوری اطلاعات شبکه در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم است. بیشتر روش های زمان بندی جمع آوری اطلاعات درون شبکه برای یک شکاف زمان ثابت اختصاص یافته طراحی شده اند به طوری که جمع آوری اطلاعات و تاخیر به طور همزمان قابل بهبود نیست. ما در کار آتی قصد داریم تا یک روش زمان بندی جمع آوری اطلاعات درون شبکه را طراحی کنیم که قابلیت حداکثر کردن جمع آوری اطلاعات و حداقل کردن تاخیر را برای شبکه های حسگر بی سیم اتلافی داشته باشد.
Abstract
A hybrid Unicast joint Broadcast Aggregation (UBA) schedule scheme is proposed for maximizing aggregation information and minimizing delay for wireless sensor networks (WSNs). UBA scheme adopts following regimes for maximizing aggregation information and minimizing delay. (a) The nodes in the far to sink region adopt broadcast manner, which can not only efficiently collect more sensing information within the same time slot but also reduce overall network delay. (b) The nodes in the near to sink region use unicast manner to collect sensing information, which can efficiently save energy consumption to extend network lifetime. This is UBA scheme with a great advantage that it can collect more sensing information and reduce delay without shortening network lifetime. Simulation and theoretical analytical results clearly indicate that the proposed scheme can significantly improve sensing information by 25% and reduce delay by 14% to 18% under the same network lifetime.
1. Introduction
The key function of wireless sensor networks (WSNs) is sensing and collecting surrounding information periodically through sensor nodes constituting the network and aggregating to sink node for further processing [1–5]. In those applications, all of the node samples are in each sample cycle. For each sample cycle, all sensor nodes do sampling once [2,5]. Data aggregation refers to the situation in which two data packets meet with each other at a node in the routing procedure and aggregated into one new data packet [1,6]. According to WSNs for real-time requirements, data aggregation can be divided into two categories. (1) Convergecast [7]. It is one of the most used non-real-time data aggregation patterns in WSNs. (2) Real-time data collection. In the real-time data aggregation network, sink node needs to gather as much sensing information as possible in a predetermined sample cycle [1]. For the node, if sensing information collected by node has no available time-slot to be sent in this sample cycle, it will cause data loss. The reason is that this node will generate a new piece of sensing information in the next sample cycle and it becomes meaningless to transmit the old sensing information [1]. After this happens, there is no doubt that sensing information aggregated by sink node will be reduced due to data loss. In general, sample cycle of real-time network is much less than non-real-time network. Real-time network time-slot schedule will not wait to receive all the sensing information from node’s children before sending them in accordance with the method of aggregation convergecast.
6. Conclusion and future work
In this paper, a hybrid Unicast joint Broadcast Aggregation (UBA) Schedule scheme is proposed for maximizing aggregation information and minimizing network delay in data collection multi-hop wireless sensor networks. The two main mechanisms of UBA scheme are the adoption of a mixed scheduling mode and the use of residual energy of nodes, the former mechanism adopts broadcast strategy in the far sink region and unicast strategy in the near sink region, and the latter is making the best use of the residual energy of nodes in non-hotspots to implement broadcast strategy. What’s more, Time-Slot Distribution Algorithm for Children (TSDAC) algorithm is also proposed, which can guide to assigning optimal time slots for children nodes and reduce network delay efficiently. Through simulation and detailed theoretical analyses of the proposed scheme, the evaluation results show that UBA scheme can improve sensing information by 25% and reduce delay by 14% - 18% under the same lifetime compared with EASDC and DAS scheme. To maximize aggregation information and minimize delay is two pivot issues for in-network aggregation in lossy wireless sensor networks. Most existing in-network aggregation schedules designed for a fixed allocated time slot which the total aggregation information and delay can not be optimized at same time. For future work, we yearn to design a integrating unallocated time slot in-network aggregation schedule scheme that is capable of maximizing aggregation information and minimizing delay for lossy WSNs.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مرتبط
3. مدل سیستم و بیان مساله
3-1 مدل شبکه
3-2 مدل جمع آوری داده ها
3-3 مدل مصرف انرژی و تعاریف مرتبط
3-4 بیان مساله
4. طراحی روش زمان بندی ترکیبی UBA
4-1 انگیزه روش UBA
4-2 الگوریتم زمان بندی انتشار تک پخشی مشترک
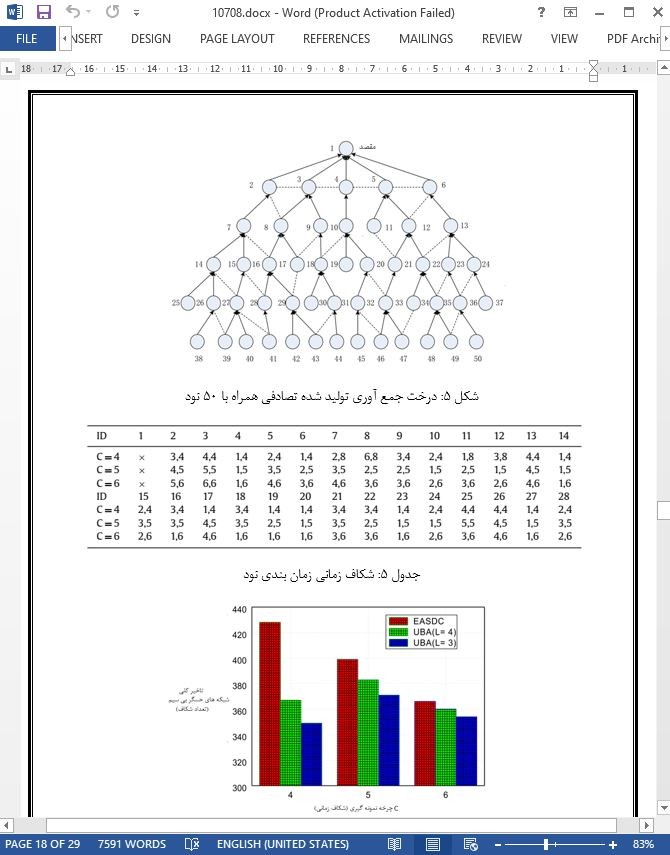
5. ارزیابی تجربی
5-1 تعیین پارامترهای تجربی
5-2 اختصاص شکاف زمانی زمان بندی
5-3 ارزیابی تاخیر
5-4 اطلاعات سنجش
5-5 ارزیابی مصرف انرژی و طول عمر
5-6 بهینه سازی سطح انتشار
5-7 تاثیر پارامترهای شبکه بر عملکرد
6. نتیجه گیری و کار آتی
abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related work
3. The system model and problem statement
3.1. The network model
3.2. Data aggregation model
3.3. Energy consumption model and related definitions
3.4. Problem statement
4. A hybrid unicast joint broadcast aggregation (UBA) schedule scheme design
4.1. The motive of UBA scheme
4.2. Unicast joint broadcast schedule algorithm
5. Experimental evaluation
5.1. Experimental parameters setting
5.2. Schedule time slot assignment
5.3. Evaluation on delay
5.4. The sensing information
5.5. Evaluation on energy consumption and lifetime
5.6. Broadcast level optimization
5.7. The influence of network parameters on the performance
6. Conclusion and future work
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
