
ارزیابی ریسک پروژه های مشارکتی عمومی – خصوصی برای زیر ساخت های شارژ وسایل نقلیه الکتریکی
چکیده
با افزایش توجه جهانی به انرژی های پاک و توسعه پایدار در محیط زیست، پروژه های وسایل نقلیه الکتریکی (EV) از نظر تعداد مقیاس در سراسر جهان افزایش پیدا کرده اند. اما، افزایش عدم تعادل بین عرضه – تقاضا در زیر ساخت های شارژ وسایل نقلیه یکی از مهم ترین مشکلات توسعه EV در چین می باشد. دولت در حالت اجرای پروژه های مشارکت بخش خصوصی – عمومی (PPP) در این زمینه می باشد تا بتواند به صورت موثر از سرمایه های موجود و ظرفیت های فنی پیشرفته در بخش خصوصی استفاده کند تا بتواند عملکرد و سرویس رسانی برای شارژ وسایل نقلیه الکتریکی را بهبود بخشد. برای تضمین موفقیت پروژه، ارزیابی خطر که خیلی مطالعات زیادی در رابطه اش انجام نشده، یکی از مهم ترین گام ها می باشد. هدف این مقاله، ارزیابی عوامل خطر از طریق یک نظر سنجی پرسش نامه ای و محاسبه سطح خطر کلی زیر ساخت های شارژ وسایل نقلیه در پروژه های PPP با یک روش یکپارچه رتبه بندی اولویت ها از طریق تشابه با راه حل ایده آل ( تاپسیس فازی) می باشد. نتایج شناسایی عوامل خطر شامل دسته بندی های خطر زیست محیطی / اجتماعی، اقتصادی، قانونی / سیاسی، فنی می باشد و ما چهار عامل خطر را به عنوان مهم ترین عوامل موثر در زیر ساخت های شارژ وسایل نقلیه در چین، انتخاب کردیم : تجربه کم در زمینه پروژه های PPP ، هزینه بالای باتری ها، دوره شارژ طولانی و افزایش قیمت توان. سطح ریسک کلی سه پروژه جایگزین نیز در این مطالعه ارزیابی شد و سپس با استفاده از روش پیشنهاد شده هم عوامل خطر آن رتبه بندی شد. سپس امکان پذیری اجرایی و تاثیر این پروژه ها نیز از طریق یک تحلیل مقایسه ای و تحلیل میزان حساسیت، بررسی شد. علاوه بر این، با آگاهی نسبت به خطرات موجود، پیشنهاداتی برای بخش خصوصی پروژه های PPP زیر ساخت های شارژ وسایل نقلیه الکتریکی ارائه شد. کارایی ها و محدودیت های دقیق این مقاله نیز در قسمت پیشنهادات و جمع بندی ارائه شده است.
1. مقدمه
به دلیل مطرح شدن بحث توسعه پایدار، صرفه جویی در هزینه و کاهش نشر گاز های آلوده کننده تبدیل به یکی از موضوعات ضروری شده است . وسایل نقلیه الکتریکی (EV ها) که نقش بسیار مهمی در توسعه استراتژیک دارند، به عنوان تکنولوژی های موفق برای ارتقای کیفیت زیست محیطی، زیست پذیری و توسعه پایدار بدون کاهش محسوس قابلیت جابجایی یا راحتی در نظر گرفته می شوند ( Stark Juliane et al., 2018; White and Sintov, 2017) و به خاطر تاثیر محسوس این وسایل در کاهش میزان نشر کربن دی اکسید، باعث شده که توجه زیادی به آن ها جلب شود ( Zhang and Han, 2017) و حفاظت زیست محیطی خوبی شکل بگیرد. به دلیل این که بخش حمل و نقل یکی از موثر ترین واحد های نشر گاز های گلخانه ای بوده است ( He and Zhan, 2018; S. Wang et al., 2017)، تلاش ها و مجموعه اندازه گیری هایی انجام شده است تا بتوان الزام های توسعه پایدار چین را فراهم کرد. در نتیجه، چین به یکی از بزرگترین بازار های وسایل نقلیه الکتریکی در جهان تبدیل شده است و همواره در حال رشد با سرعت بالا می باشد ( Lin and Wu, 2018) و میزان فروش این وسایل نقلیه به 777.000 مورد رسیده است. با وجود مقیاس توسعه EV ، باید به این نکته اشاره کرد که عدم تعادل بین عرضه – تقاضا در زیر ساختار های وسایل نقلیه الکتریکی شارژی (EVCI) تبدیل به یکی از مهم ترین موانع توسعه EV در چین شده است. برای تامین نیاز شارژ ضروری برای این وسایل نقلیه، مشارکت بخش خصوصی- عمومی (PPP) یکی از روش هایی است که پیشنهاد شده و می تواند باعث جذب بخش خصوصی شده و در نتیجه از مزیت های تامین مالی آن ها ،طراحی، ساخت و ساز و عملیات برای فراهم کردن کیفیت بالا، سرویس های متنوع شارژ و ایجاد مزایای اجتماعی استفاده کرد (Ou,2016)
7. جمع بندی
توسعه EV می تواند نقش بسیار مهمی برای رسیدن به مزایای زیست محیطی تمیز ایفا کند و باعث توسعه پایدار یک جامعه شود. معرفی روش اجرای پروژه به صورت PPP در ساخت زیر ساخت های شارژ EV برای حل عدم تعادل بین عرضه – تقاضا ، توسط دولت به عنوان یک روش موثر برای جذب سرمایه های خصوصی و بهبود عملکرد و خدمات، پشتیبانی شده است. تحلیل ریسک پروژه های PPP یکی از مهم ترین موضوعات ضروری برای بخش خصوصی می باشد تا نسبت به موفقیت پروژه مطمئن شود و باید مشخص شود کدام عوامل ریسک ممکن است بر روی پروژه تاثیر بگذارد. همچنین ما باید روش هایی داشته باشیم تا با استفاده از آن ها بتوانیم سطح ریسک کلی را با روش های علمی اندازه گیری کنیم. برای حل این مسئله، این مقاله یک روند شناسایی عوامل ریسک و ارزیابی پروژه EVCI PPP را با روش TOPSIS فازی ارائه می کند. در نتیجه، ما 17 عامل ریسک بحرانی را به عنوان معیار ارزیابی از طریق مرور مقالات و نظر سنجی پرسش نامه ای شناسایی کردیم و وزن های معیار ها را با استفاده از روش میانگین نرمال شده مشخص کردیم و رتبه بندی روش های جایگزین را بر اساس همین روش، مشخص کردیم . یک تحلیل مقایسه ای و تحلیل حساسیت نیز برای تایید امکان پذیری و تاثیر این مدل، انجام شد. ارزیابی خطر و تحلیل پروژه های PPP مهم ترین موضوعات در این زمینه هستند و می توانند توجه تمام محقق های جهان را به خودشان جلب کنند. به عنوان بخشی از ساخت و ساز زیر ساخت ها، تحلیل خطر زیر ساخت های شارژ نقش مهمی را ایفا می کند اما مقالات کمی به بررسی ریسک ها و ارزیابی جامعه در زمینه فعالیت های بخش خصوصی انجام داده اند. هدف این مقاله ، تکمیل این خلا می باشد.
Abstract
With increasing worldwide attention on clean energy and sustainability of environment development, electric vehicle (EV) projects have been growing in number and scale all over the world. However, increasing demand-supply imbalance in charging infrastructure becomes the major obstacle of Chinese EV development. Governments are applying Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode in this field to effectively make use of solid capital and advanced technological capability of private sector to improve charging performance and service. To ensure project success, risk evaluation, which has remained nebulous, has become a crucial step. This paper aims to explore risk factors through questionnaire survey and calculate the overall risk levels of EV charging infrastructure PPP projects with an integrated approach with Fuzzy Order Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (Fuzzy TOPSIS). Results of risk factors identification consisted of project/technical, political/legal, economic and social/environmental risk categories and four risk factors were selected for specific concern of charging infrastructure in China: inadequate PPP project experience, high battery cost, long charging period and power price rise. Overall risk levels of three alternative projects were evaluated and ranked with proposed approach whose feasibility and effectiveness were verified through a comparative analysis and a sensitivity analysis. Moreover, awareness of existing risks, suggestions were provided for private sectors of EV charging infrastructure PPP project. The detailed implications and limitations were presented in the suggestions and the conclusions.
1 Introduction
As global sustainable development, energy saving and emission reduction have become necessary and urgent issues. Electric vehicles (EVs), which play a key role in strategic development plans as a promising technology to promote environmental quality, livability, and sustainability without significantly reducing convenience or mobility (Stark Juliane et al., 2018; White and Sintov, 2017), has been given more attention for its outstanding performance in carbon emission reduction (Zhang and Han, 2017) and environment protection. Since transport sector has been one of the top contributors in greenhouse gas emissions (He and Zhan, 2018; S. Wang et al., 2017), significant efforts and series of measurements have been taken to satisfy China’s sustainable development requirements. As a result, China has become the world's largest electric vehicle market and continues to maintain a high-speed growth (Lin and Wu, 2018) and its sales totaled 777,000 in 2017. Despite the EV development scale, it is noteworthy that demand-supply imbalance in electric vehicle charging infrastructure (EVCI) has become the major obstacle of EV development in China. To satisfy increasingly urgent charging demand, public-private partnership (PPP) mode has been introduced and supported to attract private sectors and make use of their advantages in financing, design, construction and operation for providing high quality, efficient and diverse charging services and creating social benefit (Ou, 2016).
7 Conclusions
EV development can play a significant role in achieving clean environmental benefits and contribute to sustainability of the society. Introducing PPP mode into EV charging infrastructure construction to solve demand-supply imbalance is highly encouraged by the government as an effective mean to attract private capital and improve charging performances and services. Risk analysis of a PPP project is necessary for the private sector to ensure project success and it’s important to understand what risk factors might influence the project and how to calculate the overall risk level with scientific approach. To solve this problem, this paper constructed a risk identification and evaluation framework of EVCI PPP project with an integrated fuzzy TOPSIS approach. As the results, we selected 17 critical risk factors as evaluation criterion through literature review and questionnaire survey, determined criterion weights with normalized mean method and evaluated and ranked alternatives with proposed approach. A comparative analysis and a sensitivity analysis were constructed to verify feasibility and effectiveness of the model. Risk evaluation and analysis of PPP project are most critical issues and attract attentions from researchers all over the world. As part of main infrastructure construction, risk analysis of charging infrastructure plays a significant role though few literature has carefully identify its risk factors and conduct comprehensive evaluation in this field for the private sector. This paper intents to contribute to this section.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مرور مقالات
2.1 زیر ساختار های شارژ EV در پروژه های PPP در چین
2.2 تحلیل ریسک با حالت PPP
2.3 عوامل خطر قابل استفاده در پروژه های زیر ساخت PPP
2.4 روش TOPSPS فازی
3. روش شناسی و مواد
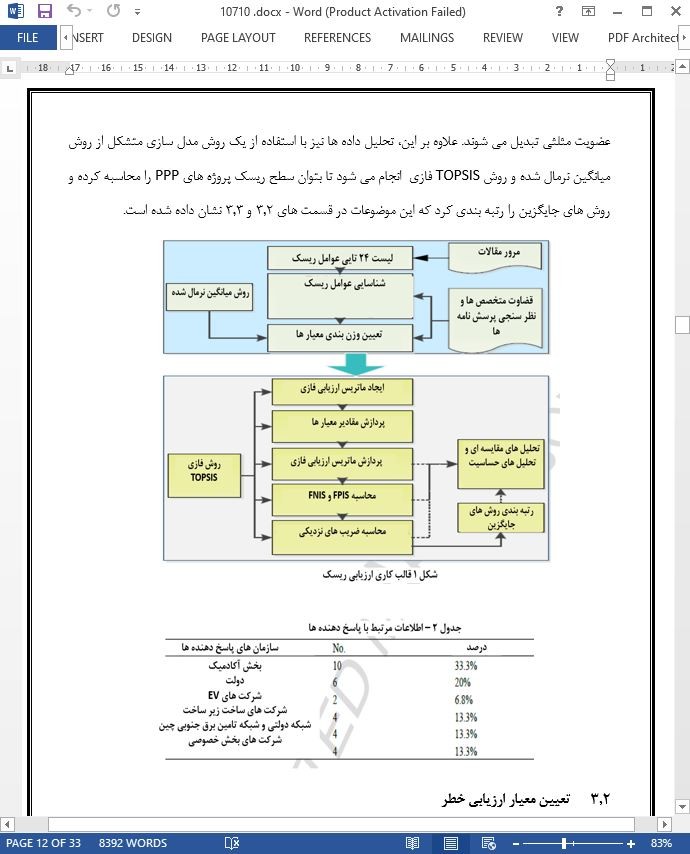
3.1 قالب کار تحقیقاتی
3.2 تعیین معیار ارزیابی خطر
3.3 یک روش یکپارچه با TOPSIS فازی
4. نتایج
5. مباحث
5.1 تحلیل مقایسه ای
5.2 تحلیل حساسیت
5.3 تفسیر نتایج
6. پیشنهادات
7. جمع بندی
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Literature review
2.1 EV charging infrastructure PPP projects in China
2.2 Risk analysis with PPP mode
2.3 Applicable risk factors of infrastructure PPP projects
2.4 Fuzzy TOPSIS method
3 Methodology and materials
3.1 Research framework
3.2 Risk evaluation criteria determination
3.3 An integrated approach with fuzzy TOPSIS
4 Results
5 Discussions
5.1 Comparative analysis
5.2 Sensitivity analysis
5.3 Interpretation of results
6 Suggestions
7 Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
