
مدل مدیریت کیفیت ساخت و ساز مبتنی بر BIM و کاربرد های آن
چکیده
پتانسیل ساختن مدلسازی اطلاعات ساختمان (BIM) برای پشتیبانی از انتقال فرایندهای طراحی و ساختوساز در صنعت ساختوساز مشهود بوده است. اگرچه، BIM با حذف تضادها و کاهش دوبارهکاری، در بهبود کیفیت طراحی مفید در نظر گرفتهشده است، تحقیقات کمی راجع به استفاده از BIM در پروژهها برای کنترل کیفیت ساختوساز و استفاده مؤثر از اطلاعات صورت گرفته است. به دلیل سازگاری دادههای طراحی با دادههای کیفی و فرایند ساختوساز با فرایند کنترل کیفیت، پتانسیل اجرای BIM در مدیریت کیفیت، در توانایی آن در ارائه دادههای چندبعدی شامل دادههای طراحی و توالی زمان واقع است. این مقاله مزیتهای BIM 4 بعدی را با ساختن یک مدل در ساختار تعریف داده محصول، سازمان و فرایند (POP) برای کاربرد کیفی مبتنی بر کدهای ساختوساز، کشف و بررسی میکند. یک مطالعه موردی برای اعتبار دهی استفاده نرمافزار BIM 4 بعدی ارائهشده برای کنترل کیفیت در طی فاز ساختوساز مرکز نمایشگاهی بینالمللی Wuhan ارائهشده است.
1. مقدمه
کیفیت یک کالا در توانایی آن برای ارضای نیازهای بیانشده یا ضمنی و ویژگیهای درونی یک محصول تمامشده علاوه بر طراحی خارجی آن، منعکسشده است. لذا، کیفیت محصول ساختوساز را میتوان بدین شکل تعریف کرد: میزانی که نیازهای بیانشده و ضمنی و ویژگیهای درونی در طی فرایند ساختوساز تضمین میشوند. این پژوهش، کیفیت را انطباق با خصوصیات و کدهای ساختوساز تعریف میکند.
7. نتیجهگیری و توصیهها
یافتههای ارائهشده در درک استفاده بالقوه از BIM در مدیریت کیفیت ساختوساز و پر کردن شکاف موجود در دانش استفاده از BIM برای مدیریت کیفیت ساختوساز نقش دارد. این مقاله اجرای BIM را در مدیریت کیفیت و راهحلهای تلفیقشده ارائهشده برای بهبود فرایندهای مدیریت کیفیت فعلی با کمک یک محیط کاری BIM بررسی میکند. یک مدل کیفیت مبتنی بر BIM ارائهشده است که BIM و مدل POP کیفیت موجود را ترکیب میکند. همچنین این مقاله بحث میکند که چگونه این دو مدل باهم برای تسهیل مدیریت کیفیت عمل میکنند. این کار به شرکتکنندگان پروژه کمک میکند تا بهتر پیشرفت کیفیت را درک کند و بهصورت مؤثرتری همکاری کنند که به دلیل فرمت داده بصری شده است. منافع اصلی مدل کیفیت ساختوساز در این مقاله در جنبههای زیر واقع است: اول، استفاده از اطلاعات طراحی، سازگاری اطلاعات را تضمین میکند و فرایند مدیریت کیفیت را تسهیل میکند. دوم، کدهای ساختوساز استانداردشده و ساختاربندی شده در مدل ادغام شدهاند تا الزامات کاری ساختوساز واضحتری را برای آموزش و تأیید ارائه کنند. میتوان از خطاهای معمولی ایجادشده به دلیل بدفهمیدن کدهای ارجاع متقابل اجتناب کرد. سوم، نرمافزار 4 بعدی تضمینکننده بازرسی زمانی و مجازی کردن تمام فرایند است که به شرکتکنندگان پروژه کمک میکند تا بهتر پذیرش الزامات کیفیت را درک کنند و به شیوهای مجازی شده همکاری کنند.
Abstract
The potential of Building Information Modeling (BIM) to support a transformation of the processes of design and construction has been evident in the construction industry. Although BIM is considered helpful in improving design quality by eliminating conflicts and reducing rework, there has been little research into using BIM throughout the project for construction quality control and efficient information utilization. Due to the consistency of design data with quality data and construction process with quality control process, the potential of BIM implementation in quality management lies in its ability to present multi-dimensional data including design data and time sequence. This paper explores and discusses the advantages of 4D BIM for a quality application based on construction codes, by constructing the model in a product, organization and process (POP) data definition structure. A case study is provided to validate the use of the proposed 4D BIM application for quality control during the construction phase of the Wuhan International EXPO Center.
1. Introduction
The quality of a product is reflected in its ability to satisfy stated or implied needs and internal characteristics of a finished product in addition to its external design [1]. Therefore, construction product quality can be defined as: the degree to which the stated or implied needs and the internal characteristics are guaranteed during the process of construction [2]. This research defines quality as compliance with construction codes and specifications.
7. Conclusions and recommendations
The presented findings contribute to the understanding of the potential use of BIM in construction quality management and fill an existing gap in the knowledge on the use of BIM for construction quality management. This paper explored the implementation of BIM in quality management and proposed integrated solutions to improve current quality management processes with assistance of a BIM working environment. A BIM-based quality model has been proposed to combine BIM and the existing quality POP model. Also this paper discusses how these two models will work together to facilitate construction quality management. It helps the project participants to better understand the quality progress and to collaborate more effectively thanks to a visualized data format. The key benefits of the construction quality model proposed in this paper lie in the following aspects: First, the utilization of design information ensures information consistency and facilitates quality management process. Second, the fully standardized and structured construction codes are integrated in the model to provide clear construction task requirements for instruction and verification. Typical errors caused by misunderstanding of cross-reference codes can be avoided. Third, 4D application ensures the timely inspection and virtualization of the whole process, which helps the project participants to better understand the quality requirements acceptance, and to collaborate in a visualized manner.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
1.1. پیشینه تحقیق
1.2. BIM و کاربرد آن در مدیریت کیفیت پروژه
2. هدف تحقیق و روششناسی
3. طرح مدیریت کیفیت در ساختوساز زیرساخت بزرگ
4. معماری مدل کیفیت ساختوساز مبتنی بر BIM
4.1. روش مدلسازی POP
4.2. مدل کیفیت ساختوساز مبتنی بر BIM
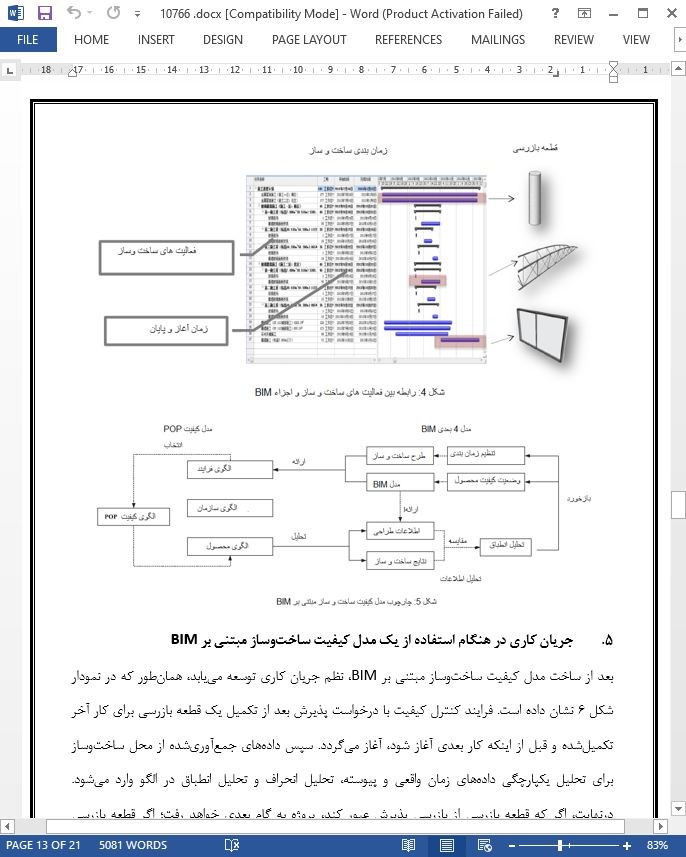
5. جریان کاری در هنگام استفاده از یک مدل کیفیت ساختوساز مبتنی بر BIM
6. اجرا
7. نتیجهگیری و توصیهها
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Research background
1.2. BIM and its applications in project quality management
2. Research objective and methodology
3. Quality management plan in large infrastructure construction
4. Architecture of BIM-based construction quality model
4.1. POP modeling method
4.2. BIM-based construction quality model
5. Workflow when using a BIM-based construction quality model
6. Implementation
7. Conclusions and recommendations
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
