
مقاومت برشی بلوک و طراحی تیرهای سازگار با اتصالات خط پیچ دوگانه
چکیده
داده های تست موجود درباره رفتار برشی بلوک تیرهای سازگار با اتصالات خط پیچ دوبل کاملا محدود است و بررسی های اولیه نشان می دهد که ظرفیت های برشی بلوک تست را نمی توان به طور دقیق با قواعد طراحی موجود پیش بینی کرد چرا که به روشی متناقض این مد شکست را بررسی می کند. برای نشان دادن این موضوع، یک بررسی جامع با تمرکز بر رفتار برشی مجموعه تیرهای سازگار با اتصالات خط پیچ دوگانه در این مقاله گزارش شده است. تحقیق با 17 آزمون مقیاس تمام با درنظر گرفتن پارامترهای آزمون نسبت ابعاد بلوک جان، خروج ازمرکز خارج ازصفحه، سختی دورانی اتصال، و آرایش نامنظم (Stagger) پیچ شروع شد. دو نمونه به دلیل کمانش جان محلی و 15 نمونه دیگر به دلیل برش بلوک فروریختند. سه مد شکست برشی بلوک، به نام های پارگی کل بلوک (WBT)، شکست تنشی (TF)، و شکست تنشی ناشی از پارگی کل بلوک (TF-WBT) در بار نهایی مشاهده شد. تاثیر پارامترهای موردنظر آزمون بر مد شکست و ظرفیت برشی بلوک نمونه های آزمون به طور کامل بررسی شد. سپس نتایج آزمون با قواعد طراحی موجود به منظور ارزیابی ثبات و دقت استانداردهای مهم مقایسه و دریافته شد که این استانداردها منجربه نسبت آزمون به پیش بینی متناقض می شوند و به سمت شیوه های سنتی (محافظه کارانه) گرایش دارند. با خلاصه سازی تمامی داده های آزمون موجود، شامل آزمون های کنونی و آزمون های انجام شده توسط دیگر محققان، تحلیلی مطمئن به منظور بررسی بیشتر سطح ایمنی استانداردهای مهم انجام شد. نهایتا توصیه های طراحی با هدف دستیابی به رویکردهای طراحی مطمئن اما اقتصادی با سطح ایمنی پایدار ارائه شد.
1. مقدمه
در طراحی سازه های فولادی حذف بخشی از بال تیرهای ثانویه به منظور تضمین ارتفاع یکسان در موقعیت تقاطع قطعات کاملا معمول است. تیرهای با بال بالایی حذف شده (یا حذف هردوبال درصورت نیاز) نزدیک ناحیه اتصال تیرهای مقابله/بریده نامیده می شود. اگرچه حذف بخشی از بال یکی از راه حل های ساده برای فراهم کردن فضای آزاد موردنیاز است، اما حضور درپوش ناچارا مقاومت تیر در ناحیه مقابله را کاهش می دهد و برش بلوک یکی از مدهای شکست رایج برای تیرهای مقابله است. این مد شکست معمولا به وسیله بلوک ماده جداشده از جان تیر مقابله نمایان می شود و این امر در اتصالات پیچ کاری یا جوشکاری شده رخ می دهد. برای اتصال پیچ کاری شده، که درآن تعداد مختلفی از خطوط /ردیف های پیچ (تعریف هریک در شکل 1(a) نشان داده شده است) برای تهیه الزامات مختلف طراحی مرتب شده اند، شکست برشی بلوک اغلب با شکست تنشی ایجادشده بر روی صفحه جلوی ردیف پیچ پایین (یعنی ناحیه تنش) و شکست برشی (یا تسلیم مفرط یا شکست کامل) ایجادشده برروی خط پیچ بحرانی نمایان می شود. مدهای شکست برشی بلوک نوعی برای تیرهای مقابله با اتصالات خط پیچ واحد و خط پیچ دوگانه در شکل 1(a) نشان داده شده است.
7. خلاصه و نتایج
مقاله حاضر یک بررسی جامع از رفتار و طراحی شکست برشی بلوک تیرهای مقابله با اتصالات خط پیچ دوگانه را گزارش کرد. درمجموع 17 آزمون مقیاس تمام انجام شدند، و پارامترهای آزمون شامل نسبت ابعاد بلوک جان، خروج از مرکز خارج از صفحه، سختی دورانی اتصال، و آرایش نامنظم پیچ ها بود. دو نمونه به وسیله کمانش جان محلی و 15 نمونه دیگر به وسیله برش محلی گسیخته شدند. سه مد شکست برشی بلوک در بار نهایی مشاهده شد که عبارتند از: پارگی کل بلوک (WBT)، شکست تنشی (TF)، و شکست تنشی ناشی از پارگی کل بلوک (TF-WBT). دریافته شد که مد شکست متاثر از نسبت ابعاد و نوع اتصال است. اضافه برآن، پیچش جان در برخی نمونه ها مشاهده شد، و اهمیت پیچش جان متاثر از سختی جانبی اتصالات بود.
Abstract
Available test data on block shear behaviour of coped beams with double bolt-line connections are quite limited, and earlier investigations found that the test block shear capacities could not be accurately predicted by existing design rules which deal with this failure mode in an inconsistent manner. To address this, a comprehensive investigation focusing on the block shear behaviour of coped beams with double bolt-line connections was reported in this paper. The research commenced with 17 full-scale tests considering the test parameters of web block aspect ratio, out-of-plane eccentricity, connection rotational stiffness, and bolt stagger. Two specimens were found to fail by local web buckling, and the remaining 15 specimens failed by block shear. Three typical block shear failure modes were observed at ultimate load, namely, whole block tear-out (WBT), tensile fracture (TF), and tensile fracture followed by whole block tear-out (TF–WBT). The influences of the considered test parameters on the failure mode and block shear capacity of the test specimens were thoroughly discussed. The test results were then compared with existing design rules to evaluate the consistency and accuracy of the major standards, and it was found that these standards led to inconsistent test-to-predicted ratios and tended to be conservative. Summarising all available test data, including the current tests and those previously conducted by other researchers, a reliability analysis was conducted to further examine the level of safety of the major standards. Design recommendations were finally proposed aiming to achieve reliable yet economical design approaches with consistent safety levels.
1. Introduction
It is very common in structural steel design to remove part of the flange of secondary beams in order to ensure the same elevation at member junctions. The beams with removed top flange (or both flanges if necessary) near the connection zone are called coped/notched beams. While the removal of part of the flange is one of the easiest solutions to provide the required clearance, the presence of the cope will inevitably reduce the strength of the beam in the coped region, and block shear is one of the most common failure modes for coped beams. This failure mode is typically featured by a block of material torn out from the coped beam web, and it can happen in either bolted or welded connections. For a bolted connection, where different numbers of bolt lines/rows (the definitions of which are shown in Fig. 1(a)) can be arranged to cater for various design requirements, block shear failure is often featured by a tensile fracture developed on the plane along the bottom bolt row (i.e. tension area) and a shear failure (either excessive yielding or complete fracture) developed over a critical bolt line (i.e. shear area). The typical block shear failure modes for the coped beams with single bolt-line and double bolt-line connections are shown in Fig. 1(a).
7. Summary and conclusions
This paper has reported a comprehensive investigation on the behaviour and design of block shear failure of coped beams with double bolt-line connections. A total of 17 full-scale tests have been conducted, and the test parameters included web block aspect ratio, out-of-plane eccentricity, connection rotational stiffness, and bolt stagger. Two specimens were found to fail by local web buckling, and the remaining 15 specimens failed by block shear. Three typical block shear failure modes were observed at ultimate load, namely, whole block tear-out (WBT), tensile fracture (TF), and tensile fracture followed by whole block tear-out (TF–WBT). The failure mode was found to be affected by the aspect ratio and connection type. In addition, web twisting was observed in some specimens, and the significance of web twisting was influenced by the lateral stiffness of the connections.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. برنامه آزمایشی
2 – 1: نمونه های آزمون
2 – 2: مجموعه آزمون، تجهیزات اندازه گیری و شیوه های آزمون
3. نتایج آزمون
3 – 1: نتایج کلی
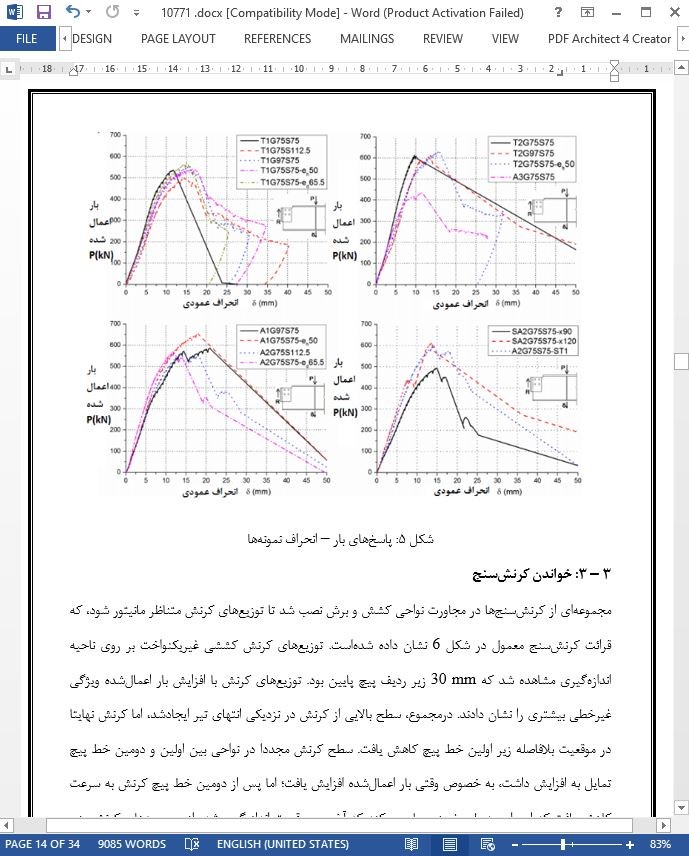
3 – 2: پاسخ بار – انحراف
3 – 3: خواندن کرنش سنج
4. بحث وبررسی نتایج آزمون
4 – 1: فاکتورهای مؤثر بر مد شکست
4 – 2: تاثیر نسبت ابعاد
4 – 3: تاثیر سختی دورانی اتصال
4 – 4: تاثیر خروج از مرکز خارج از صفحه
4 – 5: اثر آرایش نامنظم پیچ
5. مقایسه نسبت به استانداردهای طراحی
5 – 1: قواعد طراحی موجود
5 – 2: مقایسه نسبت به قواعد طراحی موجود
6. تحلیل قابلیت اطمینان و ملاحظات طراحی
6 – 1: نتایج کلی
6 – 2: شیوه تعیین ضریب مقاومت
6 – 3: نتایج تحلیلی و ملاحظات طراحی
7. خلاصه و نتایج
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental programme
2.1. Test specimens
2.2. Test setup, instrumentations, and test procedures
3. Test results
3.1. General
3.2. Load–deflection response
3.3. Strain gauge readings
4. Discussion of test results
4.1. Factors influencing failure mode
4.2. Influence of aspect ratio
4.3. Influence of connection rotational stiffness
4.4. Influence of out-of-plane eccentricity
4.5. Influence of bolt stagger
5. Comparisons against design standards
5.1. Existing design rules
5.2. Comparisons against existing design rules
6. Reliability analysis and design recommendations
6.1. General
6.2. Procedure of determining resistance factor
6.3. Analysis results and design recommendations
7. Summary and conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
