
موفقیت تبلیغات ویروسی: پیشبینی کننده های اجتماعی و نگرشی رفتار اشتراک گذاری مشتریان
چکیده
مطالعه حاضر به بررسی فاکتورهایی میپردازد که اشتراکگذاری ارتباطات تبلیغات ویروسی مشتریان در بین دوستانشان در شبکههای اجتماعی را پیشبینی میکند. چارچوب مفهومی شامل سه پیشبینی کننده اجتماعی و سه پیشبینی کننده نگرشی از ارسال محتوای آنلاین است که با استفاده از سه کمپین تبلیغاتی واقعی بررسی و همزمان از طریق سایتهای شبکه اجتماعی Hyves هلند منتشر شدند. نتایج نشان داد که رفتار اشتراکگذاری تبلیغات ویروسی بهطور چشمگیری با نگرش مثبت نسبت به برند، تبلیغات و بهطورکلی نسبت به تبلیغات ویروسی قابل پیشبینی بود. برای دو مورد از سه مورد تبلیغات، شرکتکنندگان بیشتر تمایل به ارسال تبلیغاتی داشتند که از بهجای کمپین از دوست خود دریافت کرده بودند. مطالعه حاضر اولین مقاله در بررسی پیشبینی کنندههای رفتار اشتراکگذاری واقعی در زمینه سایت شبکه اجتماعی است، که به موجب آن مشارکت قابلتوجهی در دانش موجود درباره محورهای موفقیت تبلیغات ویروسی داراست. 1. مقدمه سایتهای شبکه اجتماعی (SNSs) محیطی با محبوبیت فزاینده برای بازاریابی است (تیلور، لوین و استراتون، 20111) . تبلیغکنندگان با استفاده از ارتباطات همتا با همتا جهت بهبود برندها، محصولات و خدمات خود در بین گروههای هدف، قدرت مجابکننده تبلیغات ویروسی را کشف کردهاند. تبلیغکنندگان با ایجاد پیامهای تبلیغاتی جذاب و سرگرمکننده، مشتریان را تشویق میکنند تا این پیامها را با دوستان خود در شبکههای اجتماعی آنلاین به اشتراک بگذارند (برگر و لینگار، 20132). چون موفقیت شرکتهای تبلیغات ویروسی تا حد زیادی به گسترش پیام افراد با دیگران وابسته است، محققان شروع به بررسی عوامل مؤثر بر اشتراکگذاری محتوای آنلاین مشتریان کردهاند. بااینحال، این تحقیقات عمدتاً بر بازاریابی ویروسی از طریق ایمیل متمرکز بوده است. مطالعات اندکی تبلیغات ویروسی در زمینه SNSs را بررسی کردهاند و این مطالعات نیز صرفاً بر اهداف خود گزارش مشتریان در ارسال پیامهای تبلیغاتی متکی هستند.
6. بحث و بررسی
مطالعه حاضر به بررسی فاکتورهایی پرداخت که اشتراکگذاری اعضای SNSs از ارتباطات تبلیغات ویروسی را پیشبینی میکند. همچنین این مقاله یافتههای تحقیقات قبلی درباره پیشبینی کنندههای اشتراکگذاری محتوای آنلاین در چارچوب مفهومی جدید را ادغام و این مدل را با استفاده از سه کمپین تبلیغاتی واقعی که روی سایت شبکه اجتماعی Hyves هلند راهاندازی شدند، بررسی کرد. با بررسی محدوده ورای رفتارها و مقاصد خود گزارششده و بررسی رفتار اشتراکگذاری واقعی، این مطالعه مشارکت چشمگیری را در زمینه محورهای موفقیت تبلیغات ویروسی فراهم میکند. در مقایسه با تبلیغات ویروسی از طریق ایمیل، رفتار اشتراکگذاری در SNSs تا حد زیادی متأثر از پیشبینی کنندههای اجتماعی، مانند فرستنده تبلیغ، بهجای پیشبینی کنندههای اجتماعی مانند نگرش مشتریان نسبت به برند تبلیغشده است. این اختلاف انتظار میرود زیرا در مقابل با دیگر انواع محتوای آنلاین ارسالشده، نوع تبلیغات ویروسی در SNSs که در این مقاله بررسیشده است، در ماهیت شخصیتر، تعاملیتر و اجتماعیتر است: کمپینهای تبلیغاتی اجرای بازی را شامل میکنند که در آن نه برند تبلیغشده، بلکه شبکه اجتماعی شخصی فرد نقش مرکزی را ایفا میکند.
Abstract
This study investigates which factors predict whether consumers will pass on viral advertising communications to their friends on a social network site. A conceptual framework consisting of three attitudinal and three social predictors of forwarding online content was tested using three real-life advertising campaigns that were spread simultaneously through the Dutch social network site Hyves. Results show that viral advertising pass-on behavior was significantly predicted by a positive attitude toward the brand, the advertisement, and toward viral advertising in general. For two of the three advertisements participants were more likely to forward the advertisement when the advertisement was received from a friend rather than a company. The present study is the first to investigate the predictors of actual pass-on behavior of viral advertisements in the context of a social network site, thereby significantly contributing to existing knowledge on the drivers of viral advertising success.
1. Introduction
Social network sites (SNSs) are an increasingly popular venue for marketing (Taylor, Lewin, & Strutton, 2011). Advertisers have discovered the persuasive power of viral advertising, using online peer-to-peer communication to promote their brands, products, and services among their target groups. By creating appealing and entertaining advertising messages, advertisers encourage consumers to pass on these messages to friends in their online social networks (Berger & Iyengar, 2013). Since the success of viral advertising campaigns largely depends on people spreading the message to others, researchers have started to investigate which factors may influence whether consumers pass along online content. However, this research has mainly focused on viral marketing through e-mail (e.g., Chiu, Hsieh, Kao, & Lee, 2007; Bruyn, de, & Lilien, 2008; Dobele, Lindgreen, Beverland, Vanhamme, & Wijk, 2007; Huang, Lin, & Lin, 2009; Phelps, Lewis, Mobilio, Perry, & Raman, 2004). Few studies have investigated viral advertising in the context of SNSs, and these studies solely relied on consumers' self-reported intentions to forward a campaign message (e.g., Chu, 2011; Van Noort, Antheunis, & Van Reijmersdal, 2012).
6. Discussion
The present study investigated which factors predict whether members of SNSs will pass on viral advertising communications. The present study integrated previous research findings on the predictors of passing on online content into a new conceptual framework, and tested this model using three real-life advertising campaigns that were spread on the Dutch social network site Hyves. Going beyond self-reported behavior and intentions, and investigating actual pass-on behavior, this study significantly adds to existing knowledge on the drivers of viral advertising success. Compared to viral advertising through e-mail, pass-on behavior on SNSs was expected to be more strongly influenced by social predictors, such as the sender of the ad, rather than attitudinal predictors, such as consumers' attitude toward the advertised brand. This difference was expected because in contrast to other types of forwarded online content, the type of viral advertisements on SNSs that were studied in this paper were more personal, interactive, and social in nature: the ad campaigns involved playing a game in which not the advertised brand, but an individual's private social network played a central role.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. پیشبینی موفقیت تبلیغات ویروسی
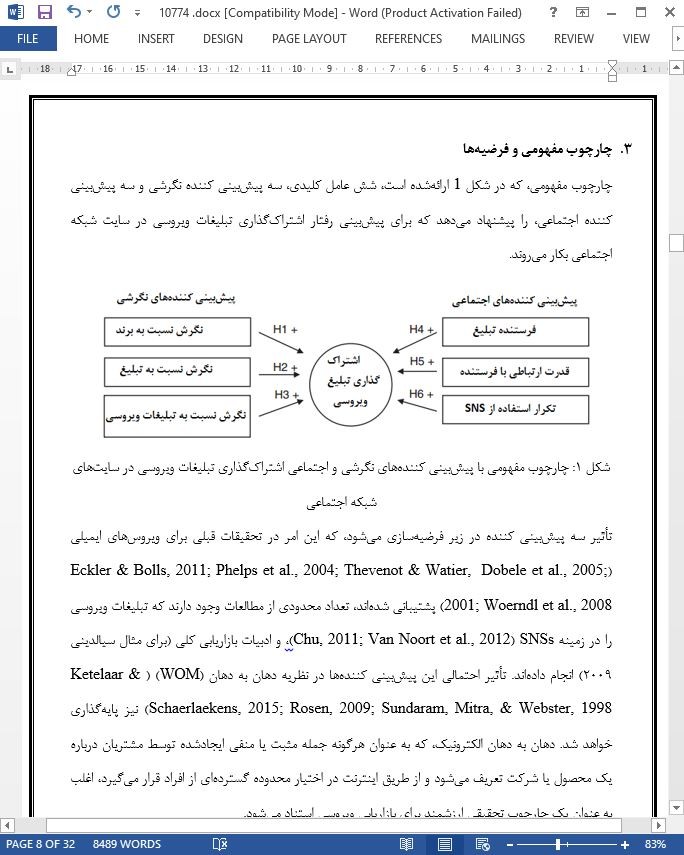
3. چارچوب مفهومی و فرضیهها
3 – 1: پیشبینی کنندههای نگرشی رفتار اشتراکگذاری
3 – 2: پیشبینی کنندههای اجتماعی رفتار اشتراکگذاری
4. روش
4 – 1: روند
4 – 2: شرکتکنندگان
4 – 4: معیارها
4 – 5: تحلیل
5. نتایج
5 – 1: رفتار اشتراکگذاری و فرستنده تبلیغ
5 – 2: بررسی فرضیهها
6. بحث و بررسی
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Predicting viral advertising success
3. Conceptual framework and hypotheses
3.1. Attitudinal predictors of pass-on behavior
3.2. Social predictors of pass-on behavior
4. Method
4.1. Procedure
4.2. Participants
4.3. Viral advertising communications
4.4. Measures
4.5. Analyses
5. Results
5.1. Pass-on behavior and sender of the advertisement
5.2. Testing the hypotheses
6. Discussion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
