
رویکردی انطباقی برای بهبود بافت بر اساس یک اپراتور تفاضلی کسری با گام و ترتیب غیرعددی
چکیده
بهبود بافت تصویر موضوع مهمی در گرافیک و دید کامپیوتری و شناخت الگو است. با استفاده از مشتق کسری برای تحلیل مشخصه بافت، یک ماسک اپراتور تفاضلی کسری جدید با گام و مرتبه غیر عددی انطباقی در این مقاله برای بهبود تصویر بافت ارائه شده است. یک منطقه پشتیبان خود مشابه غیر منظم طبق مقیاس تشابه بافت محلی ایجاد شد که به طور موثر پیکسل با همبستگی و نویز پایین را حذف می کند. سپس از طریق تقسیم پیکسل و معرفی یک مدل قطعه خطی محلی برای برآورد مقدار خاکستری بین پیکسلها، گام غیر عددی حاصل میتواند مشخصه خود تشابه ذاتی در بسیاری از انواع تصویر را بهبود بخشد. به علاوه با درک عمیق توزیع الگو بافت محلی در منطقه پشتیبان، انتخاب انطباقی مرتبه مشتق کسری نیز برای بررسی جزئیات بافت پیچیده اجرا میشود. در آخر ماسک اپراتور تفاضلی کسری غیر عددی که گام و مرتبه غیر عددی انطباقی را تلفیق میکند ایجاد میشود. نتایج تجربی نشان داد که برای تصاویری با محتوای بافت غنی مشخصه موثر درجه خود تشابه در الگو بافت طبق رویکرد پیشنهادی ما منجر یه بهبود تصویر در مقایسه با دیگر رویکردها شد.
1. مقدمه
هدف بهبود بافت تصویر بهبود کیفیت یک تصویر با اصلاح مشخصههای آن است. تعدادی تکنیک برش لبه مطرح شدهاند که به دو مقوله تقسیم میشوند: مبتنی بر تغییر و دامنه فضایی. روش مبتنی بر تغییر ضریب مرتبط با دامنه فرکانس را برای رسیدن به بهبود تصویر تعدیل میکند. با این حال این روش دارای اثر و نویز اضافی است. از طرف دیگر روش مبتنی بر دامنه فضایی مانع این مسائل بدون نیاز به اجرای تغییر دامنه فرکانس منجر به محاسبه کمتر میشود. در میان رویکردهای بهبود مختلف اپراتور ماسک تفاضلی یک نمونه مهم است. به علاوه این میتواند به عنوان اپراتور تفاضلی انتگرال و کسری طبقه بندی شود. برای بهبود تصویر، بیشتر اپراتورهای انتگرال – تفاضلی در بهبود مشخصه فرکانس بالا به خوبی عمل میکنند. با این وجود عملکرد به طور قابل توجهی در مناطق صاف کاهش مییابد.
4. نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله یک ماسک اپراتور تفاضلی کسری انطباقی برای بهبود تصویر ارائه شد. با شناسایی محدودیت اصلی روش های قبلی عملکرد بهتر با معرفی منطقه پشتیبان نامنظم و تعیین مرتبه کسری نظیر درجه خود تشابه در بیشتر تصاویر مورد نظر است. از نظر قابلیت بهبود رویکرد پیشنهادی، می توان از دیگر الگوریتم ها در مرحله پیش پردازش مناطق مختلف نظیر تحلیل و شناسایی استفاده کرد.
Abstract
Image texture enhancement is an important topic in computer graphics, computer vision and pattern recognition. By applying the fractional derivative to analyze texture characteristics, a new fractional differential operator mask with adaptive non-integral step and order is proposed in this paper to enhance texture images. A non-regular self-similar support region is constructed based on a local texture similarity measure, which can effectively exclude pixels with low correlation and noise. Then, through applying sub-pixel division and introducing a local linear piecewise model to estimate the gray value in between the pixels, the resulting non-integral steps can improve the characterization of self-similarity that is inherent in many image types. Moreover, with in-depth understanding of the local texture pattern distribution in the support region, adaptive selection of the fractional derivative order is also performed to deal with complex texture details. Finally, the non-regular fractional differential operator mask which incorporates adaptive non-integral step and order is constructed. Experimental results show that, for images with rich texture contents, the effective characterization of the degree of self-similarity in the texture patterns based on our proposed approach leads to improved image enhancement results when compared with conventional approaches.
1. Introduction
Image texture enhancement aims to improve the quality of an image by modifying its attributes. A number of cutting-edge techniques have been proposed which can be divided into two categories: transform-based [1] and spatial domain-based [2]. Transform-based methods regulate coefficients associated with the frequency domain, followed by an inverse transform to obtain the resulting image, based on which image enhancement can be achieved. However, these methods may introduce ringing effect and additional noise. On the other hand, spatial domain-based methods can avoid these problems without the need to perform frequency domain transform, resulting in less computation. Among the different enhancement approaches, the differential mask operator stands out as a particularly important example. Differential operator masks can be further categorized as integral differential and fractional differential operators. As for image improvement, most integral-differential operators (e.g., Sobel, Prewitt, and Laplacian of Gaussian operators) behave well when used for enhancing high-frequency features. Nevertheless, their performance deteriorates significantly when applied to smooth regions.
4. Conclusion
In this paper, we have proposed an adaptive fractional differential operator mask for image enhancement. Through the identification of the main limitations of the previous fractional derivativebased methods, we obtain better performance by introducing a non-regular support region, and adaptively determining the associated fractional order such that the high degree of self-similarity in most images could be judiciously taken into consideration. In view of the capability of our proposed approach in enhancing important details of a large variety of image types, we shall further apply the algorithm as a pre-processing step to different areas such as object recognition and biometric analysis.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. ماسک اپراتور تفاضلی کسری با گام و مرتبه غیر عددی انطباقی
2.1 منطقه پشتیبان نامنظم خود تشابه
2.2 برآورد دینامیکی مقادیر پیکسل فرعی
2.3 مکانیسم انتخاب انطباقی برای ترتیب کسری
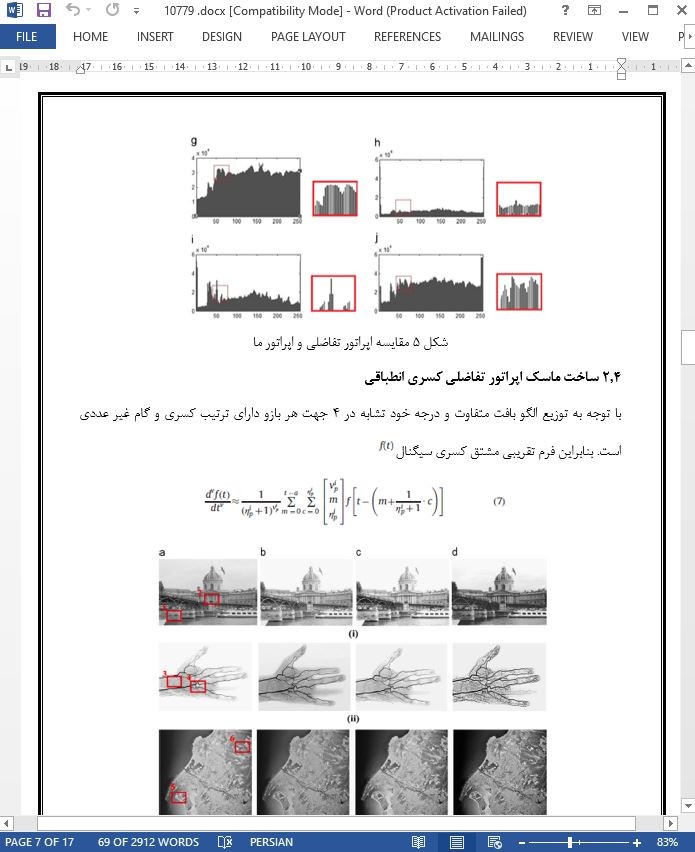
2.4 ساخت ماسک اپراتور تفاضلی کسری انطباقی
3. آزمایش و تحلیل
3.1 مقایسه ماسک های اپراتور تفاضلی انتگرال
3.2 مقایسه با دیگر رویکرد اپراتور تفاضلی کسری
3.3 مقایسه با روش های بهبود تصویر مختلف
4. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fractional differential operator mask with adaptive nonintegral step and order
2.1. Non-regular support region with self-similarity
2.2. Dynamic estimation of sub-pixel values
2.3. Adaptive selection mechanism for the fractional order
2.4. Adaptive fractional differential operator mask construction
3. Experiments and analysis
3.1. Comparison with integral differential operator masks
3.2. Comparison with other fractional differential operator approaches
3.3. Comparison with different image enhancement methods
4. Conclusion
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
