
CLB: معماری و الگوریتم جدید توازن بار (Load Balancing) برای سرویس های ابری
چکیده
سرویسهای ابری به شکل وسیعی در ساخت، محاسبه، کاربردهای دیجیتال، متن پردازی استفاده می شوند. خدمات ابری بایستی قادر به کارگیری از دهها هزار تقاضای همزمان بوده و سرورها را قادر سازد تا علاوه بر اینکه به کاربران اجازه میدهد تا اطلاعات را به سرعت و دقت به دست آورند، به طور کامل مقدار ظرفیت توازن بار (Load Balancing) لازم برای پاسخ به ترافیک اپلیکیشن وروردی را فراهم کند. در گذشته، محققان استفاده از توازن بار ساکن یا زمانهای پاسخ سرور به ارزیابی ظرفیت توازن بار، یعنی فقدان زمانی که باعث بارگذاری نامنظم سرور می شد را پیشنهاد کردند. در این مطالعه، از یک روش متعادلسازی پویای الحاقی برای حل مشکل استفاده شده است. توازن بار ابری (CLB) شامل هر دو مورد قدرت پردازش سرور و بارگذاری کامپیوتر است، لذا کمتر حالتی پیش میآید که سرور قادر به اداره نیازهای بیش از حد محاسباتی نباشد. در آخر، دو الگوریتم در CLB با آزمایش های مربوطه، برای اثبات اینکه رویکرد پیشنهادی ابتکاری است، مورد توجه قرار گرفته است.
1. مقدمه
با پیشرفت سریع اینترنت، بسیاری از فروشندهها شروع به فراهم کردن خدمات ابری کردهاند. رفته رفته خدمات متعددی می تواند در فضای ابری فراهم شده و کاربران دیگر مجبور به انجام عملیات در کامپیوتر محلی خود نیستند. تمامی عملیات در ابر (Cloud) محاسبه می شود. زمانی که تعداد زیادی از کاربران قصد دستیابی به ابر را داشته باشند، این امر باعث میشود تا سرور در پاسخگویی موفق عمل نکند. تعیین روشی که بهوسیله آن برای کاربران پاسخی دقیق و بهموقع فراهم شود، موضوعی برای مطالعهای دقیق و پیشرفته است. مطالعات متعددی برای ارزیابی و توسعه الگوریتمها و روش بررسی توازن بار کاربردهای مبتنی بر ابر، پیشنهاد شده است. برای یک سرورو مشکل است که به طور موثری جریان اطلاعات تولید شده توسط تمام سازمانهایی که در تلاش برای دسترسی به آن هستند را مدیریت نماید. جریان بیش از حد اطلاعات، باعث اضافه بار سرور و متعاقب آن فقدان اطلاعات میشود. توازن بار سرور مکانیسمی است که می تواند انتقال جریان اطلاعات و عملیات داده را پراکنده ساخته و باعث کاهش احتمال زمان محاسباتی افزایش یافته و فقدان اطلاعات شود. زمانی که یک سرور معین در ابر عملکرد موفقی نداشته باشد، سرویسهای دیگر ابر میتوانند به سرور دیگری انتقال یابند. بنابراین سرویسها بدون وقفه هستند.
6. نتایج
در این تحقیق، مکانیسمهای جدیدی از توازن بار ابر از طریق مقایسه با مطالعات قبلی ارائه شد. نمونه جدید ارائه شده CLB برای معماری توازن بار بوده و الگوریتمی است که میتواند به هر دو سرور مجازی و فیزیکی اعمال شود. با توجه به آزمایشهای سرورهای مجازی و فیزیکی با CLB فعال، نتایج نشان میدهند که عملکرد سرور ابری مبتنی بر معماری ارائه شده در این تحقیق، میتواند عملکرد بارگیری را به هنگام ورود همزمان کاربرها به تعدیل نمود.
Abstract
Cloud services are widely used in manufacturing, logistics, digital applications, and document processing. Cloud services must be able to handle tens of thousands of concurrent requests and to enable servers to seamlessly provide the amount of load balancing capacity required to respond to incoming application traffic in addition to allowing users to obtain information quickly and accurately. In the past, researchers have proposed the use of static load balancing or server response times to evaluate load balancing capacity, a lack of which may cause a server to load unevenly. In this study, a dynamic annexed balance method is used to solve this problem. Cloud load balancing (CLB) takes into consideration both server processing power and computer loading, thus making it less likely that a server will be unable to handle excessive computational requirements. Finally, two algorithms in CLB are also addressed with experiments to prove the proposed approach is innovative.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the Internet, many vendors have started to provide cloud services. More and more services can be obtained in the cloud, and users do not have to do operations on a local computer. All operations are computed on the cloud. When a large number of users attempt to access cloud services, this often causes the server to fail to respond. Determining a method by which to provide users with timely and accurate responses is a subject worthy of advanced study. Several studies have been proposed to evaluate and to develop algorithms and load balancing methodologies for cloudbased applications. It is difficult for a server to deal effectively with the flow of information generated by all of the various enterprises attempting to access it. Excessive flow causes server overload with a subsequent loss of information. A server load balancing mechanism can disperse the transmission of information flow and data operations and can also reduce the probability of increased computational time and loss of information. When one server fails in the cloud, the cloud services can be transferred to another server. Services are therefore non-stop.
6. Conclusions
In this study, a new cloud load balancing mechanisms is proposed by comparing previous studies. The proposed new paradigm CLB for load balancing architecture and an algorithm can be applied to both virtual web servers and physical servers. From the experiments for CLB-enabled physical servers and virtual servers, the results show that cloud server performance based on the architecture proposed in this study can balance the loading performance when users logged in at the same time.
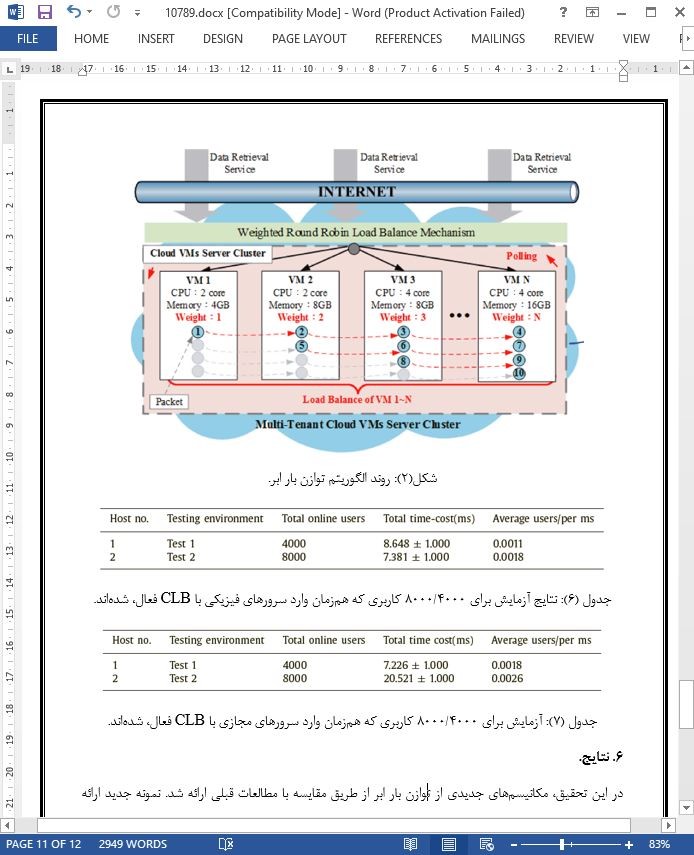
1. مقدمه
2. توازن بار برای سرورهای وب
2.1. زمانبندی کمترین ارتباط
2.2. بار متوازن حداقل-حداقل
3. زمانبندی وزندارشده
4. عملیات حفظ تعادل بار ابر
4.1.معماری توازن بار ابری
4.2. الگوریتم توازن بار ابری
5. نتایج آزمایشگاهی و بحث و بررسی
6. نتایج
abstract
1. Introduction
2. Dynamic load balance for web servers
2.1. Least connection scheduling
2.2. Load balanced min–min
3. Weighted scheduling
4. Cloud load balance
4.1. The cloud load balance architecture
4.2. The cloud load balance algorithm
5. Experiment results and discussions
6. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
