
تحلیل عملکرد روش های زمانبندی وظیفه بر اساس منبع در شبکه های سنسور بی سیم
شبکههای سنسور بیسیم (WSNها) پایگاه جذابی برای نظارت و سنجش پدیدههای فیزیکی هستند. WSNها معمولا شامل صدها یا هزاران گره سنسور کوچک هستند که با باتری عمل میکنند و از طریق شبکه بیسیم با سرعت داده پایین متصل شدهاند. کاربرد WSN مثل ردیابی شی یا نظارت محیطی متشکل از وظایف منفردی است که باید روی هر گره زمانبندی شود. معمولا ترتیب اجزای وظیفه بر عملکرد کاربرد WSN تاثیر میگذارد. زمانبندی وظایف به صورتی که عملکرد در عین پایین ماندن مصرف انرژی، افزایش یابد یک چالش کلیدی است. در این مقاله یادگیری آنلاین را به زمانبندی وظیفه اعمال میکنیم تا توازن بین عملکرد و مصرف انرژی را بررسی نماییم. این امر به شناسایی دینامیک سیاستهای موثر زمانبندی برای گرههای سنسور کمک میکند. مصرف انرژی برای محاسبه و ارتباط توسط پارامتری برای هر وظیفه کاربردی ارائه میشود. زمانبندی وظیفه براساس منبع را مبتنی بر سه روش یادگیری آنلاین مقایسه میکنیم: یادگیری تقویتی مستقل (RL)، یادگیری تقویتی مشارکتی (CRL) و وزن نمایی برای اکتشاف و بهرهبرداری (Exp3). ارزشیابی ما مبتنی بر عملکرد و مصرف انرژی برنامه مسیریابی هدف وابسته به طرح اصلی است. به علاوه هزینه ارتباط و تلاش محاسباتی این روشها را نیز تعیین مینماییم.
1. مقدمه
شبکه سنسور بیسیم (WSN) پایگاه جذابی برای کاربردهای متنوع از جمله مسیریابی هدف، نظارت محیطی، تجمیع داده و محیطهای هوشمند است. این برنامه شامل وظایفی است که باید طی عملیات روی گرههای سنسور اجرا شوند. گرههای سنسور معمولا با باتری تامین نیرو میشوند و بنابراین محدودیتهای زیادی را نه تنها از نظر انرژی، بلکه از نظر مصرف، ذخیرهسازی و قابلیتهای ارتباط نیز تحمیل میکنند.
7. نتیجهگیری
در این مقاله الگوریتمهای یادگیری آنلاین را برای زمانبندی وظیفه براساس منبع در WSNها به کار بردیم. عملکرد روشهای زمانبندی وظیفه آنلاین را مبتنی بر سه الگوریتم یادگیری تحلیل کرده و مقایسه نمودیم: RL, CRL و Exp3. نتایج ارزشیابی ما نشان میدهد این روشها ویژگیهای متفاوتی در زمینه عملکرد قابل دستیابی و آگاهی نسبت به منبع ارائه میدهند. انتخاب الگوریتم خاص به شروط برنامه و منابع در دسترس گرههای سنسور بستگی دارد. کار آینده شامل استفاده از رویکرد زمانبندی براساس منبع در برنامههای WSN مختلف، پیادهسازی در پایگاههای شبکه سنسور بصری و مقایسه رویکرد ما با سایر انواع روشهای یادگیری تقویتی است.
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) are an attractive platform for monitoring and measuring physical phenomena. WSNs typically consist of hundreds or thousands of battery-operated tiny sensor nodes which are connected via a low data rate wireless network. A WSN application, such as object tracking or environmental monitoring, is composed of individual tasks which must be scheduled on each node. Naturally the order of task execution influences the performance of the WSN application. Scheduling the tasks such that the performance is increased while the energy consumption remains low is a key challenge. In this paper we apply online learning to task scheduling in order to explore the tradeoff between performance and energy consumption. This helps to dynamically identify effective scheduling policies for the sensor nodes. The energy consumption for computation and communication is represented by a parameter for each application task. We compare resource-aware task scheduling based on three online learning methods: independent reinforcement learning (RL), cooperative reinforcement learning (CRL), and exponential weight for exploration and exploitation (Exp3). Our evaluation is based on the performance and energy consumption of a prototypical target tracking application. We further determine the communication overhead and computational effort of these methods.
1. Introduction
A wireless sensor network (WSN) is an attractive platform for various applications including target tracking, environmental monitoring, data aggregation, and smart environments. The application is composed of tasks which need to be executed during the operation on the sensor nodes. The sensor nodes are typically supplied by batteries and thus pose strong limitations not only on energy but also on computation, storage, and communication capabilities [1–4].
7. Conclusion
In this paper we applied online learning algorithms for resource-aware task scheduling in WSNs. We analyzed and compared the performance of online task scheduling methods based on the three learning algorithms: RL, CRL, and Exp3. Our evaluation results show that these methods provide different properties concerning achieved performance and resource-awareness. The selection of a particular algorithm depends on the application requirements and the available resources of sensor nodes. Future work includes the application of our resourceaware scheduling approach to differentWSN applications, the implementation on our visual sensor network platforms [23], and the comparison of our approach with other variants of reinforcement learning methods.
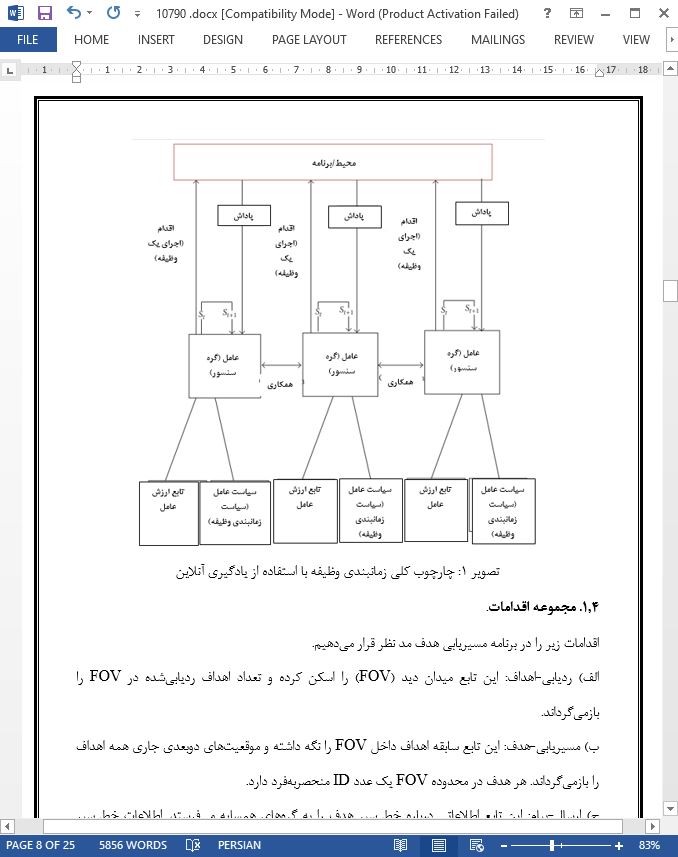
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مرتبط
3. فرمولبندی مشکل
4. مدل سیستم
1.4. مجموعه اقدامات.
2.4. مجموعه وضعیتها
3.4. تابع پاداش
5. روشهای یادگیری آنلاین برای زمانبندی وظیفه
5.1 . یادگیری تقویتی مستقل (RL)
5.2 . یادگیری تقویتی مشارکتی
3.5. حلکنندههای متمرد (Exp3)
6. نتایج آزمایشی و ارزشیابی
7. نتیجهگیری
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Problem Formulation
4. System Model
4.1. Set of Actions
4.2. Set of States
4.3. Reward Function
5. Online Learning Methods for Task Scheduling
5.1. Independent Reinforcement Learning (RL)
5.2. Cooperative Reinforcement Learning (CRL)
5.3. Bandit Solvers (Exp3).
6. Experimental Results and Evaluation
7. Conclusion
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
