عوامل مؤثر بر اعتماد در شبکه های بانکی
چکیده
این مقاله عوامل مؤثر بر اعتماد در شبکه های بانکی را بررسی و بنابراین چندین نیروی مؤثر در اثر پایداری شبکه ها را شناسایی می کند. با استفاده از مجموعه داده منحصر به فرد از 249 بانک پس انداز در آلمان، نتایج تجربی نشان می دهد که تعامل قوی با هماهنگ کننده های مرکزی، ایجاد اعتماد در بین شبکه را پشتیبانی می کند. بانک های بزرگ و بانک های با حالت رقابتی شدید و درآمد بالا، کمتر در رابطه عمیق با شبکه سرمایه گذاری می کنند. علاوه برآن، اعتماد خود بانک یک مؤلفه مرتبط با ایجاد اعتماد می باشد. اگر بانک ها باور کنند که می توانند بر تصمیمات گروه بانکی تاثیر بگذارند، تمایل بیشتری به اعتماد دارند. این یافته ها به توضیح نحوه عملکرد مناسب شبکه های بانکی حتی در دوره های بحران مالی کمک می کند.
1. مقدمه
بحران های مالی نیاز شدید برای درک نقش اعتماد در شبکه های پیچیده و مرتبط را افشا کرد. شریکان بازار، سیاستمداران و محققان دریافتند که سطح اعتماد در بین یک سیستم یا شبکه از موسسات مالی برای پایداری آن شبکه مهم می باشد. این مقاله یک بررسی تجربی از شرایطی که تحت آن اعتماد در مکانیزم های شبکه ایجاد و حفظ شده است و همچنین نحوه عملکرد مطلوب شبکه های بانکی حتی در دوره های بحران مالی می باشد.
بحران های بانک به طور گسترده ای مورد مطالعه قرار گرفته است و منابع مختلفی از ریسک سیستماتیک شناسایی شده اند. مهم ترین منبع از ریسک سیستماتیک، سرایت می باشد. درک عموم این است که ارتباط پیوسته ممکن-است ریسک سرایت مالی را ایجاد کند (برای مثال، Brusco and Castiglionesi, 2007; Dasgupta, 2004 را ببینید). با این حال، نظریه اقتصاد نشان می دهد که خطر سرایت بستگی به الگوی دقیق روابط بین بانکی دارد.
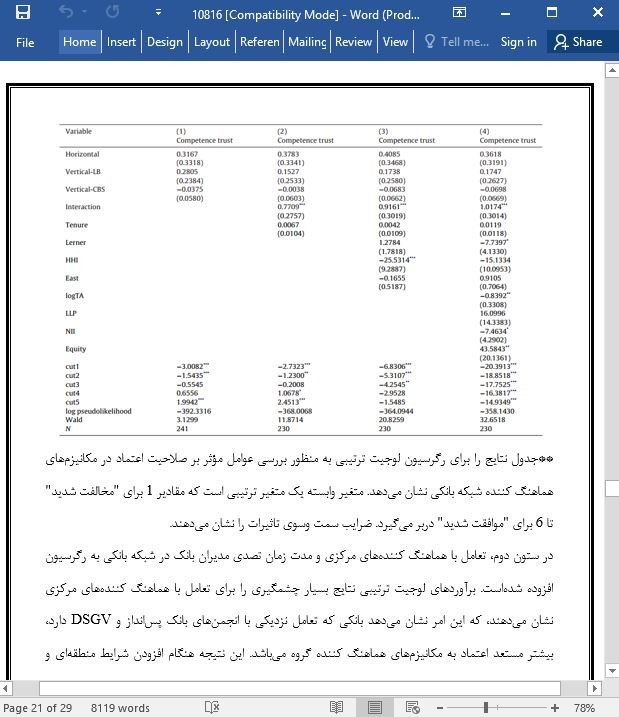
7. نتایج
در این مقاله، من عوامل مؤثر بر اعتماد در شبکه های بانکی را بررسی کردم و ادعا می کنم که سطح اعتماد برای پایداری سیستم و طرح ریزی مسیر از بحران های مالی اخیر مهم می باشد. سقوط اعتماد یک نقش حیاتی در بحران اخیر ایفا می کند. بنابراین، درک عوامل مؤثر بر اعتماد در شبکه های بانکی، مرحله اول در دستیابی به درک بهتر سیستم های مدرن مالی می باشد.
با استفاده از گروه مالی بانک های پس انداز آلمانی به عنوان یک مورد واقعی به منظور بررسی عوامل مؤثر بر صلاحیت اعتماد در شبکه های بانکی، من چندین نیروی تعیین کننده مؤثر بر پایداری شبکه های بانکی را شناسایی کردم.
Abstract
This paper investigates the determinants of trust in banking networks and, thus, identifies several forces determining the stabilizing effect of networks. Using a unique dataset of 249 German savings banks, the empirical results show that intense interaction with central coordinators supports trust-building within the network. Larger banks and banks with strong competitive standing and high income invest less in a deeper relationship with the network. Moreover, bank's own trustworthiness is a relevant component in building trust. The banks are more willing to trust if they believe that they can influence the banking group's decisions. These findings may help to explain how banking networks can function well even in periods of financial crisis.
1. Introduction
The financial crisis has revealed a strong need for understanding the role of trust in complex and interlinked networks. Market participants, politicians and researchers have once more realized that the level of trust within a system or a network of financial institutions is important for the stability of the network. This paper is an empirical investigation of the circumstances under which trust in network mechanisms is created and maintained and of how banking networks can function well even in periods of financial crisis.
Bank crises have been studied extensively, and various sources of systemic risk have been identified. The most important source of systemic risk is contagion. The common perception is that interlinkages may create a risk of financial contagion (see e.g. Brusco and Castiglionesi, 2007; Dasgupta, 2004). However, economic theory shows that the risk of contagion is dependent on the precise pattern of interbank linkages.
7. Conclusion
In this paper, I investigated the determinants of trust in banking networks and argued that the level of trust is important for the stability of a system, drawing guidance from the recent financial crisis. The collapse in trust played a crucial role in the recent crisis. Therefore, understanding the determinants of trust in banking networks is the first step toward gaining a better understanding of modern financial systems.
Using the German Savings Banks Finance Group as a concrete case to investigate the determinants of competence trust in banking networks I have identified several forces determining the stabilizing effect of banking networks.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. گروه مالی بانک های پس انداز آلمان
3. چارجوب مفهومی و فرضیه ها
3-1: مفهوم صلاحیت اعتماد
3-2: عوامل مؤثر بر صلاحیت اعتماد در شبکه ها
4. مشخصات مدل و برآورد متغیر
4-1: روش تجربی
4-2: متغیرها
5. داده ها و خلاصه آمار
5-1: داده ها
5-2: آمارهای توصیفی
6. نتایج تجربی
6-1: تحلیل خط پایه
6-2: تحلیل حساسیت: تاثیرات سطح بانک و ادغام بازار سرمایه
6-3: تحلیل حساسیت: ساختار زیرشبکه
6-4: تحلیل بیشتر حساسیت
6-5: محدودیت های تحلیل
7. نتایج
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The German Savings Banks Finance Group
3. Conceptual framework and hypotheses 3.1. The concept of competence trust
3.2. Determinants of competence trust in networks
4. Model specification and variable estimation
4.1. Empirical methodology
4.2. Variables
5. Data and summary statistics
5.1. Data
5.2. Descriptive statistics
6. Empirical results
6.1. Baseline analyses
6.2. Sensitivity analyses: bank level effects and capital market engagement
6.3. Sensitivity analyses: structure of the sub-network
6.4. Further sensitivity analyses
6.5. Limitations of the analyses
7. Conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه