
اثرات ریسک نقدینگی و ریسک اعتباری بر ثبات بانک
چکیده
بحران مالی جهانی موجب ایجاد شکستهای بیشتر بانکهای متداول شده است. این مطالعه به بررسی منابع اصلی شکنندگی بانکداری میپردازد. ما از یک نمونه با 49 بانک فعال در منطقه منا در طول سالهای 2006 تا 2013 استفاده میکنیم تا رابطه بین ریسک اعتباری و ریسک نقدینگی و تأثیر آن بر ثبات بانکی را بررسی کنیم. نتایج ما نشان میدهد که ریسک اعتباری و ریسک نقدینگی به طور همزمان و يا با فاصله زماني داراي رابطه متقابل و از لحاظ اقتصادی معنیدار نيستند. با این حال، هر دو ريسك به طور جداگانه بر ثبات بانک تاثیر میگذارند و تعامل آنها موجب بیثباتی بانک میشود.این یافتهها مدیران بانک را بیشتر با ریسک بانکها آشنا كرده و به عنوان پایهای برای تلاشهای نظارتی اخیر که با هدف تقویت مدیریت ریسک مشترک خطرات نقدینگی و اعتباری است، به کار میرود.
1. مقدمه
بحران مالی اخیر منجر به شکستهای بانکی شده است که تاثیر منفی بر اقتصاد واقعی داشته است. بنابراین، توجه ویژهای به پیامدهای بیثباتی مالی در اقتصاد ایجاد شده است (آگنلو و سوسا ، 2012). علاوه بر این، در محیطی با نقص بازار، حفظ سپردهگذاران از شكست بانکها ضروری است (دواتريپنت و تيرول ، 1994). در نتیجه، سیستم بانکداری باید منابع شکنندگی بانکی را شناسایی کند. از سوی دیگر، بانک ها در معرض خطرات مالی بسياري هستند.طبق گفته سچتي و شونهولتز (2011)، این خطرات مالی عبارتند ازاحتمال اين كه سپردهگذاران به طور ناگهانی سپردههای خود را برداشت كنند (ريسك نقدينگی)، وامگیرندگان وامهای خود را به موقع بازپرداخت نكنند (ريسك اعتباری)، نرخ بهره تغییر کند (ریسک نرخ بهره)، سیستمهای کامپیوتری بانک دچار نقص شوند يا ساختمانهایشان دچار آتشسوزي شوند (ریسک عملیاتی). با این وجود، در میان این خطرات، خطرات اعتباری و نقدینگی نه تنها مهمترین خطراتی هستند که بانکها با آن روبرو ميشوند، بلکه به طور مستقیم با فعاليت بانکها و دلیل شكست بانکها در ارتباط هستند.
5. نتیجهگیری و رويههاي مفهومي
خطرات نقدينگی و اعتباري دو عامل مهم برای بقاي بانکداری هستند. این مقاله تأثیر ریسک نقدینگی و ریسک اعتباری بر روي ثبات بانکی را با استفاده از مجموعه دادههای پانل 49 بانکفعال در کشورهای منطقه منا در طول سالهای 2006 تا 2013 بررسی میکند. علاوه بر این، ما دریافتیم که ریسک اعتباری و ریسک نقدینگی رابطه معکوس معنادار اقتصادی همزمان یا با تاخير ندارند، علاوه بر این، هر دسته ریسک تاثیر قابل توجهی بر ثبات بانکی دارد.ما همچنین دريافتيم که تعامل دو دسته ریسک تأثیر قابل توجهی بر ثبات بانکداری دارد. بنابراین، برآورد نتایج نشان دهنده اهمیت خطرات اعتباری و نقدینگی در درک پایداری بانکی در منطقه منا است.
Abstract
The global financial crisis has induced a series of failures of most conventional banks. This study investigates the main sources of banking fragility. We use a sample of 49 banks operating in the MENA region over the period 2006e2013 to analyze the relationship between credit risk and liquidity risk and its impact on bank stability. Our results show that credit risk and liquidity risk do not have an economically meaningful reciprocal contemporaneous or time-lagged relationship. However, both risks separately influence bank stability and their interaction contributes to bank instability. These findings provide bank managers with more understanding of bank risk and serve as an underpinning for recent regulatory efforts aimed at strengthening the joint risk management of liquidity and credit risks.
1. Introduction
The recent financial crisis has led to bank failures that have had a negative impact on the real economy. Therefore, a particular attention to the consequences of financial instability on the economy has been established (Agnello & Sousa, 2012). Furthermore, in an environment characterized by market imperfections, it is imperative to protect the depositors against bank failures (Dewatripont & Tirole, 1994). Consequently, the banking system needs to identify the sources of banking fragility. On the other hand, banks are exposed to several financial risks. According to Cecchetti and Schoenholtz (2011), these financial risks include the chance that depositors will suddenly withdraw their deposits (liquidity risk), borrowers will not repay their loans on time (credit risk), interest rates will change (interest rate risk), the bank's computer systems will fail or their buildings will burn down (operational risk). Nevertheless, among these risks, credit and liquidity risks are not only the most important risks that banks face, but they are also directly linked to what banks do and why banks fail.
5. Conclusion and policy implications
Liquidity and credit risks are the two most important factors for banking survival. This paper studies the effect of liquidity risk and credit risk on banking stability using a panel dataset of 49 banks operating in the MENA countries over the period 2006e2013. Moreover, we found that credit risk and liquidity risk do not have an economically meaningful reciprocal contemporaneous or time-lagged relationship, besides, each risk category has a significant impact on banking stability. We also documented that the interaction of the two risk categories has a significant impact on banking stability. Therefore, the estimation results showed the importance of credit and liquidity risks in understanding banking stability in the MENA region.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. بررسی مقالات
2-1- رابطه متقابل بین ریسک نقدینگی و ریسک اعتباری
2-2- تأثیر ریسک نقدینگی و ریسک اعتباری بر ثبات بانک
3. مدلسازی اقتصادسنجي و دادهها
3-1- مدلسازی اقتصادسنجي
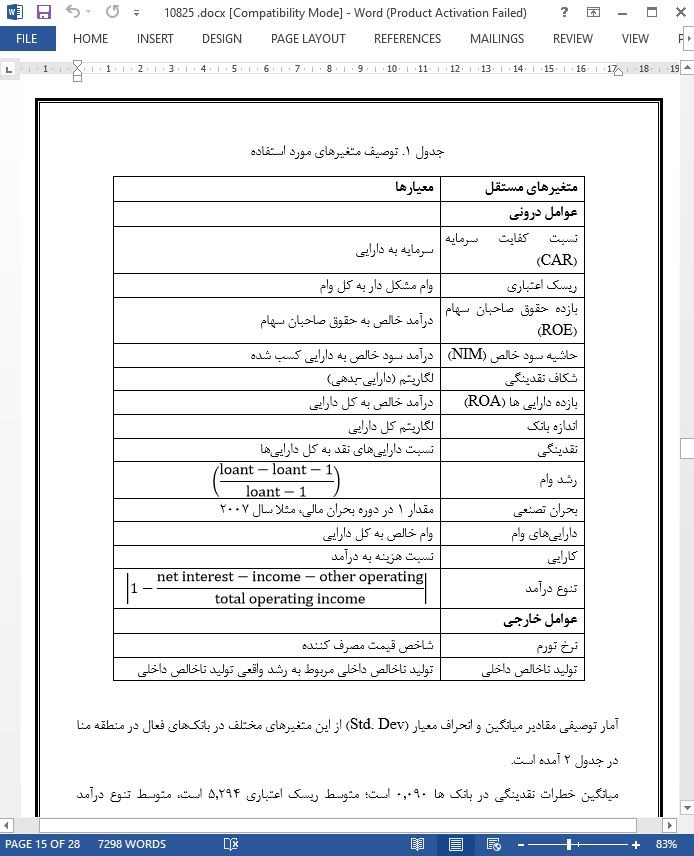
3-2- منابع دادهها و آمار توصیفی
4. نتایج و بحث
4-1- رابطه بین ریسک اعتباری و ريسك نقدینگی
4-2- تأثیر ریسک نقدینگی و ریسک اعتباری بر ثبات بانک: روش GMM
5. نتیجهگیری و رويههاي مفهومي
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature review
2.1. The reciprocal relationship between liquidity risk and credit risk
2.2. The influence of liquidity risk and credit risk on bank stability
3. Econometric modeling and data
3.1. Econometric modeling
3.2. Data sources and descriptive statistics
4. Results and discussions
4.1. The relationship between credit risk and liquidity risk
4.2. The impact of liquidity risk and credit risk on bank stability: GMM method
5. Conclusion and policy implications
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
