تاخیرها در مدل های بازار برق
چکیده
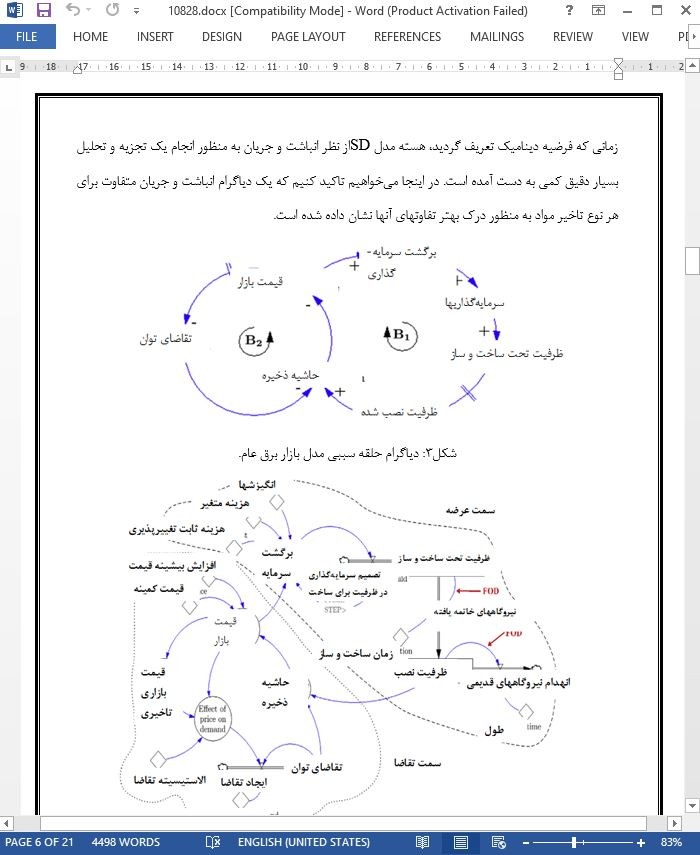
از چندین نوع تاخیر مواد که می توانند در منابع و مراجع یافت شوند، اغلب مدلسازها دینامیک های سیستم (SD) را ظاهرا برای سادگی تاخیرهای درجه اول (FODها) برای بیان ساخت و ساز و انهدام نیروگاههای تولید برق در مدلهای بازار برق استفاده می کنند حتی اگرچه تاخیرهای خط لوله یا تاخیرهای انتقال (PLDها) ورودی و خروجی نیروگاههای تولید برق را بهتر مدل می کنند. اگرچه هر دو نوع تاخیر می توانند برای بازنمایی تاخیرهای مواد مورد استفاده قرار گیرند، هرکدام نتایج متفاوت با مزایا و معایب مربوط به خود را پیشنهاد می کنند که نیاز است تا به خوبی به این مزایا ومعایب پرداخته شود. بنابراین، این مقاله به دنبال پیاده سازی FODها و PLDها در یک مدل بازار برق عام به منظور ارزیابی کارایی و کفایت آنها در نزدیکترین بازنمایی از واقعیت می باشد. به عنوان یک نتیجه، مدلسازهای SDباید از طریق این تحقیق و بررسی اهمیت و پیامدهای تاخیرهای مواد در مدلهای خود را مشاهده کنند و همچنین آنها قادر خواهند بود تا تاخیرهای مواد مناسب برای کاربردهای انتخاب نمایند. در واقع، نتایج شبیه سازی با مقایسه هردو مدل به طور قابل توجه نشان می دهند که PLDها یک تقریب بهتر برای مدلسازی تاخیرهای ساخت و ساز نیروگاههای جدید و نیز انهدام نیروگاههای قدیمی می باشند. بر این اساس، اگر صرفا FODها مورد استفاده قرار گرفته باشند، مدلهای بازار برق نه تنها همیشه برق کمتری را در یک سال یا سالهای متعدد فراهم می کنند بلکه همچنین مقادیر برق ناصحیحی را تولید می کنند که می توانند منجر به آسیب به برنامه ریزی انرژی شوند که این اساسا به این دلیل می باشد که دینامیکهای کل سیستم را تغییر می دهند.
1-مقدمه
SD(دینامیکهای سیستم) به یک تکنیک مدلسازی قدرتمند از زمان شکل گیری آن در اواسط دهه 1950 توسط پروفسور جی فورستر در موسسه تکنولوژی ماساچوست بدل شده است [1]. این رهیافت می تواند یک تکنیک مدلسازی ریاضی مفید و سودمند برای درک و بحث مسائل و مشکلات پیچیده در چندین حوزه شود [2]. مدلسازی SDبه طور گسترده برای مطالعه بازارهای برق مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است و همچنین به عنوان یکی از مناسب ترین تکنیک های مدلسازی در نظر گرفته شده است هنگامی برای آنالیز سیستم های پیچیده مطلوب می-باشد [2 تا 5]. بنابراین، آنالیزها در ایمنی تامین (عرضه) [6 تا 8]، کارایی انرژی [9 تا 12]، اصلاحات (رفرم) بازار [13 تا 15]، گازهای گلخانه ای [16 تا 18] در میان دیگر موارد کانتریبیوشن هایی هستند که نه تنها منعکس کننده اهمیت مدلسازی بازارهای برق می باشند بلکه همچنین ضرورت توسعه مدلها با یک درجه ای از واقع گرایی به طور فزآینده بالاتر را نیز منعکس می کنند. بنا به این دلیل، هدف مطالعه کنونی ارزیابی یک خصوصیت مهم از بازارهای برق می باشد: تاخیرها . یک مدل کافی از تاخیرها تضمین می کند که دینامیکهای سیستم واقعیت را به صورت بهتری منعکس نمایند.
4- بحث و نتیجه گیری
در زمینه بازارهای برق، متدولوژی شبیه سازی SDبه طور گسترده استفاده و توسعه داده شده است؛ به هر حال، تاخیرها اغلب به طور صحیح مدل نشده و در نظر گرفته نشدند که منجر به برخی سردرگمی ها بین مدلسازهای SDو نتایج نادقیق از مدلهای آنها می شود. بنابراین، این تحقیق هدف تعیین تاخیر مناسب را دارد که وقتی که ضروری است تا ساخت و ساز نیروگاههای جدید و انهدام آنها را مدلکرد، مورد استفاده قرار گیرد. برای تجزیه و تحلیل دو گزینه اصلی تاخیرها، یک بازار برق عام با در نظرگیری یک سناریوی مشابه با بخش برق کلمبیا در نظر گرفته شدند.
Abstract
From several types of material delays that can be found in literature, most System Dynamics (SD) modelers select, apparently for simplicity, first-order delays (FODs) to represent the construction and decommissioning of power plants in electricity market models, even though pipeline delays, or transport delays (PLDs) model better the entry and exit of power plants. Although both types of delays can be used for representing material delays, each one offers different results with pros and cons that need to be well considered. Therefore, this paper seeks to implement FODs and PLDs in a generic electricity market model in order to assess their effectiveness and adequacy in the closest representation of the reality. As a result, SD modelers shall see through this investigation the importance and implications of material delays in their models, but also they will be able to choose the appropriate material delays for their applications. In fact, the simulation results comparing both models markedly show that PLDs are a better approximation to model the delays of construction of new plants as well as the retirement of old plants. Accordingly, if FODs are solely used, the electricity market models not only always provide less electricity in one or various years, they also produce inaccurate values that can lead to a dangerous energy planning, mainly because they modify the dynamics of the entire system.
1. Introduction
SD has become a powerful modeling technique since its foundation in the mid-1950s by Professor Jay Forrester of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology [1]. This approach can be a useful mathematical modeling technique for understanding and discussing complex issues and problems in several areas [2]. SD modeling has been extensively used to study electricity markets and has also been considered one of the most appropriate modeling techniques when it is desired to analyze complex systems [2e5]. Therefore, analysis in security of supply [6e8], energy efficiency [9e12], market reforms [13e15], greenhouse gases [16e18] among others [4,19,20], are contributions that not only reflect the importance of modeling electricity markets, but also the necessity of developing models with an increasingly higher degree of realism. For this reason, the purpose of the present study is to assess an important characteristic of the electricity markets: the delays. An adequate model of delays guarantees that the dynamic of the systems reflect better the reality.
4. Discussion and conclusions
In the field of electricity markets, the SD simulation methodology has been broadly used and developed; however, delays are often not properly modeled or treated causing some confusion between SD modelers and inaccurate results from their models. Therefore, this research is aimed at determining the appropriate delay that must be used when it is necessary to model the construction of new plants and their decommissioning. To analyze the two main options of delays, a generic electricity market was considered taking into account a similar scenario to the Colombian electricity sector
چکیده
1-مقدمه
2- مدل SDدقیق
2-1- فرضیه دینامیک
2-2- ساختار مدل با استفاده از FODها
2-3- ساختار مدل با استفاده از PLDها
3- نتایج شبیه سازی
4- بحث و نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1.Introduction
2.Detailed SD model
2.1.Dynamic hypothesis
2.2.Model structure using FODs
2.3.Model structure using PLDs
3.Simulation results
4.Discussion and conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه