
تاثیر رهبری تحول گرا و انگیزه های شخصی بر پیامدهای کار داوطلبانه
ما در این مطالعه به بررسی تاثیرات انگیزههای شخصی داوطلبان کار و رفتار رهبر تیم آنها بر رضایت و همکاری داوطلبانه، و تحقیق بر روی فرآیندهای واسطهای که در نظریه خودانگیزشی بیان شده است پرداختهایم. شرکت کنندگان در این مطالعه 302 نفر داوطلب بودهاند که در تیمهای کاری در مشاغل مختلف در یک سازمان مرکزی کار میکردهاند. همانطورکه پیشبینی میشد، هم انگیزههای شخصی برای انجام کار داوطلبانه و هم رهبری تحولگرا بر رضایت از کار داوطلبانه، بر اساس ارتقاء معنادار بودن کار و کیفیت بالای روابط کاری بین اعضای تیم، تاثیرگذارند. اگرچه، انگیزههای افراد از همکاری داوطلبانه از انگیزههای رضایت شغلی آنان متفاوت بوده است. درحالیکه برای ارتقاء عزتنفس افراد و ابراز ارزش، رضایت شغلی رابطهای مثبت با انگیزه داشته است، همکاری شغلی رابطهای مثبت با انگیزه کسب تفاهم داشته است و رابطهای منفی با انگیزههای مربوط به ارتقاء سطح عزتنفس و ارتباطات اجتماعی داشته است.
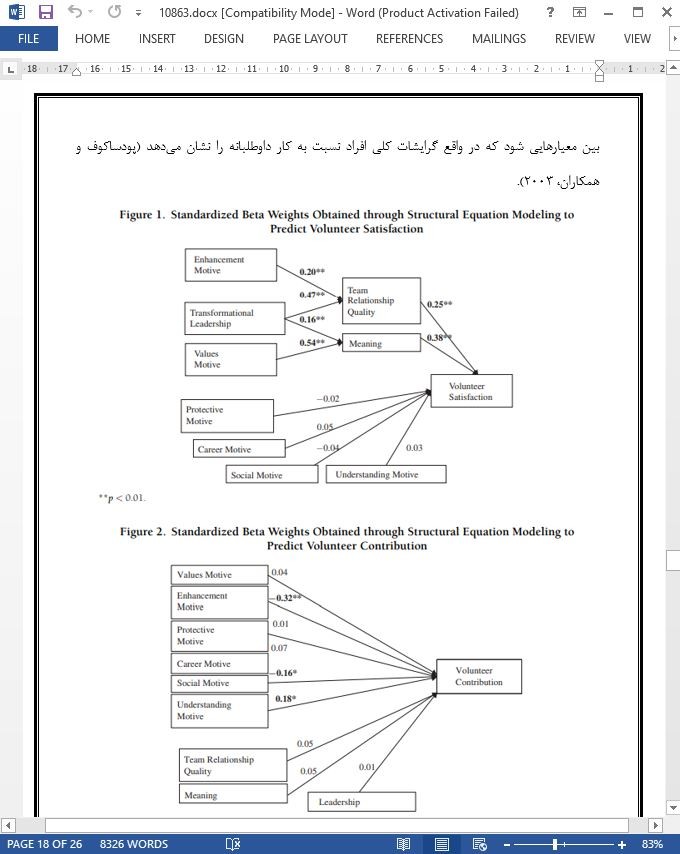
بیشتر مردم در آمریکا بر این باورند که کارهای داوطلبانه، به ساختن جهانی بهتر کمک میکند (سازمان بخش مستقل، 1988). کار داوطلبانه، علاوه بر اینکه به مخاطبین مستقیم آن سود میرساند، میتواند برای خود داوطلبان و به طور کلی برای کل جامعه سودمند باشد (سیندر و اوموتو، 2007؛ ویلسون، 2000). اگر بخواهیم از منظر اقتصادی به این موضوع بنگریم، ارزش کار داوطلبانه بر حسب دلار، فقط در سال 2009 در کشور ایالات متحده آمریکا 169 میلیارد دلار برآورد شده است (شرکت خدمات ملی و اجتماعی، اداره تحقیق و تدوین راهبرد، 2010). علاوه بر این، گفته میشود که کار داوطلبانه و دیگر انواع مشارکت شهروندان نقش مهمی را در مبارزه با مسائلی که امروزه جهان با آن مواجه است ایفا میکند. به دلیل اینکه بسیاری از این مسائل توسط انسانها به وجود آمدهاند، حل شدن آنها نیز نیازمند تلاشهای انسانها است (سیندر، 1993).
نتیجهگیری مباحث
ما در این مقاله تاثیر انگیزههای شخصی داوطلبان و رفتار رهبر آنها را بر رضایت شغلی و همکاری داوطلبان، علاوه بر فرآیندهایی که واسطه این تاثیرات بودهاند، بررسی نمودهایم. همانطور در فرضیات بیان شده است، سطوح بالاتر رهبری تحولگرا با افزایش رضایت شغلی داوطلبان رابطه دارد، و شاهد این ادعا، افزایش معنادار بودن کار برای داوطلبان و کیفیت روابط بین اعضاء تیم کاری است. اگرچه، در این مطالعه، رهبری تحولگرا با مشارکت داوطلبان ارتباط معناداری نداشته است. علاوه بر این، همانطور در فرضیات بیان شده، اقدام به کار داوطلبانه برای ابراز ارزشها انساندوستانه، رضایت شغلی داوطلبان را موجب شده است، که به واسطه معنادار بودن کار برای داوطلبان محقق شده است.
We examined the separate influences of volunteers’ personal motives and their team leaders’ behaviors on volunteer satisfaction and contributions, along with mediating processes suggested by self-determination theory. Participants were 302 volunteers who worked in teams at various sites through a central agency. As predicted, both personal motives for volunteering and transformational leadership influenced volunteer satisfaction through enhanced work meaningfulness and higherquality team relationships. However, motives that predicted volunteer contribution were different from those that predicted satisfaction. Whereas satisfaction was positively associated with motives concerning esteem enhancement and value expression, contribution was positively associated with motives to gain understanding and negatively related to motives pertaining to esteem enhancement and social concerns. Transformational leadership was positively associated with volunteer satisfaction, but not with volunteer contributions. The theoretical ramifications of these findings are discussed, along with practical implications for the recruitment and retention of volunteers.
MOST AMERICANS BELIEVE THAT volunteerism helps create a better world (Independent Sector 1988). In addition to benefiting its direct recipients, volunteerism can also benefit the volunteers themselves and society as a whole (Snyder and Omoto 2007; Wilson 2000). Considered in economic terms, the dollar value of volunteerism in the United States was calculated to be $169 billion in 2009 alone (Corporation for National and Community Service, Office of Research and Policy Development 2010). Moreover, it has been argued that volunteerism and other forms of citizen participation play an essential role in combating problems that face the world. Because many of these problems are caused by human action, they require further human action in order to be successfully managed (Snyder 1993).
Discussion
We examined the influence of volunteers’ personal motives and their leaders’ behaviors on volunteer satisfaction and contribution, along with the processes mediating these influences. As hypothesized, higher levels of transformational leadership were associated with greater volunteer satisfaction, with evidence that this link was mediated by enhanced meaningfulness of the work and higherquality team relationships. However, transformational leadership was not associated with volunteer contributions in this study. Moreover, as hypothesized, volunteering in order to express humanitarian values predicted greater volunteer satisfaction, and this link was found to be mediated by enhanced meaningfulness of the work.
انگیزههای شخصی برای کار داوطلبانه
رهبری داوطلبان
فرآیندهایی که انگیزههای شخصی و رهبری را با نتایج کار داوطلبانه مرتبط میکنند
روششناسی
شرکتکنندگان و روش تحقیق
معیارهای ارزیابی
نتایج
آمار توصیفی
رضایت شغلی داوطلبان
مشارکت داوطلبان
مدلسازی معادلات ساختاری
نتیجهگیری مباحث
Personal Motives for Volunteering
Leadership of Volunteers
Processes Linking Personal Motives and Leadership to Volunteer Outcomes
Methodology
Participants and Procedure
Measures
Results
Descriptive Statistics
Volunteer Satisfaction
Volunteer Contribution
Structural Equation Modeling
Discussion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
