
معیاری جدید برای ارزیابی رهبری اجرایی خدمتگذار
چکیده
این مقاله به معرفی معیاری جدید برای ارزیابی رهبری اجرایی خدمتگذار میپردازد و جایگاه نیاز به این معیار را در زمینه رهبری اخلاقی و پیامدهای آن بر پیروان، سازمانها، و عموم جامعه مشخص مینماید. در این راستا، ادبیات تحقیق رهبری خدمتگذار بررسی میشود و با مفاهیم دیگری که اشتراکاتی با ابعاد رهبری اخلاقی دارند (برای مثال، رهبری تحولگرا، رهبری اصیل، و رهبری معنوی) مقایسه میگردند. سپس مفهوم معیار رهبری اجرایی خدمتگذار تبیین میشود و فوائد و محدودیتهای آن مورد بحث قرار میگیرد. در نهایت ما با ارائه پیشنهاداتی برای انجام تحقیقات آتی، به توضیح شیوههایی که میتوان از این معیار برای آزمون فرضیات درباره فضای اخلاقی سازمان، فرهنگ اخلاقی سازمان، مسئولیتپذیری شرکت، و نظریه نهادی، استفاده نمود میپردازیم.
مقدمه
رسواییهای اخیر در شرکتهای تجاری، دولتها، رشتههای ورزشی، سازمانهای غیردولتی، و موسسات دیگر، موجب مطرح شدن سوالاتی راجع به کیفیت رهبری سازمانی شده است. در واقع، بحران اقتصادی جهانی که در اواسط سالهای 2008 بروز نمود، صاحبنظران سازمانی را بر آن داشت تا مفروضات پذیرفته شده فعلی درمورد راهبردهای کسب و کارهای تجاری اثربخش را زیر سوال ببرند و مدلهای جدیدی از رهبری اخلاقی که بتواند پاسخگوی نیازهای متقابل جامعه جهانی باشد ارائه نمایند.
نتیجه گیری
یکی از مفاهیم ضمنی در مباحث مستمر راجع به رهبری اخلاقی آن است که رهبران قدرت بسیار زیادی در دست دارند و رهبرانی که سازمانها و افراد را فراتر از ”ورودیهای شایسته“ و ”خروجیهای عملکرد“ تلقی میکنند، که جزء روشهای سنتی برای ارزیابی اثربخشی رهبران است، اهمیت فزایندهای در یک جامعه به هم وابسته پیدا نمودهاند. از آنجائیکه این رویکرد مدلهای پذیرفته شده مدیریت تجاری را به چالش میکشد، رهبری اخلاقی نیز نیازمند شجاعت روانشناختی و اخلاقی رهبران کسب و کارهای تجاری است. درحالیکه اجرای رهبری خدمتگذار نیازمند شجاعت رهبر است، این ویژگی یک” راه حل سریع“ محسوب نمیشود، بلکه این ویژگی یکی از محاسن اخلاقی است که به مرور در مدیران، کارمندان، و کل سازمان پرورش مییابد. بنابراین رهبران باید بدانند که آیا این روش با ”ما واقعا چه کسانی هستیم“ تناسب دارد یا خیر یا اینکه شکل ایدهآل ”ما قصد داریم چه کسانی باشیم“ باید چه چیزی باشد.
ABSTRACT
This article introduces a new scale to measure executive servant leadership, situating the need for this scale within the context of ethical leadership and its impacts on followers, organizations and the greater society. The literature on servant leadership is reviewed and servant leadership is compared to other concepts that share dimensions of ethical leadership (e.g., transformational, authentic, and spiritual leadership). Next, the Executive Servant Leadership Scale (ESLS) is introduced, and its contributions and limitations discussed. We conclude with an agenda for future research, describing ways the measure can be used to test hypotheses about organizational moral climate, ethical organizational culture, corporate responsibility, and institutional theory.
Introduction
Recent scandals in business, government, sports, nonprofits, and other institutions raise questions regarding the quality of organizational leadership. Indeed, the worldwide economic crisis erupting in mid-2008 has challenged organizational scholars to question deeply held assumptions about effective business strategy and to define new models of ethical leadership that can more adequately respond to the demands of a profoundly interdependent global society.
Conclusion
Implicit in the ongoing conversation regarding ethical leadership is the notion that leaders hold tremendous power, and that those leaders who perceive organizations and people beyond the ‘‘competency inputs’’ and ‘‘performance outputs’’ traditionally used to measure leader effectiveness are increasingly important in a profoundly interdependent society. As this perspective challenges most established models of business management, ethical leadership also demands profound psychological and moral courage on the part of business leaders. While the practice of servant leadership described in this article clearly embodies such courage, it is not a ‘‘quick fix.’’ Rather it is a developmental process for executives, employees, and the organization as a whole. Leaders must therefore decide if this paradigm is even consistent with ‘‘who we really are’’ or rather, an idealized representation of ‘‘whom we would like to be.’’
چکیده
مقدمه
رهبری اخلاقی در ادبیات تحقیق مدیریت
سه مدل رهبری اخلاقی
رهبری تحولگرا
رهبری
اصیل
رهبران معنوی
رهبری خدمتگذار
رهبری خدمتگذار به عنوان رهبری اخلاقی
روشها
نتایج
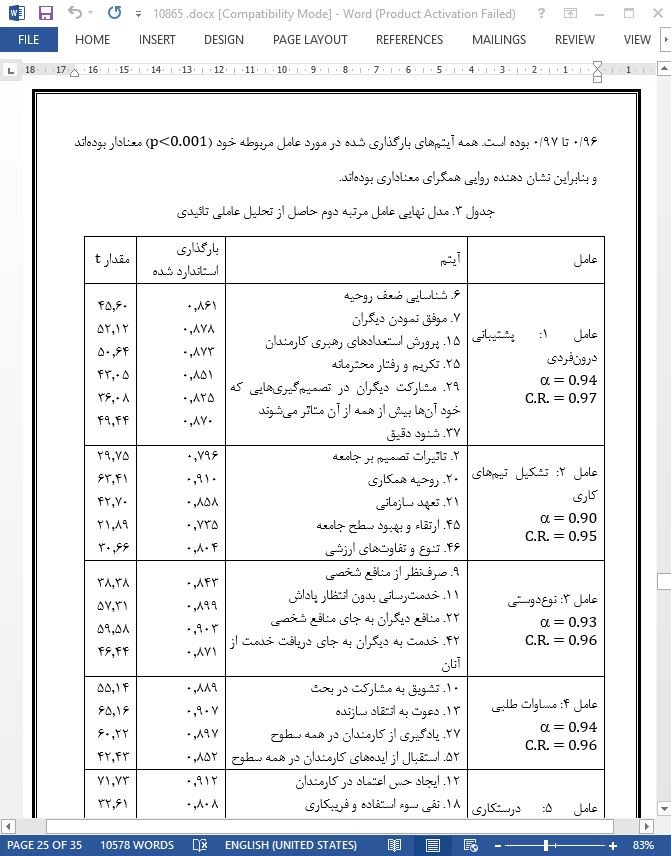
عامل مرتبه اول برای رهبری اجرایی خدمتگذار
پشتیبانی درونفردی
تشکیل تیم کاری
نوعدوستی
مساوات طلبی
درستكارى اخلاقی
خصوصیات روانشناختی مدل
تشريح مطالب
محدودیتها
افقهای تحقیقات آتی
رهبری اخلاقی
فضای اخلاقی و مسئولیتپذیری شرکت
ارتقاء نظریه نهادی
افقهای دیگر
نتیجه گیری
ABSTRACT
Introduction
Ethical leadership in the management literature
Three models of ethical leadership
Transformational leadership
Authentic leadership
Spiritual leadership
Servant leadership
Servant leadership as ethical leadership
Methods
Results
First-order factors for executive servant leadership
Building community
Altruism
Egalitarianism
Moral integrity
Psychometric properties of the model
Discussion
Limitations
Directions for future research
Ethical leadership
Moral climate and corporate responsibility
Advancing institutional theory
Further directions
Conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
