
گذردهی عظیم دی الکتریک با اتلاف کم در سرامیک های SnO2 روتیل کو دوپ شده با (Al+Nb)
اکتشاف مواد دارای گذردهی عظیم دی الکتریک (CP) همراه با اتلاف کم دی الکتریک در طیف گسترده ای از فرکانس ها / دماها، همچنان علاقه قابل توجهی را جلب می کند. ما در این مقاله، سرامیک های SnO2 روتیل کو دوپ شده با (Al+Nb) همراه با اتلاف کم دی الکتریک در دمای اتاق را گزارش می کنیم. سرامیک های Al0.02Nb0.05Sn0.93O2 و Al0.03Nb0.05Sn0.92O2 گذردهی های دی الکتریک نسبتا بالا (بالای 103) و اتلاف-های دی الکتریک کم (0.015<tanδ<0.1) را در طیف گسترده ای از فرکانس ها و دماها از 140 تا 400 درجه کلوین نشان می دهند. دوپ کردن آلومینیوم می تواند با افزایش مقاومت های دانه و مرز دانه، رفتار دی الکتریک را تعدیل کند. تفاوت های موجود در مقاومت و انرژی فعال سازی رسانا در دانه ها و مرز دانه ها نشان می دهد که می توان CP را در سرامیک های SnO2 کو دوپ شده به اثر خازنی لایه ی مانع داخلی نسبت داد.
ترکیبات دارای گذردهی عظیم دی الکتریک (CP˃103) به علت کاربردهایشان در ذخیره سازی چگالی با انرژی بالا و میکروالکترونیک ها، در نتیجه تقاضای فزآینده کاربردهای میکروالکترونیک، توجه بسیاری را جلب کرده اند. مواد CP فروالکتریک، از قبیل BaTiO3، Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3، (K,Na)NbO3 و (1-x)[Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3]O3-x[PbTiO3] (PMN-PT) به طور گسترده ای مطالعه شده اند؛ با این حال، CP تنها در یک محدوده ی دمایی کوچک در اطراف دمای کوری حاصل می شود، که این امر کاربرد آنها را محدود می کند. CP در طیف گسترده-ای از دماها در مواد غیر فروالکتریک مرسوم، از قبیل CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO)، NiO دوپ شده، La2xSrxNiO4 و ZnO گزارش شده است؛ با این حال، اتلاف دی الکتریک در این مواد بسیار بالاست (˃0.1) که مورد استفاده قرار گیرند. اگرچه CCTO دوپ شده و Y2/3Cu3Ti4O12 دوپ شده، CP دارای اتلاف کم دی الکتریک را نشان می دهند، اتلاف کم دی الکتریک را تنها می توان در طیف محدودی از فرکانس بدست آورد. اخیرا، هو پی برد که سرامیک های روتیل (TiO2) کو دوپ شده با In-Nb، CP دارای اتلاف کم دی الکتریک (⁓0.05) را در طیف گسترده ای از دماها / فرکانس ها نشان می دهد؛ اما اتلاف کم دی الکتریک به شدت به شرایط سنتز بستگی دارد. بنابراین، مواد CP جدید دارای اتلاف کم دی الکتریک در طیف گسترده ای از دماها و فرکانس ها هنوز مورد بررسی قرار می گیرند.
به طور خلاصه، CP و اتلاف کم در سرامیک های SnO2 روتیل کو دوپ شده با Al+Nb را در طیف گسترده ای از فرکانس ها و دماها گزارش کردیم. سرامیک های SnO2 کو دوپ شده با Al+Nb اتلاف دی الکتریک کم تری نسبت به مواد CP غیر فروالکتریک مرسوم، همراه با یک عدم وابستگی عالی فرکانس / دما را نشان دادند. تفاوت-های زیاد موجود در مقاومت و انرژی فعال سازی رسانا بین دانه و مرز دانه نشان می دهد که اثر IBLC مسئول CP است. دوپ کردن آلومینیوم می تواند رفتار دی الکتریک را با افزایش مقاومت های دانه و مرز دانه تعدیل کند. افزایش مقاومت مرز دانه می تواند به طور موثری اتلاف دی الکتریک را کاهش دهد؛ در حالی که، افزایش مقاومت دانه، زمان آرامش τ را افزایش خواهد داد؛ که منجر به اتلاف بیشتر دی الکتریک هنگامی که سطح دوپ کردن آلومینیوم بیش از 0.04 باشد، می شود.
The exploration of colossal dielectric permittivity (CP) materials with low dielectric loss in a wide range of frequencies/temperatures continues to attract considerable interest. In this paper, we report CP in (Al þ Nb) co-doped rutile SnO2 ceramics with a low dielectric loss at room temperature. Al0.02Nb0.05Sn0.93O2 and Al0.03Nb0.05Sn0.92O2 ceramics exhibit high relative dielectric permittivities (above 103 ) and low dielectric losses (0.015 < tan d < 0.1) in a wide range of frequencies and at temperatures from 140 to 400 K. Al doping can effectively modulate the dielectric behavior by increasing the grain and grain boundary resistances. The large differences in the resistance and conductive activation energy of the grains and grain boundaries suggest that the CP in co-doped SnO2 ceramics can be attributed to the internal barrier layer capacitor effect.
The compounds with a colossal dielectric permittivity (CP > 103 ) have attracted a lot of attention because of their applications in high-energy density storage and microelectronics as a result of the continually increasing demands of microelectronics applications.1–4 Ferroelectric CP materials, such as BaTiO3, 5,6 Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3, 7 (K,Na)NbO3, 8 and (1-x)[Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-x[PbTiO3] (PMN-PT),9,10 have been widely studied; however, the CP can only be achieved in a small temperature range around the Curie temperature, which limits their application. CP has been reported across a wide range of temperatures in the traditional nonferroelectric materials, such as CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO),2,11 doped NiO,12 La2xSrxNiO4, 13,14 and ZnO;15,16 however, the dielectric loss in these materials is too high (>0.1) to be applied. Although doped CCTO17 and doped Y2/3Cu3Ti4O12 (Ref. 18) show CP with low dielectric loss, the low dielectric loss can only be achieved in a narrow frequency range. Recently, Hu et al. found that In þ Nb co-doped rutile TiO2 ceramics exhibit CP with low dielectric loss (0.05) over a very broad range of temperatures/frequencies,19 but the low dielectric loss strongly depends on the synthesis conditions.20–23 Therefore, new CP materials with low dielectric loss over a wide range of temperatures and frequencies are still being investigated.
In summary, we have reported CP and low loss in Al þ Nb co-doped rutile SnO2 ceramics across a broad range of frequencies and temperatures. Al þ Nb co-doped SnO2 ceramics exhibit lower dielectric loss than traditional nonferroelectric CP materials, with an excellent independence of frequency/temperature. The large differences in the resistance and conductive activation energy between the grain and grain boundary suggest that the IBLC effect is responsible for the CP. Al doping can modulate the dielectric behavior by increasing grain and grain boundary resistances. The increase in grain boundary resistance can effectively reduce dielectric loss; meanwhile, the increasing grain resistance will increase the relaxation time s, resulting in a higher dielectric loss when the Al doping level exceeds 0.04.
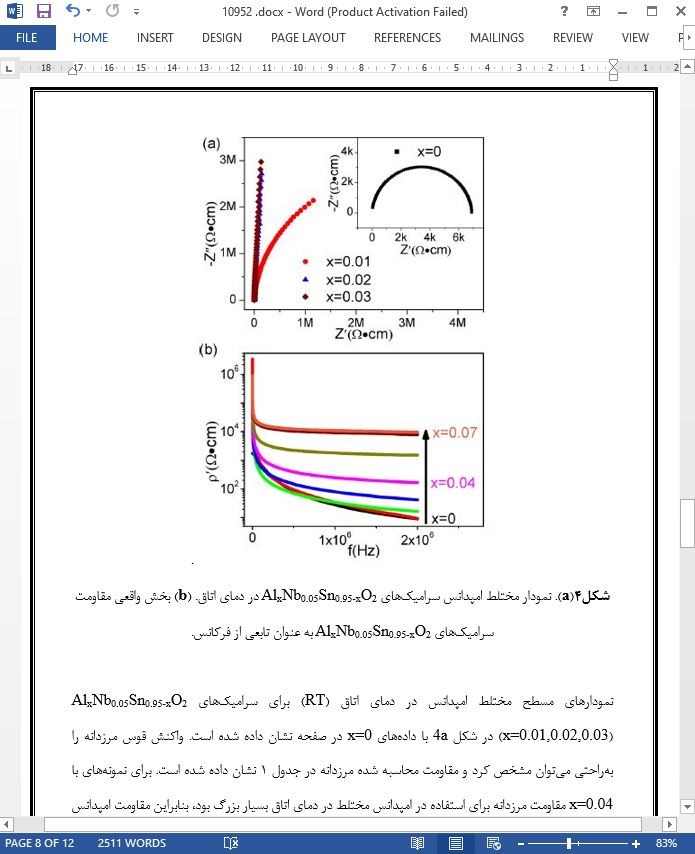
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
