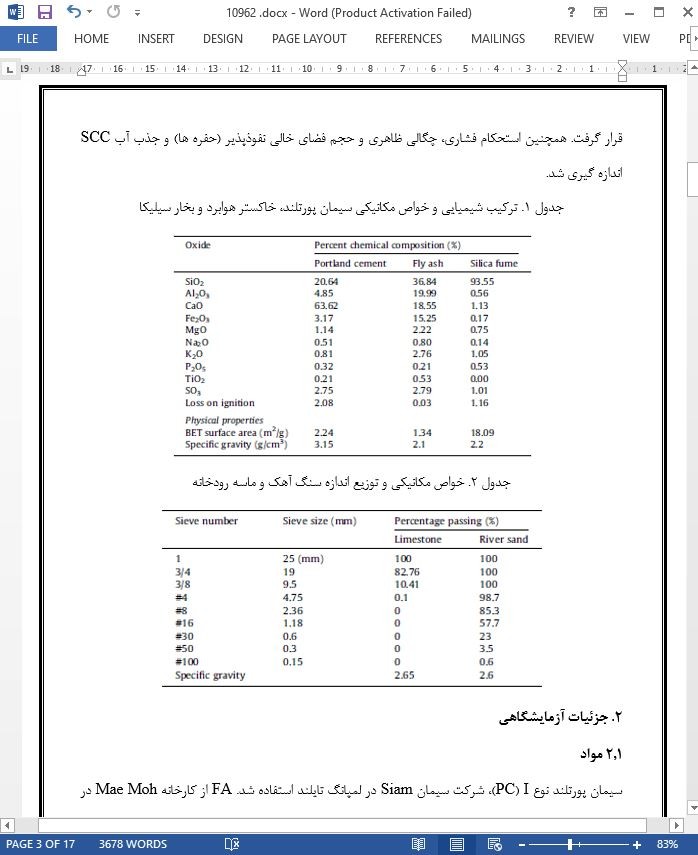
استحکام فشاری و مقاومت کلریدی بتن خود تراکمی
خلاصه
اثر خاکستر هوا برد حاوی کلسیم زیاد و بخار سیلیکا به عنوان سیمان مخلوط دو تایی و سه تایی استحکام فشاری و مقاومت کلریدی بتن خود تراکمی (SCC) در این تحقیق بررسی شد. خاکستر هوا برد حاوی کلسیم زیاد (%70-40) و بخار سیلیکا (%10-0) با درصد وزنی 50،60 و 70% جایگزین قسمتی از سیمان شدند. استحکام فشاری، چگالی، حجم فضای خالی نفوذپذیر (حفره ها) و جذب آب بررسی شد. مقدار بار رد و بدل شده به کولن به منظور تعیین مقاومت کلرید SCC سنجیده شد. نتایج نشان می دهند که سیمان دوتایی مخلوط با مقادیر بالای خاکستر هوابرد عموما مقدار استحکام فشاری SCC را در تمام طول عمر ها (3،7،28 و 90 روز) کاهش میدهد. گرچه سیمان سه تایی مخلوط با خاکستر هوابرد و بخار سیلیکا بعد از 7 روز در مقایسه با سیمان دوتایی مخلوط در همان سطح جایگزینی، استحکام فشاری بیشتری دارد. استحکام فشاری بیش ازMpa 60 (بتن استحکام بالا) را می توان با استفاده از سیمان سه تایی مخلوط با خاکستر هوا برد حاوی کلسیم زیاد و بخار سیلیکا به دست آورد. خاکستر هوا برد مقدار بار رد و بدل شده SCC را کاهش داده و با افزایش مقدار خاکستر هوا برد آن را کاهش می دهد، گرچه حجم فضای خالی نفوذپذیر (حفره ها) و جذب آب زیاد شد. علاوه بر این، با مقایسه با سیمان دوتایی مخلوط در سطح جایگزینی یکسان، بار عبوری SCC حاوی سیمان سه تایی مخلوط فقط حاوی خاکستر هوا برد از سیمان دوتایی مخلوط کم تر بود. این نشان دهنده آن است که خاکستر هوابرد و بخار سیلیکا می توانند مقاومت کلریدی SCC را در مقادیر زیاد جایگزینی سیمان پورتلند افزایش دهند.
1. مقدمه
امروزه، بتن حاوی خاکستر هوابرد زیاد (HVFA) با جایگزینی 50% یا بیشتر سیمان با خاکستر هوابرد (FA) به طور گسترده ای بررسی شده است. HVFA معمولا برای دستیابی به جریان اسلامپ خوب SCC به کار می رود. SCC یک شاخه جدید بتن با کیفیت است که توسط توانایی خود در پخش شدن در مکان با وزن خود بدون نیاز به ارتعاش و خود تراکم بدون جدایش، مشخص شده است. استفاده از FA در SCC دز فوق روان مورد نیاز را به منظور دستیابی به جریان اسلامپ یکسان برای بتن ساخته شده با سیمان پورتلند، کاهش می دهد. استفاده از FA همچنین خواص رئولوژیکی را بهبود بخشیده و ترک خوردگی سیمان را به دلیل گرمای کمتر هیدراسیون کاهش می دهد. گرچه، استحکام بتن HVFA کمتر از بتن ساخته شده از سیمان خالص پورتلند، خصوصا در طول عمر های کم به دلیل اثر رقیق سازی و واکنش پوزولانی خیلی کم است.
4. استنتاج
در این تحقیق، اثر FA کلسیم بالا و SF در سیمان مخلوط دو و سه تایی با درصد های بالای جایگزینی بر خواص SCC مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. از این نتایج می توان استنباط کرد که چگالی ظاهری تمام SCC همراه با FA چندان متفاوت نبود. گرچه چگالی ظاهری سیمان پورتلند مخلوط دو و سه تایی در تمام w/b کمی کمتر از سیمان پورتلند کنترل بود. حجم فضای خالی قابل نفوذ (حفره ها) و جذب آب SCC حاوی FA بیشتر از سیمان پورتلند کنترل بود و با افزایش مقدار FA زیاد شد. اثر SF باعث کاهش حفره ها و جذب آب SCC در سیمان پورتلند مخلوط دو و سه تایی می شود.
Abstract
The influence of high-calcium fly ash and silica fume as a binary and ternary blended cement on compressive strength and chloride resistance of self-compacting concrete (SCC) were investigated in this study. High-calcium fly ash (40–70%) and silica fume (0–10%) were used to replace part of cement at 50, 60 and 70 wt.%. Compressive strength, density, volume of permeable pore space (voids) and water absorption of SCC were investigated. The total charge passed in coulombs was assessed in order to determine chloride resistance of SCC. The results show that binary blended cement with high level fly ash generally reduced the compressive strength of SCC at all test ages (3, 7, 28 and 90 days). However, ternary blended cement with fly ash and silica fume gained higher compressive strength after 7 days when compared to binary blended fly ash cement at the same replacement level. The compressive strength more than 60 MPa (high strength concrete) can be obtained when using high-calcium fly ash and silica fume as ternary blended cement. Fly ash decreased the charge passed of SCC and tends to decrease with increasing fly ash content, although the volume of permeable pore space (voids) and water absorption of SCC were increased. In addition when compared to binary blended cement at the same replacement level, the charge passed of SCC that containing ternary blended cement was lower than binary blended cement with fly ash only. This indicated that fly ash and silica fume can improve chloride resistance of SCC at high volume content of Portland cement replacement.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, high-volume fly ash (HVFA) concrete, with 50% or more of cement replaced by fly ash (FA) has been studied extensively. HVFA is often used to achieve good slump flow of self-compacting concrete (SCC). SCC is a new category of high-performance concrete characterized by its ability to spread into place under its own weight without the need of vibration, and self-compact without any segregation [1,2]. The use of FA in SCC reduces the dosage of superplasticizer needed to obtain similar slump flow as for concrete made with Portland cement [3]. Also, the use of FA improves rheological properties and reduces cracking of concrete due to lower heat of hydration [4,5]. However, the strengths of HVFA concrete are lower than that of pure Portland cement concrete, especially at early age due to the dilution effect and very low pozzolanic reaction [6–10].
4. Conclusions
In this study, the influence of high calcium fly ash and SF as a binary and ternary blended cement at high volume replacement on properties of SCC was investigated. From these results it can be concluded that the apparent densities of all SCC in general were notsignificantly different when containing FA and SF. The volume of permeable pore space (voids) and water absorption of SCC containing FA was higher than Portland cement control and tends to increase with increasing FA content. The influence of SF seems to decrease voids and water absorption of SCC in both binary and ternary blended Portland cement.
خلاصه
1. مقدمه
2. جزئیات آزمایشگاهی
2.1 مواد
2.2 آماده سازی نمونه ها و روش های تست
3. نتایج و بحث
3.1 چگالی، جذب آب و حجم فضای خالی قابل نفوذ
3.2 استحکام فشاری
3.3 مقاومت کلرید
4. استنتاج
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental details
2.1. Materials
2.2. Samples preparation and test methods
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Density, water absorption and volume of permeable pore space
3.2. Compressive strength
3.3. Chloride resistance
4. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه