اطمینان از کیفیت صفحات مسی لحیم شده از طریق NDE التراسونیک پیشرفته
چکیده
روش های غیر مخرب التراسونیک پتانسیلی فوق العاده برای تشخیص عیوب در ماده تحت آزمایش ارائه می کنند. به خصوص، ناپیوستگی های ایجاد شده توسط جوشکاری، لحیم کاری گرم و سرد عموما از طریق روش های التراسونیک بررسی می شوند. در این مقاله، یک تکنیک غیر مخرب پیشرفته التراسونیک برای کنترل کیفیت سلول های مسی لحیم شده استفاده می شود، تا یک نمونه شتاب سنج برای درمان سرطان به دست آید. سلول ها شامل دو نیم صفحه هستند، که از مس خالص 99/99 درصد با هدایت بالا ساخته شده اند. اسکن التراسونیک کل حجم قطعه توسط روش غوطه وری انجام شد تا توموگرافی محوری التراسونیک قطعه به دست آمده و کیفیت فرایند لحیم کاری ارزیابی شود.
1. مقدمه
لحیم کاری تکنولوژی اصلی در تولید قطعات با کارکرد بالا است. فرایند لحیم کاری دو قطعه از فلز یا آلیاژ را از طریق فلز یا آلیاژ فیلر سومی به هم وصل می کند. مساحت اتصال تا دمایی بالاتر از نقطه ذوب فلز یا آلیاژ فیلر و پایین تر از دمای ذوب فلز یا آلیاژهای پایه گرم می شود. فلز یا آلیاژ فیلر ذوب شده توسط نیروی کاپیلاری به درون فاصله بین دو قطعه فلزی جریان می یابد و اتصال متالورژیکی شدیدی در حین سرد شدن ایجاد می شود. اتصالات لحیم کاری شده عموما استحکام کششی بیشتری نسبت به استحکام فلز یا آلیاژ فیلر استفاده شده دارند.
7. نتیجه گیری
یک تکنیک پیشرفته NDE بر اساس تکنیک اسکن FV US برای کنترل کیفیت سلول های مسی لحیم کاری شده نمونه شتاب دهنده استفاده شده برای درمان پروتونی استفاده شد. کیفیت فرایند لحیم کاری برای عملکرد این نمونه که هیچ محلول پیوستگی در ساختار خود نیست، ضروری است تا اطمینان از همگنی میدان مغناطیسی ایجاد شده برای شتاب دهی پروتون فراهم شود. این سلول شامل دو نیم صفحه است، که از مس 99/99 درصد OHFC روی همدیگر ساخته شده است.
Abstract
Ultrasonic non-destructive methods have demonstrated great potential for the detection of flaws in a material under examination. In particular, discontinuities produced by welding, brazing, and soldering are regularly inspected through ultrasonic techniques. In this paper, an advanced ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation technique is applied for the quality control of brazed copper cells in order to realize an accelerometer prototype for cancer proton therapy. The cells are composed of two half-plates, made of high conductivity 99.99% pure copper, brazed one on top of the other. Full volume ultrasonic scanning based on the pulse-echo immersion testing method were carried out to allow for the ultrasonic 2.5 D axial tomography of the cell, realizing the quality assessment of the brazing process.
1. Introduction
Brazing is a key technology in the production of components made of high performance materials. The brazing process joins two pieces of metal or alloy together through a third, molten filler metal or alloy. The joint area is heated above the melting point of the filler metal or alloy but below the melting point of the base metals or alloys to be joined. The molten filler metal or alloy flows into the gap between the two metal pieces by capillary action and forms a strong metallurgical bond as it cools down to solidification. Brazed joints have high tensile strength, typically higher than the strength of the utilized filler metal or alloy [1].
7. Conclusions
An advanced ultrasonic NDE technique based on the FV US scanning technique was applied for the quality control of brazed copper cells of an accelerometer prototype utilized for radionuclide production and proton therapy use. The quality of the brazing process is critical for the functionality of the prototype that does not contain any continuity solution in its structure in order to guarantee the homogeneity of the generated magnetic field responsible for protons acceleration. The back-to-back cell consist of two half-cell plates, made of high conductivity OHFC 99.99% copper, brazed one on top of the other.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. ارزیابی پیشرفته غیر مخرب التراسونیک
3. شتاب دهنده خطی پروتون
3.1 شتاب دهنده خطی LIBO
3.2 مواد و فرایند لحیم کاری
4. تست التراسونیک غیر مخرب
4.1 سیستم NDE التراسونیک
4.2 فرایند اسکن التراسونیک NDE
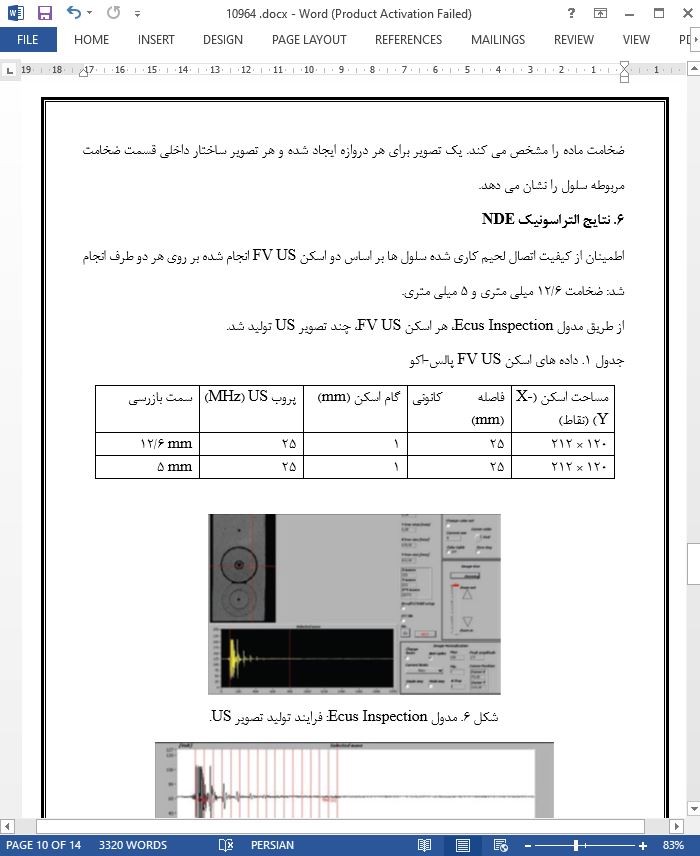
5. تولید تصویر التراسونیک
6. نتایج التراسونیک NDE
5.1 نتایج اسکن FV US از قسمت 6/12 میلی متری
5.2 نتایج اسکن FV US از قسمت 5 میلی متری
7. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Advanced ultrasonic non-destructive evaluation
3. Prototype proton linear accelerator
3.1. Linear accelerator LIBO
3.2. Material and brazing process
4. Ultrasonic non-destructive testing
4.1. Ultrasonic NDE system
4.2. Ultrasonic NDE scanning procedure
5. Ultrasonic image generation
6. Ultrasonic NDE results
5.1. Results of FV US scan from the 12.6 mm inspection side
5.2. Results of FV US scan from the 5.0 mm inspection side
7. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه