
پتانسیل و شدت انتقال کووید-۱۹ در کره جنوبی
چکیده
اهداف: ازآنجایی که اولین مورد کروناویروس جدید 2019(کووید-19) در 20 ژانویۀ 2020 در کرۀ شمالی شناسایی شد، تعداد موارد به سرعت افزایش یافت به طوری که تا 6 مارس 2020، منجربه ابتلای6284 مورد و فوت42 نفر شد. اولین تحقیق درمورد گزارش تعداد تکثیر کووید-19 در کرۀ جنوبی را برای بررسی سرعت شیوع بیماری، ارائه می دهیم.
روش کار: موارد روزانۀ تأیید شدۀ کووید-19 در کرۀ جنوبی از منابع عمومی موجود استخراج شد. با استفاده از توزیع تجربی گزارشات دارای تأخیر و شبیه سازی مدل رشد کلی، تعداد تکثیر مؤثر را برمبنای توزیع احتمال گسستۀ فاصلۀ زایشی ارزیابی کردیم.
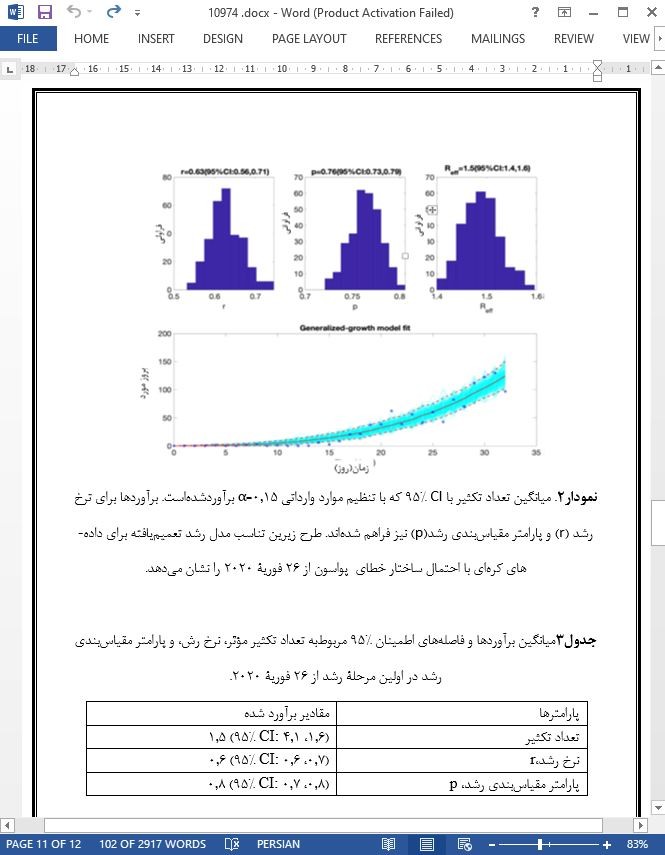
نتایج: چهار گروه اصلی را شناسایی و تعداد تکثیر را 1.5(1.6-1.4 CI: 95%) برآورد کردیم. به علاوه، نرخ رشد طبیعی 0.6 (0.7، 0.6 CI: 95%) و مقیاس بندی پارامتر رشد 0.8 (0.8،0.7 CI: 95%) برآورد شدند، که نشان دهندۀ پویایی رشد زیر نمایی کووید-19 می باشد. نرخ مرگ و میر موارد خام در بین مردان (1.1%) در مقایسه با زنان (0.4%) بیشتر است و با افزایش سن افزایش می یابد.
نتیجه گیری: نتایج ما انتقال پایدار اولیۀ کووید-19 در کرۀ جنوبی را نشان می دهد و از اجرای اقدامات فاصله-گذاری اجتماعی برای کنترل سریع شیوع بیماری حمایت می کند.
مقدمه
کروناویروس جدید (کروناویروس سندرم حاد تنفسی2) که در دسامبر 2019 در شهر ووهان چین ظاهر شد، اخیراً پتانسیل شیوع سریع در شرایط محدود و عبور بین مرزی طبق الگوی حرکتی انسان را نشان داد (میزوموتو و همکاران،2020). گرچه کووید-19 عموماً علائم خفیف متداول موجود در سایرعفونت ها را ایجاد میکند، اما توانایی ایجاد بیماری مزمن در گروه های خاصی مانند جمعیت سالخورده و افراد دارای مشکلات اساسی سلامتی مثل بیماران قلبی عروقی و دیابتی را دارد (ادلر،2020). بااین وجود، تصویر واضحی از همه گیری این کروناویروسِ جدید هنوز مشخص نشده است.
بحث
این اولین تحقیق برای گزارش براوردهای پتانسیل انتقال کووید-19 در کره براساس مسیر بیماری همه گیر است که با استفاده از تاریخ شروع اولین موارد گزارش شده در کره بازسازی شده است. برآورد R به وضوح انتقال پایدار ویروسِ کرونای جدید در کره را نشان می دهد؛ به نظر می رسد نرخ مرگ ومیر بین مردان و جمعیت کهنسال بیشتر است (جدول 1). به علاوه، موارد وارداتی نقش اندکی در انتقال ثانویۀ بیماری در کره دارند، زیرا اکثر این موارد در مراحل اولیۀ اپیدمی رخ داده اند، که جدیدترین مورد گزارش شده در 9 فوریۀ 2020 گزارش شد. این یافته ها از دامنۀ مداخلات فاصله گذاری اجتماعی حمایت می کند که دولت کره برای کنترل هرچه سریع تر شیوع آن را وضع کرد.
Abstract
Objectives: Since the first case of 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) identified on Jan 20, 2020, in South Korea, the number of cases rapidly increased, resulting in 6284 cases including 42 deaths as of Mar 6, 2020. To examine the growth rate of the outbreak, we present the first study to report the reproduction number of COVID-19 in South Korea.
Methods: The daily confirmed cases of COVID-19 in South Korea were extracted from publicly available sources. By using the empirical reporting delay distribution and simulating the generalized growth model, we estimated the effective reproduction number based on the discretized probability distribution of the generation interval.
Results: We identified four major clusters and estimated the reproduction number at 1.5 (95% CI: 1.4–1.6). In addition, the intrinsic growth rate was estimated at 0.6 (95% CI: 0.6, 0.7), and the scaling of growth parameter was estimated at 0.8 (95% CI: 0.7, 0.8), indicating sub-exponential growth dynamics of COVID-19. The crude case fatality rate is higher among males (1.1%) compared to females (0.4%) and increases with older age.
Conclusions: Our results indicate an early sustained transmission of COVID-19 in South Korea and support the implementation of social distancing measures to rapidly control the outbreak.
Introduction
A novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that emerged out of the city of Wuhan, China, in December 2019 has already demonstrated its potential to generate explosive outbreaks in confined settings and cross borders following human mobility patterns (Mizumoto et al., 2020). While COVID-19 frequently induces mild symptoms common to other respiratory infections, it has also exhibited an ability to generate severe disease among certain groups, including older populations and individuals with underlying health issues such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes (Adler, 2020). Nevertheless, a clear picture of the epidemiology of this novel coronavirus is still being elucidated.
Discussion
This is the first study to report estimates of the transmission potential of COVID-19 in Korea based on the trajectory of the epidemic, which was reconstructed by using the dates of onset of the first reported cases in Korea. The estimates of R clearly indicate the sustained transmission of the novel coronavirus in Korea; the case fatality rate appears to be higher among males and older populations (Table 1). Moreover, the imported cases contribute little to secondary disease transmission in Korea, as a majority of these cases occurred in the early phase of the epidemic, with the most recent imported case reported on Feb 9, 2020. These findings support the range of social distancing interventions that the Korean government put in place to bring the outbreak under control as soon as possible.
چکیده
مقدمه
مواد و روش ها
داده ها
وارد کردن تاریخ شروع
برآورد تعداد تکثیر از موارد روزانۀ شیوع
نتایج
شیوع مجدد کووید-19
تعداد تکثیر مؤثر (Rt) از موارد شیوع روزانه
نرخ مرگ ومیر موارد خام
گروه های انتقال
گروه کلیسای عیسوی شین چانی
گروه بیمارستان دائنام چونگدو
گروه مرتبط با سالن ورزشی چئونان
گروه مرتبط با تور زیارتی به اسرائیل
بحث
ABSTRACT
Introduction
Methods
Data
Imputing the date of onset
Estimation of reproduction number from daily case incidence
Results
Reconstructed incidence of COVID-19
Effective reproduction number (Rt) from daily case incidence
The crude case fatality rate
Shincheonji Church of Jesus cluster
Chungdo Daenam hospital cluster
Cluster related to the gym in Cheonan
Pilgrimage tour to Israel related cluster
Discussion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
