اثر ناهمسانگردی بر کشش عمیق TWB فولاد کم کربن و دوفازی
چکیده
TWB ساخته شده از مواد غیر مشابه، ضخامت همگن یا غیر همگن، دارای کاربردهای بالقوه در صنعت اتومبیل دارد. شکل پذیری TWB در مقایسه با فلز پایه، به دلیل وجود منطقه جوش و عدم مطابقت استحکام بین اجزا کم است. اکثر ورق های فلزی که برای تولید TWB استفاده می شوند، دچار ناهمسانگردی هستند که در حین مرحله قبل از فرایند به دلیل تغییر شکل زیاد در آن ها ایجاد شده است. جهت گیری مسیر نورد ورق و ترکیب مواد ورق اثر زیادی بر روی رفتار تغییر شکل دارد. اثر ناهمسانگردی در TWB و جهت گیری مسیر نورد ورق در حین فرایند کشش عمیق در این تحقیق بررسی می شود. مدل های آنالیز المان محدود کشش عمیق TWB فولاد کم کربن و دوفازی با استفاده از کد FE، DD31MP، به منظور ایجاد پایه ای برای طراحی TWB توسعه قطعات انجام شد. ناهمسانگردی در ورق ها اثر متوسطی دارد و سهم آن در جریان بیشتر ماده به خواص مکانیکی ورق بستگی دارد. ترکیب مناسبی از جهت گیری مسیر نورد ورق می تواند به طور قابل ملاحظه ای شکل پذیری TWB را در کشش عمیق جام مربعی بهبود ببخشد.
1. مقدمه
نگرانی های زیست محیطی و تخلیه سریع سوخت های فسیلی سازندگان اتومبیل را مجبور به اجرای قوانین زیست محیطی دولتی و فراهم کردن تقاضای روبه فزون مشتریان برای بهبود بازدهی سوخت کرده است. بنابراین، صنعت اتومبیل مجبور به جستجو برای مواد سبک و کیفیت بالا به منظور بهبود بازدهی سوخت، زیبایی و کاهش هزینه اتومبیل شده است. یک روش برای حل این موضوع استفاده از TWB در قطعات بدنه ماشین است. با قراردهی مناسب ماده مناسب در اتومبیل توسط TW ، عملکرد مورد نیاز قطعه با هزینه اسمی حاصل می شود. TWB از ترکیب موادی که توسط تکنیک های جوشکاری پیشرفته همچون جوشکاری لیزر، mash-seam و اشعه الکترون به یکدیگر متصل شده اند، ساخته شده است. این تکنیک ها برای تولید خط جوشی باریک با کمترین منطقه متاثر از جوش، طراحی شده اند. بنابراین TWB ساخته شده با مواد غیر مشابه، ضخامت همگن یا غیر همگن می تواند برای تولید اجزای اتومبیل تحت تغییر شکل قرار بگیرد تا قطعاتی همچون پنل های کنار بدنه، ریل های قسمت موتور، پنل های ستون مرکزی، پنل های سکانداری و دیگر اجزای بازار تولید شود.
4. نتیجه گیری
شبیه سازی عددی به منظور تعیین اثر ناهمسانگردی و جهت گیری مسیر رول ورق ها در TWB انجام شد تا پایه ای برای توسعه TWB برای یک قطعه شکل بگیرد. کد المان محدود DD31MP برای شبیه سازی کشش عمیق TWB فولاد کم کربن و دوفازی استفاده شد. شبیه سازی ها بدون در نظر گرفتن حضور منطقه جوش بین فولاد DC06 و DP600 در TWB انجام شد. نتایج TWB ناهمسانگرد با TWB ایزوتروپیک مقایسه می شود. نیروی پانچ مورد نیاز برای کشش عمیق با حضور ناهمسانگردی در ورق افزایش می یابد. تفاوت در استحکام و ناهمسانگردی اولیه، باعث ایجاد جریان ماده نابرابر در حین کشش عمیق می شود. گوشه بالایی کاپ در فولاد کم کربن تحت بیشترین کرنش پلاستیک قرار گرفته و با این وجود تا عمق کشش 35 میلی متر برای این هندسه، دچار شکست نمی شود. جریان ماده ناکافی به گوشه پایینی کاپ در فولاد دو فازی باعث نازک شدن آن می شود. ماده ضعیف تحت تغییر شکل بزرگی قرار می گیرد و بنابراین، در قسمت کاپ خط جوش به سمت ماده قوی تر حرکت کرده و در ناحیه فلنج به سمت ماده ضعیف تر حرکت می کند. سهم قابل توجه خواص ناهمسانگردی در فولاد کم کربن در TWB دیده می شود. نازک شدن در طول خط جوش در ترکیب مواد ایزوتروپیک نسبت به TWB ناهمسانگرد بیشتر است. استفاده از ترکیب مناسب جهت گیری مسیر رول و در نتیجه کنترل ناهمسانگردی، می تواند باعث حصول افزایش قابل توجهی در شکل گیری TWB شود.
Abstract
Tailor-welded blanks made of dissimilar, uniform or non-uniform thickness materials have potential applications in automobile industries. Compared to the base metal, the formability of tailor-welded blank is less due to the presence of weld area and strength mismatch between component blanks. Most sheet metals used to produce tailor-welded blanks have anisotropy induced during pre-processing stage due to large deformation. The orientation of the blank sheet rolling direction and the combination of the blank sheet materials has significant influence on the deformation behaviour. The effect of anisotropy in the tailor-welded blank and the orientation of blank sheets rolling direction during deep-drawing process are investigated in this study. Finite element analysis of deep-drawing mild steel and dual-phase steel tailor-welded blank models was carried out using research purpose FE code DD3IMP; to form a basis for tailor-welded blank design and development for a part. Anisotropy in the blank sheets has moderate influence and its contribution to increased material flow depends on the mechanical properties of the blank sheets. Appropriate combination of the blank sheets rolling direction orientation can significantly improve the formability of the tailor-welded blank in the deep-drawing of square cup.
1. Introduction
Environmental concern and fast depletion of fossil fuels have forced automobile manufacturers to implement strict government environmental regulations and to cater increased customer demands for improved fuel efficiency. Thus, the automobile industries are driven to look for high performance and light weight materials in order to improve the fuel efficiency, aesthetic and reduce the cost of the vehicle. One way of handling this issue is to increase the application of tailor-welded blanks in the automobile body parts. Through proper location of apt material in the automobile body by tailor-welding, the required functions of the body part can be accomplished at nominal cost. Tailorwelded blanks are produced from combination of materials brought together by employing advanced welding techniques, such as laser beam, mash-seam or electron beam welding. These techniques are intended to produce narrow weld-line with least heat-affected zone. Tailor-welded blanks thus produced with dissimilar and uniform or non-uniform thickness materials can be subjected to deformation to produce automobile components, such as body side panels, motor compartment rails, center pillar inner panels, wheelhouse/shock tower panels [1–4] and other market areas [5].
4. Conclusions
Numerical simulations were carried out to determine the effect of anisotropy and the rolling direction orientation of the blank sheets in tailor-welded blanks to form a basis for tailorwelded blank development for a part. In-house finite element code DD3IMP was used for the deep-drawing simulation of a mild steel and dual-phase steel tailor-welded blank. The simulations were performed without considering the presence of a weld zone between DC06 and DP600 sheet segments in the tailorwelded blank. The results of anisotropic tailor-welded blanks are compared with isotropic tailor-welded blank. The punch force required for deep-drawing increases with anisotropy in the blank sheets. The strength difference and the initial anisotropy induce uneven metal flow during deep-drawing. The top corner of the cup in mild steel sheet segment is subjected to largest plastic strains and yet does not lead to material failure until a draw depth of 35 mm for this geometry. Inadequate material flow to the bottom cup corner on the dual-phase side causes thinning. The weak material is subjected to large deformation and hence, the weld-line moves towards the stronger material side in the cup section and towards the weaker material side in the flange area. Significant contribution by anisotropic property is observed on mild steel segment in the tailor-welded blank. Thinning along the weld-line is more in isotropic material combination than anisotropic tailor-welded blank. Using appropriate combination of rolling direction orientation, and hence controlling anisotropy, significant improvement in the formability of tailor-welded blanks can be achieved.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدل سازی و شبیه سازی
2.1. مدل المان محدود
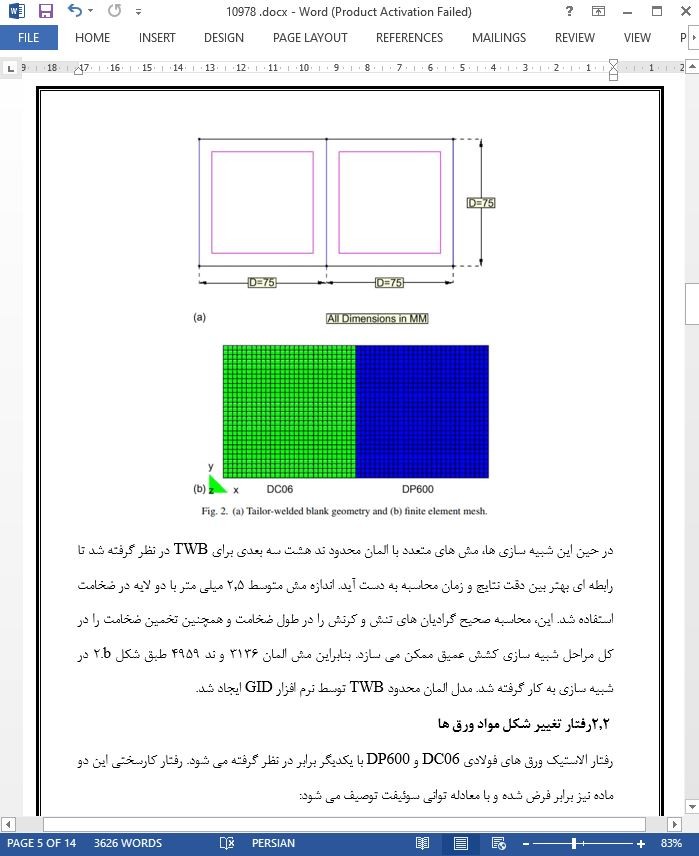
2.2رفتار تغییر شکل مواد ورق ها
2.3 شبیه سازی عددی
3. نتایج و بحث
4. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modelling and simulation
2.1. Finite element model
2.2. Deformation behaviour of blank sheet materials
2.3. Numerical simulation
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه