سیستم های فوتونیکی مجتمع مبتنی بر ابزارهای اندیس گرادیانی فعال شده با اپتیک تبدیلی
انتظار میرود که ابزارهای مجتمع فوتونیکی بتوانند نقش روزافزونی در ارتباطات نوری، تصویربرداری، رایانش و شناسایی با هدف کاهش هزینه و وزن این سیستمها ایفا نمایند. پیشرفتهای بیشتر این فناوری به شدت به توانایی توسعه اجزای نوری پکیده و قابل اطمینان و تسهیل ادغام آنها در یک بستر معمول وابسته است. در اینجا با استفاده از روش نوظهور اپتیک تبدیلی نشان میدهیم که اجزای عملکرد متشکل از مواد اندیس گرادیانی صفحهای را میتوان طراحی و به اسانی در مدارهای فوتونیکی گنجاند. انعطافپذیری بینظیر فرایند طراحی ابزارهای اپتیکی تبدیلی امکان ایجاد تعدادی از ابزارهای جدید مانند کولیماتورهای (موازیسازهای) نوری، آداپتورهای موجبر و گذرگاه موجبر را میسر میسازد که کاربردهای گستردهای در تراشههای مجتمع نوری داشته و با فناوری ساخت کنونی سازگاری دارند. برای نمایش عملکرد بینظیر نوری و مجتمعسازی موثر این ابزارها با سایر اجزای موردنظر در یک سیستم فوتونیکی روی تراشهای، شبیهسازی عددی موج کامل را با استفاده از روش تفاضل محدود دامنه زمان به اجرا درخواهیم آورد. این قطعات تنها به مواد دیالکتریک متغیر مکانی فاقد ویژگیهای مغناطیسی نیاز دارند که اتلاف اندک و عملیات پهنباند در یک محیط فوتونیک مجتمع را تسهیل میسازند.
مقدمه
اپتیک تبدیلی (TO)، روشی سیستماتیک برای دستکاری انتشار نور از طریق استفاده از نگاشتها و توزیعهای فضایی مواد ساختاری است.1، 2 TO براساس ویژگی عدم تغییر معادلات ماکسول تحت تبدیلات مختصات، ابزار طراحی جدید قدرتمندی در کنترل مسیر نور و ساخت ابزارهای جدیدی همچون پوششهای نامرئی3، متمرکزکنندههای میدان4 و جذبکنندههای ”حفره سیاه“ کامل5 را نشان میدهد. دسته مهمی از مختصات تبدیل تعبیه شده با ایجاد ناپیوستگی در امتداد مرزهای محیط تبدیلی ایجاد میشود. این ویژگی منحصر به فرد، توسعه برخی از ابزارهای TO عملیتر، اما جالب توجه شامل چنبرهها و شکافندههای باریکه بدون بازتاب7، چرخندههای قطبشی8 و لنزهای تخت مختلف9- 11 را تسهیل نموده است.
نتیجهگیری
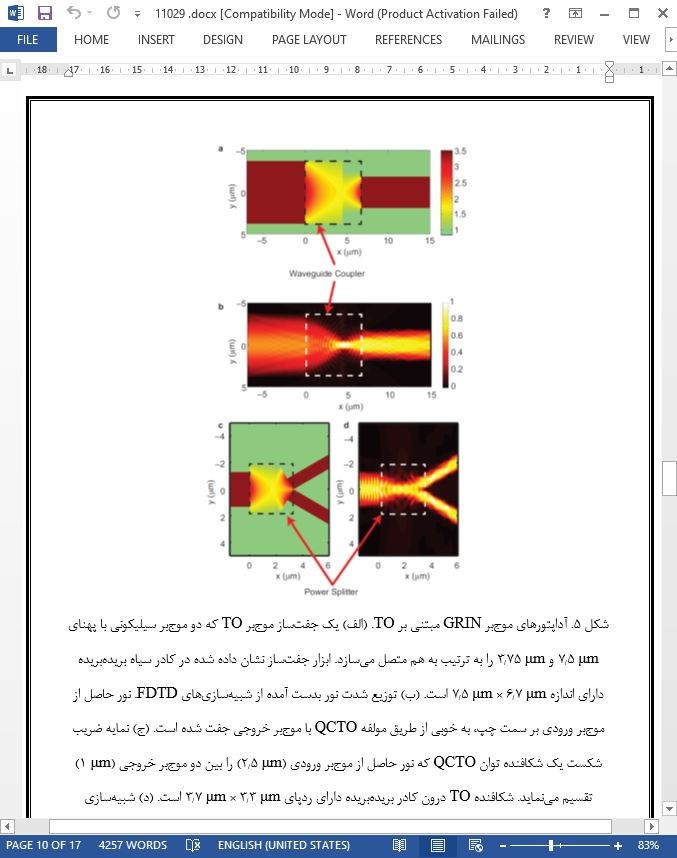
به طور خلاصه، چندین مولفه GRIN الهام گرفته از TO را با استفاده از شبیهسازیهای FDTD تمامموج برای سیستمهای فوتونیک مجتمع طراحی و ارائه نمودهایم. با استفاده از روش تبدیل QC الحاقی، ابزارهایی متشکل از مواد همسانگرد صرفاً دیالکتریک را ارائه نمودهایم. ثابت شده است که این اجزای TO در عین ارائه انعطافپذیری عمده در فرایند طراحی، توانایی جفتسازی موثر نور بین اجزای فوتونیکی همچون منابع نوری و موجبرها را میسر میسازد. این ابزارهای GRIN مبتنی بر TO با اتلاف اندک و محدوده عمل در گستره پهنباند دارای کاربردهای متعددی همچون ارتباطات نوری، رایانش و شناسایی است. روش طراحی ما و مثالهای ارائه شده، توان روش TO برای بهرهگیری از پتانسیل کامل اپتیک GRIN به منظور پیشبرد ابزارهای نوری عملی و سیستمهای فوتونیک مجتمع را نشان میدهد.
Integrated photonics is expected to play an increasingly important role in optical communications, imaging, computing and sensing with the promise for significant reduction in the cost and weight of these systems. Future advancement of this technology is critically dependent on an ability to develop compact and reliable optical components and facilitate their integration on a common substrate. Here we reveal, with the utility of the emerging transformation optics technique, that functional components composed of planar gradient index materials can be designed and readily integrated into photonic circuits. The unprecedented design flexibility of transformation optics allows for the creation of a number of novel devices, such as a light source collimator, waveguide adapters and a waveguide crossing, which have broad applications in integrated photonic chips and are compatible with current fabrication technology. Using the finite-difference time-domain method, we perform full-wave numerical simulations to demonstrate their superior optical performance and efficient integration with other components in an on-chip photonic system. These components only require spatially-varying dielectric materials with no magnetic properties, facilitating low-loss, broadband operation in an integrated photonic environment.
INTRODUCTION
Transformation optics (TO) provides a systematic method to manipulate light propagation by exploiting spatial mappings and distributions of constituent materials.1,2 Based on the property that Maxwell’s equations are invariant under coordinate transformations, TO represents a powerful new design tool in controlling the trajectory of light and creating novel devices, such as invisibility cloaks,3 field concentrators4 and perfect ‘black hole’ absorbers.5 The important class of embedded coordinate transformations6 stands out by allowing discontinuities along transformation media boundaries. This unique property has facilitated the development of some of the more practical, but nonetheless remarkable TO devices, including reflectionless beam bends and splitters,7 polarization rotators8 and various flat lenses.9–11
CONCLUSIONS
In summary, we have designed and demonstrated several TO-inspired GRIN components for integrated photonic systems using full-wave FDTD simulations. An embedded QC transformation approach is employed, yielding devices comprised of isotropic, dielectric-only materials. These TO components were shown to be able to achieve efficient light coupling between photonic elements, such as optical sources and waveguides, while exhibiting great design flexibility. Such TO-based GRIN devices, with low losses and broadband operation, have a wide range of applications including optical communications, computing and sensing. Our design approach and examples illustrate the power of the TO methodology to bring GRIN optics into their full potential for advancing practical optical devices and integrated photonic systems.
مقدمه
مواد و روشها
نتایج و بحث
نتیجهگیری
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه