ارزیابی گزینه های مختلف برای افزایش دمای کوره واکنش در Claus SRU
چکیده
کاربرد گزینههای مختلف در افزایش دمای کوره واکنش در واحدهای بازیابی سولفور Claus (SRUs) با محاسبات تعادل شیمیایی موردبررسی قرار گرفت. روش کمینهسازی انرژی آزاد گیبس بر اساس ضرایب لاگرانژ برای فرمولبندی مسئله استفاده شد. کارایی روشهای مختلف مانند افزودن گاز سوختی، پیشگرمایش گاز اسیدی و یا هوای غیرمستقیم، غنیسازی اکسیژن، غنیسازی گاز اسیدی و پیشگرمایش هوای مستقیم برای افزایش دمای کوره توسط الگوریتم ارائهشده تعیین میشود. در مورد گازهای اسیدی تغذیهای سبک، ممکن است کاربرد ترکیبی از روشها لازم باشد تا حداقل دمای کوره موردنیاز برای پایداری کوره و تخریب کامل آلایندههای هیدروکربنی گازی اسیدی به دست آید. هنگامیکه جریان زیادی از گاز اسیدی بسیار سبک در یک واحد Claus فرآوری شود، غنیسازی گازی اسیدی روشی مطمئن برای ارائه دمای موردنیاز واکنش کوره است. دماهای واکنش کوره پیشبینیشده سازگاری خوبی با مقادیر تجربی اندازهگیری شده دارد. _ 2007 Elsevier Ltd. تمام حقوق محفوظ است.
1. مقدمه
فرآیند Claus همچنان بهطور گستردهای در سراسر جهان برای تولید سولفور عنصری از سولفید هیدروژن گازی استفاده میشود [1]. الزامات برآورده شده توسط کارخانههای Claus با شرایط کاری در پالایشگاههای پیشرفته و کارخانههای گاز طبیعی و قوانین کنترل انتشار سختگیرانه مشخص میشوند.
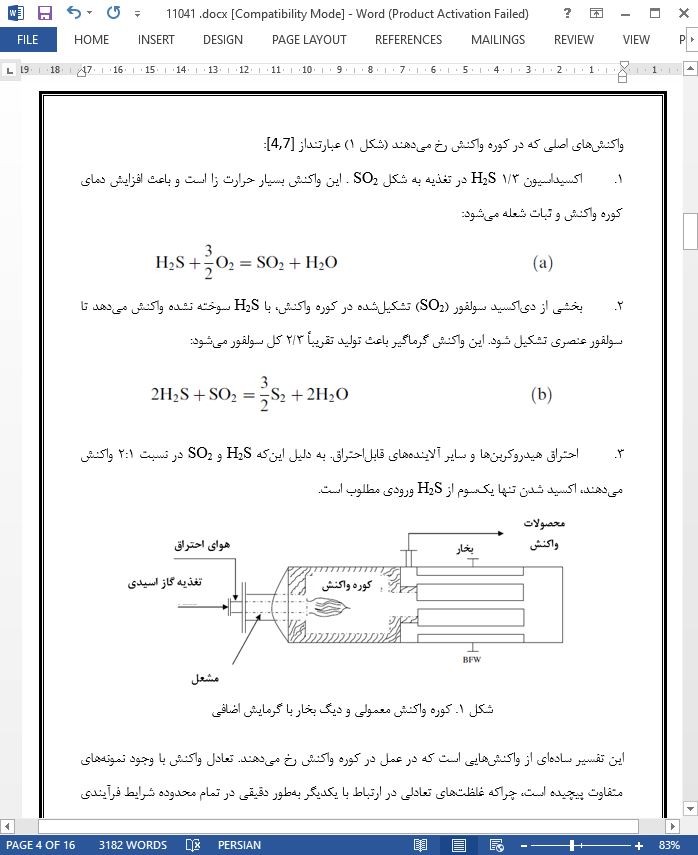
چند تغییر در فرآیند Claus اصلی بهمنظور بهکارگیری محدوده وسیعی از ترکیبات گازی تغذیهای ایجادشده است [1,7,12]. عملیات مستقیم منجر به بالاترین بازده بازیابی کلی سولفور میشود و در صورت امکان انتخاب میشود. هوا توسط دمنده تأمین میشود و احتراق در فشار 2-1 بار انجام میشود، بسته به اینکه آیا یک واحد عملیات گاز مازاد در پاییندست کارخانه Claus نصبشده است یا نه.
9. نتیجهگیری
بسیاری از واحدهای بازیابی سولفور Claus از ثبات شعله ضعیف و تخریب هیدروکربنی در کوره واکنش ناشی از دمای پایین کوره واکنش رنج میبرند. این معمولاً نشانهای از کیفیت ضعیف تغذیه گاز اسیدی است. بهمنظور حل این مشکل، چند روش تجاری مطمئن در دسترس برای افزایش دمای کوره مانند افزودن گاز سوختی، پیشگرمایش گاز اسیدی و هوا، پیشگرمایش مستقیم هوای گاز سوختی، غنیسازی اکسیژن و غنیسازی گاز اسیدی توسط محاسبات تعادل شیمیایی مورد ارزیابی قرار گرفتند. روش حداقل انرژی آزاد گیبس برای پیشبینی همزمان دمای کوره واکنش و سرعت بهینه جریان هوا در واحدهای بازیابی سولفور Claus در شرایط کاری مختلف استفاده شد و نتایج پیشبینیشده با دادههای تجربی مقایسه شدند.
Abstract
Application of different alternatives for increasing the reaction furnace temperature of Claus sulfur recovery units (SRUs) are investigated by chemical equilibrium calculations. The Gibbs free minimization method based on Lagrangian multipliers is used for formulating the problem. The usefulness of different techniques such as fuel gas spiking, indirect air and/or acid gas preheating, oxygen enrichment, acid gas enrichment and direct air preheating for increasing the furnace temperature are determined by the proposed algorithm. In the case of lean feed acid gases, it may be necessary to use a combination of methods in order to attain the minimum furnace temperature required for flame stability and complete destruction of acid gas hydrocarbon contaminants. It is found that the acid gas enrichment is a reliable technique for providing the required reaction furnace temperature when a high flow of too lean acid gas is to be processed in a Claus unit. The predicted reaction furnace temperatures are in good agreement with the measured experimental values.
1. Introduction
The Claus process continues to be the most widely used process worldwide for the production of elemental sulfur from gaseous hydrogen sulfide [1]. The requirements to be met by Claus plants are dictated by the operating conditions of modern refineries and natural gas plants and increasingly stringent emission control regulations.
Several variations of the basic Claus process have been developed to handle a wide range of feed gas compositions [1,7,12]. Straight-through operation results in the highest overall sulfur recovery efficiency and is chosen whenever feasible. Air is supplied by blower and the combustion is carried out at 1–2 bar, depending on whether or not a tail gas treatment unit is installed downstream of the Claus plant.
9. Conclusions
Many Claus sulfur recovery units suffer from poor flame stability and hydrocarbon destruction in the reaction furnace due to a low reaction furnace flame temperature. This is normally a symptom of poor acid gas feed quality. In order to mitigate this problem, several commercially viable techniques available for increasing the furnace temperature such as fuel gas spiking, air and acid gas preheating, direct fuel gas air preheating, oxygen enrichment and acid gas enrichment are evaluated by chemical equilibrium calculations. The Gibbs free minimization method is used for simultaneous prediction of reaction furnace temperature and optimum air flow rate of Claus sulfur recovery units at different operating conditions and the predicted results are compared with experimental data.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدلسازی
3. نتایج و بحث
4. افزودن گاز سوختی
5. پیشگرمایش گاز اسیدی و هوای غیرمستقیم
6. مشعل پیشگرمایش گاز سوختی مستقیم
7. غنیسازی اکسیژن
8. غنیسازی گاز اسیدی
9. نتیجهگیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling
3. Results and discussion
4. Fuel gas spiking
5. Indirect air and acid gas preheat
6. Direct fuel gas preheat burner
7. Oxygen enrichment
8. Acid gas enrichment
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه