رفتار سایش لغزشی کامپوزیت های اپوکسی شیشه E / MWCNT
چکیده
این تحقیق خواص سایش لغزشی کامپوزیتهای اپوکسی شیشهای E / MWCNT (نانولوله کربنی چند ضلعی) و کامپوزیت اپوکسی / MWCNT را ارزیابی کرده است. چهار نوع مختلف تقویت کننده (0، 5/0، 1 و 5/1 درصد وزنی) از MWCNT در یک رزین اپوکسی پراکنده میشود. طراحی آزمایش (DOE) و تجزیه و تحلیل انحراف معیار (ANOVA) برای درک رابطه بین عوامل کنترل (درصد تقویت، فاصله لغزش، سرعت لغزش و نیروی عمود) و معیارهای پاسخ (سرعت سایش ویژه و ضریب اصطکاک) مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند. متغیرهای کنترل از قبیل فاصلهی لغزش (300، 600، 900 و 1200 متر) و بارهای عمود 10، 15، 20 و 25 نیوتن و سرعت کششی 1، 2، 3 و 4 متر بر ثانیه، برای این مطالعه انتخاب شدهاند. مشاهده شده است که میزان سایش ویژه و ضریب اصطکاک میتواند با افزودن MWCNT کاهش یابد. تصویر برداری میکروسکوپ الکترونی (SEM) برای مشاهده سطوح فرسوده نمونهها استفاده میشود. در مقایسه با اپوکسی خالص، کامپوزیتهای حاوی MWCNT درصد کاهش جرم، ضریب اصطکاک و نرخ سایش کمتری را نشان دادند. بررسی میکروسکوپی سطح شکستگی نمونههای فرسوده نشان میدهد که واکنشهای فیبر نوری زمانی اتفاق میافتد که تنشها در سطح تماس ماتریس فیبر بیش از مقاومت بین فاز باشد، و فیبر را از ماتریس جدا کند. متغیرهای کنترل بهینه برای کاهش ضریب سایش و اصطکاک کامپوزیتها به دست آمدهاند.
1. مقدمه
پلیمرها [1-5] بهویژه کامپوزیتهای اپوکسی شیشهی E، به علت خواص فیزیکی و مکانیکی بالا مانند مقاومت فشاری بالا، مدول الاستیسیته و چگالی کم، بهعنوان مواد کاندیدای بالقوه برای کاربردهای مختلف تریبولوژیک در نظر گرفته میشوند. خواص مکانیکی قابل توجه نانولولههای کربنی (CNTs) الهام بخش محققان برای تولید کامپوزیت با ترکیب CNTها و ماتریکس بوده است. بهتازگی برخی از محققان [1-5] در مورد عملکرد سایش کامپوزیتهای شیشهی E / اپوکسی گزارش دادهاند. محققان کارهای کمی برای توصیف سایش لغزشی کامپوزیتهای بر پایهی CNT انجام دادهاند. وانگ و همکاران [6] رفتار مکانیکی و تریبولوژیکی ترکیب PA66 / UHMWPE با سازگاری را مطالعه کردند. نتایج نشان داد که اضافه کردن UHMWPE سرعت سایش را کاهش میدهد. فریدریش و پایپ [7] رفتار سایشی ساینده از اپوکسی تقویت شده با کربن، شیشه و آرامید را مورد مطالعه قرار دادند. هارشا و تواری [8] رفتار سایش ساینده برشی و سایش سه جسمی کامپوزیتهای پلی آریل اتر کتون را گزارش کردند.
4. نتیجه گیری
نتیجه گیریهای زیر به دست آمدهاند:
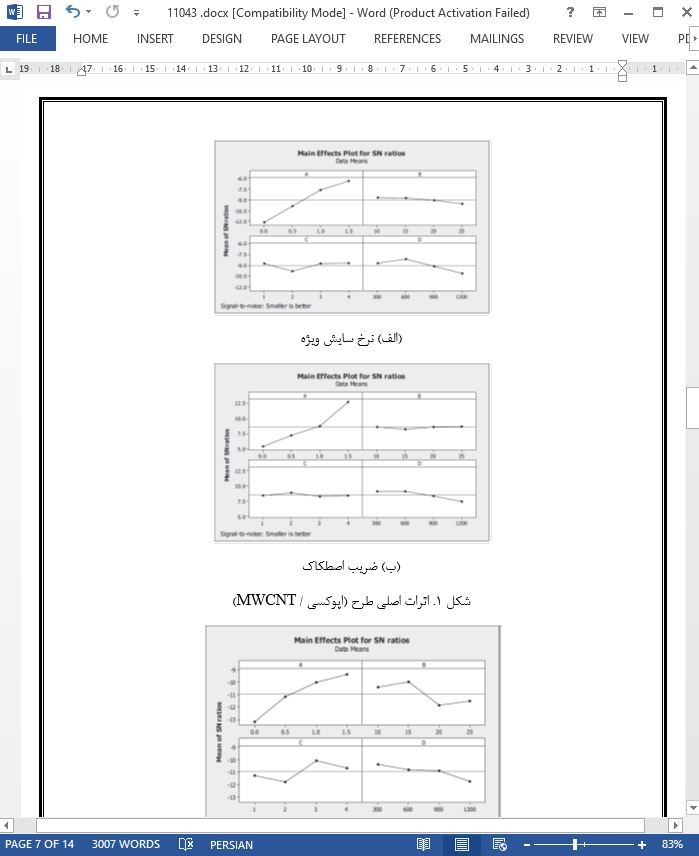
1. افزودن MWCNT به ماتریکس اپوکسی بهطور قابل توجهی باعث افزایش رفتار سایش لغزشی آن میشود. درصد تقویت کننده تنها بر میزان سایش ویژه و ضریب اصطکاک در هر دو این کامپوزیت تأثیر بسزایی دارد.
2. برای هر دو نوع کامپوزیت (اپوکسی - MWCNT و اپوکسی شیشهی E / MWCNT) روشن است که سرعت سایش ویژه با افزایش درصد MWCNT کاهش مییابد.
3. بررسی میکروسکوپی سطح شکستگی نمونههای فرسوده شده نشان میدهد که خروج و انفصال فیبر زمانی رخ میدهد که تنشها در سطح تماس ماتریس فیبر بیش از مقاومت بین فاز باشد، و فیبر را از ماتریس جدا کند.
4. متغیرهای کنترل بهینه برای کاهش ضریب سایش و اصطکاک کامپوزیتها به دست آمدهاند.
5. نتایج ANOVA نشان میدهد که فاصلهی لغزش، سرعت لغزش و نیروی عمودی برای هر دو کامپوزیت اپوکسی / MWCNT و اپوکسی شیشهی E / MWCNT کمتر است.
Abstract
This investigation has evaluated the sliding wear properties of E-glass-epoxy/MWCNT (multiwalled carbon nanotube) composite and Epoxy/MWCNT composite. Four different reinforcements (0, 0.5,1 and 1.5 wt %) of MWCNTs are dispersed into an epoxy resin. Design of experiments (DOE) and Analysis of variance (ANOVA) are employed to understand the relationship between control factors (Percentage of reinforcement, Sliding distance, Sliding velocity and Normal load) and response measures (specific wear rate and friction coefficient). The control variables such as sliding distance (300, 600, 900 and 1200 m) and normal loads of 10, 15, 20 and 25 N and at sliding velocities of 1, 2, 3 and 4 m/s are chosen for this study. It is observed that that the specific wear rate and friction coefficient can be reduced by the addition of MWCNTs. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is used to observe the worn surfaces of the samples. Compared with neat epoxy, the composites with MWCNTs showed a lower mass loss, friction coefficient and wear rate and these parameters decreased with the increase of MWCNT percentage. Microscopic investigation of worn out sample fracture surface has revealed that fiber debonding happens when the stresses at the fiber matrix interface exceeds the interfacial strength, causing the fiber to debond from the matrix. The optimum control variables have been derived to reduce both wear and friction coefficient of composites.
1. Introduction
Polymers [1–5] particularly E-glass epoxy based composites are considered as potential candidate materials for various tribological applications [2–4] due to their superior physical and mechanical properties such as high compressive strength, elastic modulus and low density. The remarkable mechanical properties of the carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have inspired the researchers to produce composites by combined CNTs with matrix. Recently, some researchers [1–5] have reported regarding the wear performance of E-glass/ epoxy composites. Very little work has been done by researchers to describe the sliding wear of CNT based composites. Wang et al. [6] studied the mechanical and tribological behavior of the blend of PA66/UHMWPE with compatibilizer. The results showed that the addition of UHMWPE reduced the wear rate. Friedrich and Pipes [7] studied the abrasive wear behavior of epoxy reinforced with carbon, glass and aramid fabrics. Harsha and Tewari [8] reported the two-body and three-body abrasive wear behavior of polyaryletherketone composites.
4. Conclusions
The following conclusions are drawn:
1. The inclusion of MWCNTs to the epoxy matrix considerably enhances its sliding wear behavior. Percentage of reinforcement has only significant effect on specific wear rate and friction coefficient in both these composites.
2. It is clear, for both types of composites (Epoxy–MWCNT and E-glass-epoxy/MWCNT) that the specific wear rate decreases with increase of percentage of MWCNT.
3. Microscopic investigation of worn out sample fracture surface has also revealed that fiber debonding and fiber pullout happens when the stresses at the fiber matrix interface exceed the interfacial strength, causing the fiber to debond from the matrix.
4. The optimum control variables have been derived to reduce both wear and friction coefficient of composites. 5. The ANOVA results reveal that Sliding distance, Sliding velocity and Normal load are less significant for both Epoxy/MWCNT composites E glass-epoxy/MWCNT composites.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. جزئیات آزمایش
1.2 مواد و روشها
2.2 دستگاه آزمایش
3.2 روش تاگوچی : طراحی آزمایشات
4. نتیجه گیری
ABSTRACT
1. Introduction
2. Experimental details
2.1. Materials and methods
2.2. Test apparatus
2.3. Taguchi method: design of experiments
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه