طراحی ایزوله سازی ارتعاش برای غشاهای تقویت شده پریودیک با روش المان محدود Wave
چکیده
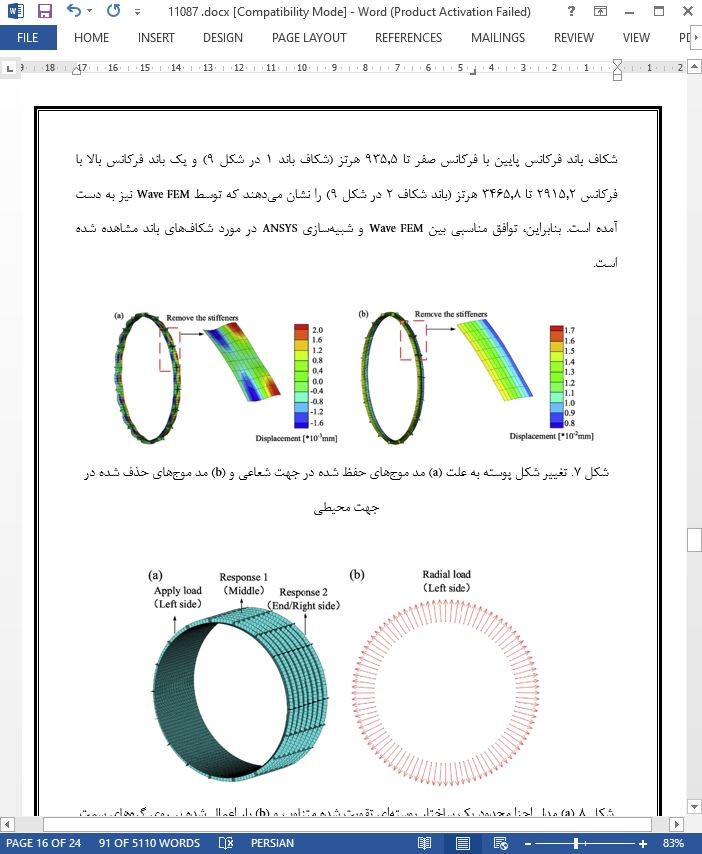
سازه های غشائی سخت شده به دلیل قدرت ویژه و منحصر بفرد خود، به ویژه در اجزای مربوط به صنعت هوا-فضا پیوسته مورد استفاده قرار می گیرند. این مقاله یک روش المان محدود Wave اصلاح شده را ارائه می دهد که می-تواند به طور موثری برای پیش بینی ویژگی های شکاف باند در ساختارهای پوسته ای سخت شده مورد استفاده قرار گیرد. برای تأیید اعتبارسنجی و کارایی Wave FEM، یک پوسته موتور هواپیما، که معمولایک سازه غشایی تقویت شده است، مورد استفاده قرار گرفت. توافق مناسب بین روش المان محدود موجی و روش المان محدود کلاسیک برای شرایط مرزی مختلف یافت شد. بدین ترتیب بر اساس Wave FEM، یک روش موثر جهت انتخاب موج به منظور فیلتر کردن مدهای شعاعی یک ساختار غشائی ارائه شده است. علاوه بر این، یک استراتژی بهینه با ترکیبی از Wave FEM و الگوریتم ژنتیک برای ساختارهای پوسته ای تقویت شده پریودیک ارائه شده است. شکاف باند مطلوب خارج از صفحه و جرم کل ساختار می تواند با استراتژی بهینه سازی تحت یک بار آیرودینامیکی به دست آید. نتایج همچنین نشان دادندکه پارامترهای هندسی تقویت کننده ها می توانند به صورتی انتخاب شوند که ارتعاش خارج از صفحه را بطور قابل توجهی در نوار فرکانسی مطلوب کاهش دهند. این مطالعه می تواند رفرنس ارزشمندی برای طراحی شکاف باند در ایزوله سازی ارتعاش ارائه دهد.
1. مقدمه
سازه های پوسته ای نازک به طور گسترده ای برای کاهش وزن در سیستم های مکانیکی مدرن، مخصوصا در صنعت هوا فضا استفاده می شوند. تقویت کننده ها معمولا رفتار مکانیکی ساختارهای پوسته ای نازک را با تشکیل یک ساختار خاص با استحکام بیشتر بهبود می دهند، با این حال، یک سازه پوسته ای سخت شده همچنان نسبت به ارتعاشات حساس است. از بین بردن ارتعاشات با توجه به مدهای طبیعی مربوط به سازه، خصوصا در محدوده فرکانسی بالا، همواره دشوار است. در کاربردهای مهندسی، ممکن است به علت ارتعاش، رزونانس تشدید رخ داده و منجر به آسیب های شدید در ماشین ها شود.
5. نتیجه گیری ها
یک روش بهبود یافته Wave FEM با در نظر گرفتن دقیق شرایط مرزی و گره های داخلی در یک مختصات استوانه-ای با معرفی ایده انتخاب موج ارائه شده است. بنابراين ويژگي هاي شکاف باند پوسته تقویت شده پریودیک را مي-توان به طور موثر به دست آورد. روش بهینه سازی GA برای طراحی یک پوشش فن استفاده شد. پارامترها بهینه شدند، به طوری که موج در گستره وسیعی از فرکانس های مربوط به پهنای باند محدود نمی شود. روش ایزولاسیون ارتعاش در این مقاله می تواند یک مرجع برای کاربرد عملی در طراحی بهینه سازی پوسته های تقویت شده باشد.
Abstract
Periodically stiffened shell structures are widely used due to their excellent specific strength, in particular for aeronautical and astronautical components. This paper presents an improved Wave Finite Element Method (FEM) that can be employed to predict the band-gap characteristics of stiffened shell structures efficiently. An aero-engine casing, which is a typical periodically stiffened shell structure, was employed to verify the validation and efficiency of the Wave FEM. Good agreement has been found between the Wave FEM and the classical FEM for different boundary conditions. One effective wave selection method based on the Wave FEM has thus been put forward to filter the radial modes of a shell structure. Furthermore, an optimisation strategy by the combination of the Wave FEM and genetic algorithm was presented for periodically stiffened shell structures. The optimal out-of-plane band gap and the mass of the whole structure can be achieved by the optimisation strategy under an aerodynamic load. Results also indicate that geometric parameters of stiffeners can be properly selected that the out-of-plane vibration attenuates significantly in the frequency band of interest. This study can provide valuable references for designing the band gaps of vibration isolation.
1. Introduction
Thin shell structures have been widely used to reduce weight for modern mechanical systems, in particular for aeronautical and astronautical components Stiffeners are usually employed to improve the mechanical behaviour of thin shell structures, via forming a higher specific-strength structure, however, a stiffened shell structure is still susceptible to vibration. It is always difficult to suppress vibration due to natural modes inherent to the structure, in particular in the high frequency range. In engineering applications, the intense resonance may occur due to vibration and lead to severe hazards to machines [1e3].
5. Conclusions
An improved Wave FEM method has been put forward by considering the boundary and the internal nodes accurately in a cylindrical coordinate and by introducing a wave selection idea. Therefore the vibration band-gap characteristics of the stiffened periodic shell can be achieved efficiently. The optimisation method GA was adopted for the design of a fan casing. The configuration parameters are optimised so that the wave does not span across the concerned broad frequency range. The vibration isolation method developed in this article can provide a reference for the practical application on the optimisation design of the stiffened shells.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. تئوری موج و روش Wave FEM
2-1 قضیه Bloch و ناحیه Brillouin
2-2 روش Wave FEM
3. انتخاب موج
3-1 روش
3-2 تایید
4. بهینه سازی عددی
4-1 پارامترهای بهینه سازی و اهداف
4-2 الگوریتم بهینه سازی (الگوریتم ژنتیک)
4.3. طراحی شکاف باند
4-4 شبیه سازی و تأیید
5. نتیجه گیری ها
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Wave theory and wave FEM
2.1. Bloch theorem and Brillouin zone
2.2. Wave FEM
3. Wave selection
3.1. Method
3.2. Verification
4. Numerical optimisation
4.1. Optimisation parameters and aims
4.2. Optimisation algorithm (genetic algorithm)
4.3. Band-gap design
4.4. Simulation and verification
5. Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه