مقایسه مدیریت ریسک در بانک های خصوصی و موسسات مالی در مقایسه با سایر بانک ها
چکیده
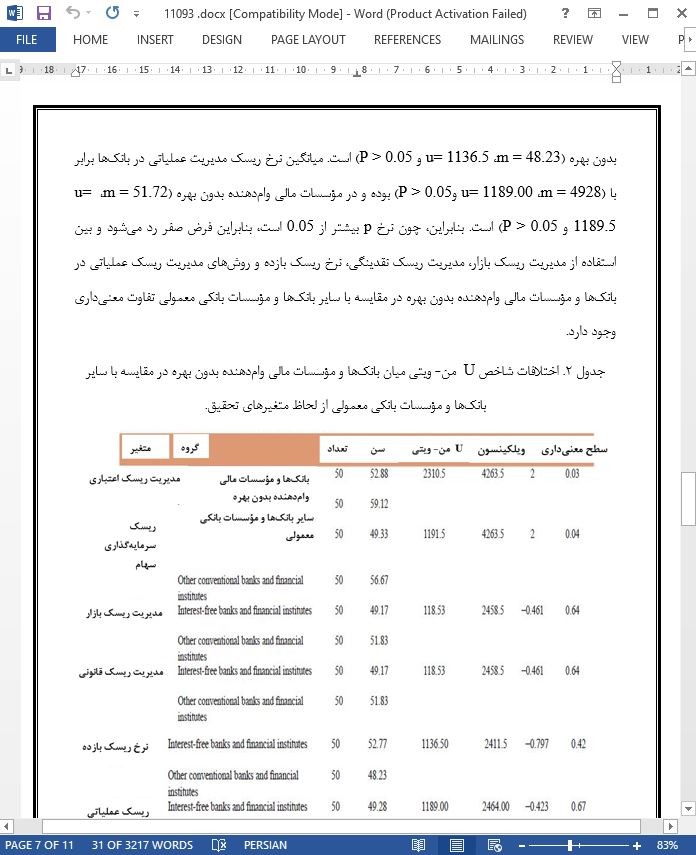
این مطالعه با هدف مقایسه تفاوتهای مدیریت ریسک در بانکها و مؤسسات مالی وامدهنده بدون بهره در مقایسه با سایر بانکها و مؤسسات مالی متعارف در ایران انجام شده است. این مطالعات از نظر معیارهای زمانی بر حسب تطبیقی و مقطعی (طولی- مقطعی) انجام شده است. پرسشنامه جوادی و قوچیفرد (2009) که توسط محقق ترجمه شده و مورد تأیید قرار گرفته است، برای جمعآوری دادهها مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. جمعیت شامل کلیه بانکها، مؤسسات مالی وامدهنده بدون بهره و سایر بانکها و مؤسسات مالی معمولی در ایران است. با توجه به تعداد محدود جمعیت (100 مؤسسه و بانک)، آن را به عنوان نمونه به دو گروه (بانک و مؤسسات مالی وامدهنده بدون بهره) تقسیم کردیم. نتایج تحقیق بر اساس آزمون U من- ویتی نشان میدهد که تفاوت قابل توجهی در استفاده از مدیریت ریسک اعتباری، سرمایهگذاری در سرمایه و مدیریت ریسک نقدینگی در بانکها، مؤسسات مالی وامدهنده بدون بهره و سایر مؤسسات مالی متعارف وجود دارد. اما تفاوت معنیداری در استفاده از مدیریت ریسک بازار، نرخ ریسک بازده و روشهای مدیریت ریسک عملیاتی در بانکها، مؤسسات مالی وامدهنده بدون بهره و سایر بانکها و مؤسسات مالی متعارف در ایران وجود ندارد.
1. مقدمه
بانکها با خطرات مختلفی روبرو هستند، اما خطرناکترین ریسک در حوزه مالی و بانکی، اعتبارات مالی است که به معنی از دست دادن سود به دلیل وامگیرندگان غیرمتعهد است. این خطر زمانی رخ میدهد که وامگیرنده به طور منظم قادر به پرداخت اصل و سود بدهی نباشد و یا از پرداخت بدهیها اجتناب کند (اداره کنترل ریسک بانک تجارت ، 2006). وام بیش از حد بدون ارزیابی و پیشبینی نشده منجر به افزایش مشتریان غیرقابل اعتماد و تعویق وامها میشود. بحران مالی (2007-2008) روشن کرد که درک ریسک از طریق بازارهای مالی برای توانمندسازی بانکها و افزایش مراکز جدیدشان بسیار مهم و ضروری است (سلتمن ، 2007).
4. بحث و نتیجهگیری
مطالعه حاضر با هدف مقایسه تفاوتهای مدیریت ریسک در بانکها و مؤسسات مالی وامدهنده بدون بهره در مقایسه با سایر بانکها و مؤسسات بانکی معمولی در ایران انجام شده است. نتایج نظریههای تحقیق نشان داد که در ریسک اعتباری بین بانکها و مؤسسات مالی وامدهنده بدون بهره در مقایسه با سایر بانکها و مؤسسات بانکی معمولی در ایران تفاوت معنیداری وجود دارد. نتیجه مشابه نتیجه شعبانی و راستخیز (2012) است که ریسکهای بانکی متداول و بانکداری بدون بهره را بر اساس قراردادهای اسلامی تحلیل کردهاند و هیچ تفاوت معنیداری بین قوانین بانکداری معمولی و قوانین بانکداری بدون بهره گزارش نکردهاند، به جز دو مورد: ریسک نقدینگی و ریسک عملیاتی. قادری ، چارفیدن و یوسف (2015)، بانکداری اسلامی و بانکداری سنتی را در کشورهای شورای همکاری خلیج فارس مورد بررسی قرار داده و نشان دادند که بانکداری اسلامی دارای متوسط سود بیشتر و کمترین میزان اعتبار است.
ABSTRACT
This present study has been done to compare risk management differences in banks and interest-free loan financial institutes with other conventional banks and financial institutes of Iran. This study is descriptive-comparative and cross-sectional in terms of time criteria (longitudinal - cross sectional). The questionnaire by Javadi and Qouchifard (2009), which translated and validated by researcher, was used to collect data. Population consisted of all banks, interest-free loan financial institutes and other conventional and financial institutes of Iran. Due to limited number of population (100 institutes and banks), it was divided in two groups (banks and interest-free loan financial institutes) as samples. Research results based on U Mann-Whitney Test showed that there were remarkable differences in using credit risk management, capital investment on stocks and liquidity risk management in banks, interest-free loan financial institutes and other conventional banks and financial institutes. But there were no significant differences in using market risk management, return risk rate, and methods of operational risk management in banks, interest-free loan financial institutes and other conventional banks and financial institutes of Iran.
1. INTRODUCTION
Banks face with various risks but the most dangerous one is credit risk in financial and banking area which means losing profit due to non-committed borrowers to its contract. The risk happens when the borrower is not able to pay principal and interest of Debt regularly or avoid to pay debts (Tejarat Bank Control Risk Administration, 2006). Excessive loan with no assessment and predictions have been led to increasing non-credit worthy customers and deferred loans. Financial crisis (2007-2008) made it clear that for banks capabilities and increasing their new capitals, it is very important and vital to understand the risk through financial markets (Seltman, 2007).
4. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
The present study has been done to compare the differences between risk management in banks and interest-free loan financial institutes with other banks and conventional financial institutes of Iran. The results of research theories showed that there is significant difference between credit risk management in banks and interest-free loan financial institutes and other banks and conventional financial institutes of Iran. The result is similar to the previous research results by Shabani and Rastkhiz (2012) that have been analyzed the risks of conventional banking and interest-free banking based on Islamic contracts, and they reported no significant difference in conventional banking risks and interest-free banking risks, except two cases: Liquidity risk and operational risk. Qaderi, Charfedin and Youssef (2015), studied about Islamic banking and traditional banking in countries of Persian Gulf Cooperation Council and showed that Islamic banking has more profit and less credit risk in average.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روش
3. نتایج
4. بحث و نتیجهگیری
ABSTRACT
1. INTRODUCTION
2. METHODOLOGY
3. RESULTS
4. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSION
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه