کنترل تطبیقی سامانه های مرتبه کسری، با استفاده از روش فازی T-S
چکیده
به دلیل توانایی برترِ معادلات تفاضلی در مدلسازی و توصیف مشخصات دینامیکی دقیقِ بسیاری از سامانههای دنیای واقعیِ دارای فناوریِ بالا، طراحی و کنترل سامانههای مرتبهکسری، در دهههای اخیر توجه زیادی را به خود معطوف کرده است. در مقالهی حاضر، یک رویکرد فازی تطبیقیِ هوشمند را به منظور کنترل و باثباتسازیِ سامانههای مرتبهکسریِ غیرمستقل غیرخطی مطرح میسازیم. از آنجا که معادلات دینامیکِ سامانههای مرتبهکسریِ بکاررفته، معمولاً حاوی پارامترها و عبارت غیرخطیِ متعددی هستند، مدلهای فازی تاکاگی-سوگنو (T-S) با قواعد «اگر-آنگاه» اتخاذ میشوند تا دینامیکهای سامانه را شرح دهند. همچنین از آنجا که پارامترهای سامانه غیرخطی نامشخص هستند، قوانین تطبیقی را به منظور برآورد این قبیل نواسانات استخراج میکنیم. قواعد سادهی کنترل شِبهخطیِ تطبیقی، بر مبنای نظریهی کنترل فازی T-S شکل میگیرند. پایداری سامانهی لوپ بستهیِ حاصله را نظریهی پایداری لیاپونوف تضمین میکند. دو مثال عددی توصیفی را به منظور تاکید بر عملکرد و کاربردپذیریِ صحیح روششناسی کنترل فازیِ تطبیقی پیشنهادی، ارائه میدهیم. لازم به ذکر است که کنترل پیشنهادی ما، برای پایدارسازی گروه وسیعی از سامانههای مرتبهکسریِ غیرقطعیِ خطیِ مستقل یا سامانههای پیچیدهی غیرمستقل با پارامترهای نامشخص، موثر هست.
1. مقدمه
حساب مرتبهکسری (FO) پیشینهای و تاریخچهای سهقرنه دارد و در سالهای اخیر توجه زیادی را در زمینه فیزیک و مهندسی به خود معطوف داشته است. امروزه مشخص شده است که با استفاده از معادلات تفاضلیِ کسری و بسیاری از سامانههای دینامیکی در حوزههای کاربردیِ مختلف نظیر بیولوژی، فیزیک و الکترومکانیک و علوم اجتماعی، ماهیت بسیاری از پدیدههای واقعی را میتوان بهخوبی توصیف کرد.
5. نتیجه
در این مقاله، مسالهی کنترل و پایدارسازی سیستمهای مرتبهکسریِ نامستقل، مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. نخست اینکه مدلهای فازیِ هوشمندِ تاکاگی-سوجنو (تی-اس) با قواعد اگر-آنگاه، به این دلیل ساخته میشوند تا دینامیکهای سیستم را ارائه دهند. آنگاه یک رویکرد تطبیقی انتخاب میشود تا پارامترهای نامشخص و عدمقطعیتهای سیستم را برآورد نماید. در نتیجه، بر مبنای تکنیک کنترل فازی تی-اس و قضیهی پایداری لیاپونوف، قواعد کنترل شِبهخطیِ مرتبط با برخی از معیارهای بهره، فراهم شدند تا اطمینان یابیم که وضعیتهای سیستم با میلِ زمان به سمت بینهایت، به سمت صفر میل میکنند. پس از آن، کنترلرِ توسعهیافته، برای پایدارسازی گروهی بزرگ از سیستمهای نامستقلِ مرتبه کسری بکار میرود. دو نمونهی عددی نیز ارائه میشوند تا نتایج تحلیلیِ مقاله را معتبر سازد و نشان دهد که طرحهای تطبیقی طراحیشده، در کاربردهای دنیای واقعی انجامپذیرند. لازم به ذکر است که علیرغم اطلاعات محدودی که ما از پارامترهای متغیردرزمان و نامتغیردرزمان از سیستم داریم، نتایج این مقاله را میتوان برای کنترل سیستمهای مرتبه کسریِ دنیای واقعی، نظیر مدارهای الکتریکیِ مرتبه کسری و ابزارهای مکاترونیک، بکار برد. توسعهی نتایج این مقاله برای طراحی کنترلرهای فازی تی-اس برای سیستمهای مرتبه کسری با اشباع ورودی، همچنان پژوهشی است که نویسندگان باید در آینده انجام دهند.
Abstract
Owing to the superior capability of fractional differential equations in modeling and characterizing accurate dynamical properties of many high technology real world systems, the design and control of fractional-order systems have captured lots of attention in recent decades. In this paper, an adaptive intelligent fuzzy approach to controlling and stabilization of nonlinear non-autonomous fractional-order systems is proposed. Since dynamic equations of applied fractional-order systems usually contain various parameters and nonlinear terms, the Takagi–Sugeno (T–S) fuzzy models with if-then rules are adopted to describe the system dynamics. Also, as the nonlinear system parameters are assumed to be unknown, adaptive laws are derived to estimate such fluctuations. Simple adaptive linear-like control rules are developed based on the T–S fuzzy control theory. The stability of the resulting closed loop system is guaranteed by Lyapunov’s stability theory. Two illustrative numerical examples are presented to emphasize the correct performance and applicability of the proposed adaptive fuzzy control methodology. It is worth to notice that the proposed controller works well for stabilization of a wide class of either autonomous nonlinear uncertain fractionalorder systems or non-autonomous complex systems with unknown parameters.
1 Introduction
Fractional-Order (FO) calculus has a long history and a retrospect as long as three centuries, and it has attracted increasing attentions in physics and engineering in recent years [1–4]. Nowadays, it has been known that the nature of many real phenomena can be perfectly characterized and modeled using fractional differential equations and many dynamical systems in various applied fields, such as biology [5], medicine [6], physics [7, 8], electro-mechanics [9] and social sciences [10, 11].
5 Conclusions
In this paper, the problem of control and stabilization of uncertain non-autonomous fractional-order systems is investigated. First, the intelligent Takagi–Sugeno (T–S) fuzzy models with if-then rules are constructed to represent the system dynamics. Then, an adaptive approach is adopted to estimate the unknown parameters and uncertainties of the system. Subsequently, based on the T–S fuzzy control technique and Lyapunov’s stability theorem, linear-like control rules associated with some gain matrices provided to ensure that the system states will approach to zero as time goes infinite. After that, the developed controller is applied for stabilization of a large class of fractional-order non-autonomous systems. Two numerical examples are also presented to validate the analytical results of the article and to illustrate that the designed adaptive schemes are feasible in real world applications. It is worth to note that the results of this paper can be applied for control of real fractionalorder systems, such as fractional-order electrical circuits and mechatronic devices, in spite of having limited knowledge about the time-variant and time-invariant parameters of the system. Extending the results of this paper for design of T–S fuzzy controllers for fractional-order systems with input saturation remains as the future work of the authors.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مقدمات و توصیف سیستم
2.1 حساب کسری
2.2 مدل فازی تی-اس تعمیم یافته سیستم های مرتبه کسری
3. نتایج اصلی
4. نتایج شبیه سازی
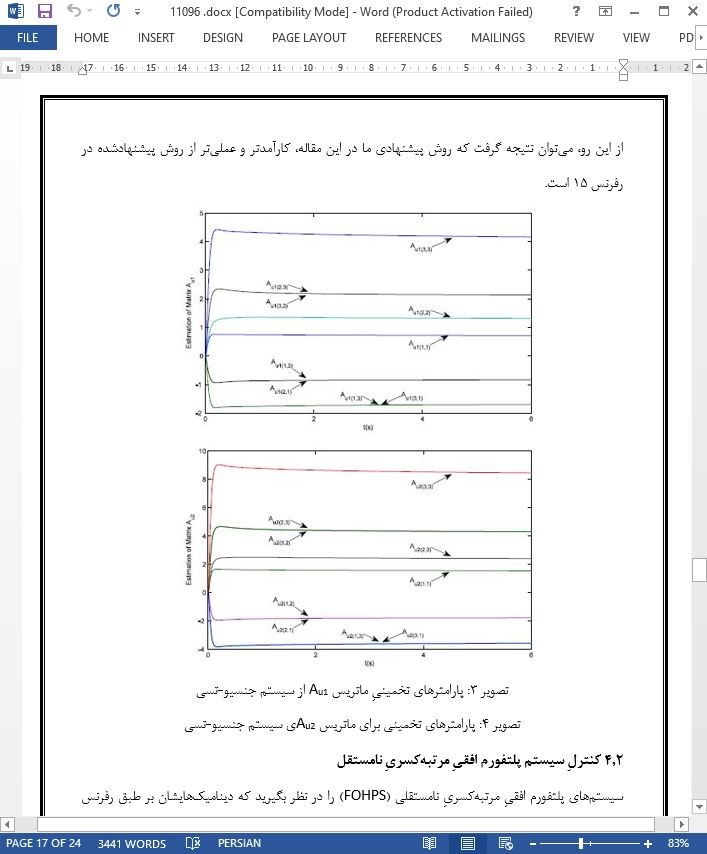
4.1 کنترل سیستم جنسیو-تسی مرتبه کسری مستقل
4.2 کنترل سیستم پلتفورم افقی مرتبه کسری نامستقل
5. نتیجه
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Preliminaries and system description
2.1 Fractional calculus
2.2 Generalized T–S fuzzy model of fractional-order systems
3 Main results
4 Simulation results
4.1 Control of autonomous fractional-order Genesio– Tesi system
4.2 Control of non-autonomous fractional-order horizontal platform system
5 Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه