تجزیه سه ماده ای با CT طیفی دو لایه ای در مقایسه با MRI برای تشخیص ادم مغز استخوان
چکیده
اهداف بررسی اینکه آیا ادم مغز استخوان در بیماران مبتلا به شکستگیهای حاد مهرهای را میتوان بصورت درست با تجزیه سه مادهای با CT طیفی دو لایهای تشخیص داد.
مواد و روش کار شکستگیهای حاد (n = 41) و مزمن (n = 18) مهرهای کمری سینهای ناشی از پوکی استخوان که در 27 نفر (72 ± 11 سال؛ 17 خانم) که از طریق MRI (سیگنال پر شدت در توالیهای STIR) تشخیص داده شده بود با DCLT بررسی شد. دادههای طیفی با استفاده از یک الگوریتم که بصورت داخلی توسعه داده شد به نقشههای شدت هیدروکسی آپاتیت، معادل ادم و معادل چربی تجزیه شدند. دو رادیولوژیست که نسبت به یافتههای بالینی و MRI کور شدند، با استفاده از مقیاس لیکرت (بدون ادم 1=؛ احتمالاً بدون ادم 2 =؛ احتمالاً ادم 3=؛ ادم 4 = ) DLCT و CT مرسوم را بررسی کردند. صحت، حساسیت و ویژگی DLCT و CT مرسوم برای تشخیص شکستگیهای حاد (مقیاس لیکرت 3 و 4) بطور جداگانه با استفاده از MRI به عنوان یک استاندارد مرجع تحلیل شدند.
یافتهها: برای تشخیص شکستگیهای حاد، CT مرسوم حساسیت 0.73-0.76 و ویژگی 0.78-0.83 را نشان داد اما حساسیت (0.93 – 0.95) و ویژگی (0.89) تصاویر DLTC تجزیهای بطور قابل توجهی بالاتر بود. صحت برای CT مرسوم 0.76 بود که از همین مقدار تا 0.92-0.93 برای DLCT افزایش یافت. همسانی بین پویش برای ارزیابی شکستگی در CT مرسوم بالا بود (k وزنی [فاصله اطمینان 95%]؛ 0.81 [0.70;0.92] و DLCT (0.96[0.92;1.00])).
نتیجهگیری: تجزیه مادهای دادهها DLCT بطور قابل توجهی صحت و درستی تشخیص شکستگیهای حاد مهرهای را با همسانی بین پویشی بالا ارتقاء داد. این نتیجه ممکن است معاینات اضافی بیماران را کاهش داده و تشخیص شکستگیهای مهرهای را تسهیل کند.
مقدمه
شکستگیهای فشرده مهرهای از آسیبهای شایع در بیماران مبتلا به کاهش چگالی مواد معدنی استخوان (BMD) ناشی از پوکی استخوان به شمار میرود اما در بیماران فاقد پوکی استخوان که دچار تروما شدهاند نیز مشاهده میشود. شکستگیهای مهرهای با شیوع 26% در خانمها و 24% در مردان بالای 49 سال 32% احتمال مرگ را افزایش میدهد. مدیریت مناسب شکستگیها نه تنها به ارزشیابی درست مورفولوژیکی از جمله ارزیابی پایداری واحدهای متأثر بلکه به ارزشیابی درست سن شکستگی نیز بستگی دارد. اگر چه چندین معیار طبقهبندی مبتنی به CT وجود دارد، CT در مسیر معمول بالینی از لحاظ تعیین سن شکستگی فاقد صحت و درستی هست. بنابراین، تصویربرداری MR اغلب برای شناسایی تغییرات مغز استخوان معادل ادم صورت میگیرد که اختصاصاً تروماهای حاد را در نظر میگیرند. از این رو تصویر برداری با تعداد دفعات معاینات اضافی و هزینههای قابل توجه همراه بود و برخی از بیماران به دلیل منع استفاده مانند ضربانسازها، دیگر کاشتنیها و درد شدید برای این نوع از تصویربرداری واجد شرایط نیستند.
بحث
در مطالعه ما، تشخیص ادم مغز استخوان و بنابراین شناسایی بیماران مبتلا به شکستگیهای حاد مهرههای سینهای کمری با استفاده از تجزیه سه مادهای و نقشههای تراکم مخصوص مواد بدست آمده از CT طیفی دو لایه عملی بود. با استفاده از تصویربرداری MR به عنوان استاندارد مرجع صحت، حساسیت و ویژگی برای تشخیص شکستگیهای حاد مهرهای با تجزیه سه مادهای تولید شده از CT طیفی دو لایه در مقایسه با تصایر CT معمولی به طرز قابل توجهی بالاتر بود.
Abstract
Objectives To assess whether bone marrow edema in patients with acute vertebral fractures can be accurately diagnosed based on three-material decomposition with dual-layer spectral CT (DLCT).
Materials and methods Acute (n = 41) and chronic (n = 18) osteoporotic thoracolumbar vertebral fractures as diagnosed by MRI (hyperintense signal in STIR sequences) in 27 subjects (72 ± 11 years; 17 women) were assessed with DLCT. Spectral data were decomposed into hydroxyapatite, edema-equivalent, and fat-equivalent density maps using an in-house-developed algorithm. Two radiologists, blinded to clinical and MR findings, assessed DLCT and conventional CT independently, using a Likert scale (1 = no edema; 2 = likely no edema; 3 = likely edema; 4 = edema). For DLCT and conventional CT, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity for identifying acute fractures (Likert scale, 3 and 4) were analyzed separately using MRI as standard of reference.
Results For the identification of acute fractures, conventional CT showed a sensitivity of 0.73–0.76 and specificity of 0.78–0.83, whereas the sensitivity (0.93–0.95) and specificity (0.89) of decomposed DLCT images were substantially higher. Accuracy increased from 0.76 for conventional CT to 0.92–0.93 using DLCT. Interreader agreement for fracture assessment was high in conventional CT (weighted κ [95% confidence interval]; 0.81 [0.70; 0.92]) and DLCT (0.96 [0.92; 1.00]).
Conclusions Material decomposition of DLCT data substantially improved accuracy for the diagnosis of acute vertebral fractures, with a high interreader agreement. This may spare patients additional examinations and facilitate the diagnosis of vertebral fractures.
Introduction
Vertebral compression fractures are a common pathology found in patients with reduced bone mineral density (BMD) caused by osteoporosis [1], but also in otherwise healthy patients after adequate trauma. With a prevalence of up to 26% in women and 24% in men older than 49 years [1], vertebral fractures are associated with an age-adjusted 32% increased risk of mortality [2]. Adequate management of fractures not only depends on accurate morphologic assessment, including the evaluation of the stability of the affected spinal units, but also on accurate assessment of fracture age. Although several CT-based classification criteria for spine injuries exist [3], CT in clinical routine lacks accuracy regarding the determination of the age of vertebral fractures. Therefore, MR imaging is often performed to identify edema-equivalent bone marrow changes, which are considered highly specific for acute trauma [4–6]. However, MR imaging is associated with additional examination times and substantial costs, and some patients are not eligible due to contra-indications such as pacemakers, other implants, or severe pain.
Discussion
In our study, the detection of bone marrow edema, and thus the identification of patients with acute thoracolumbar vertebral fractures, was feasible using three-material decomposition and material-specific density maps calculated from duallayer spectral CT. The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity for the diagnosis of acute vertebral fractures was substantially higher with three-material decomposition generated from dual-layer spectral CT images compared to the conventional CT images, using MR imaging as standard of reference.
چکیده
مقدمه
روش کار
بیماران
پروتکل تصویربرداری CT و پسا پردازش
تحلیل تصویربرداری CT و تعیین سن شکستگی
تصویربرداری MR به عنوان استاندارد مرجع
تحلیل آماری
نتایج
بیماران و وضعیت شکستگی
عملکرد CT معمولی و طیفی دو لایه
بحث
Abstract
Introduction
Methods
Patients
CT imaging protocol and post-processing
CT imaging analysis and fracture age determination
MR imaging as standard of reference
Statistical analysis
Results
Subjects and fracture status
Performance of conventional and dual-layer spectral CT
Discussion
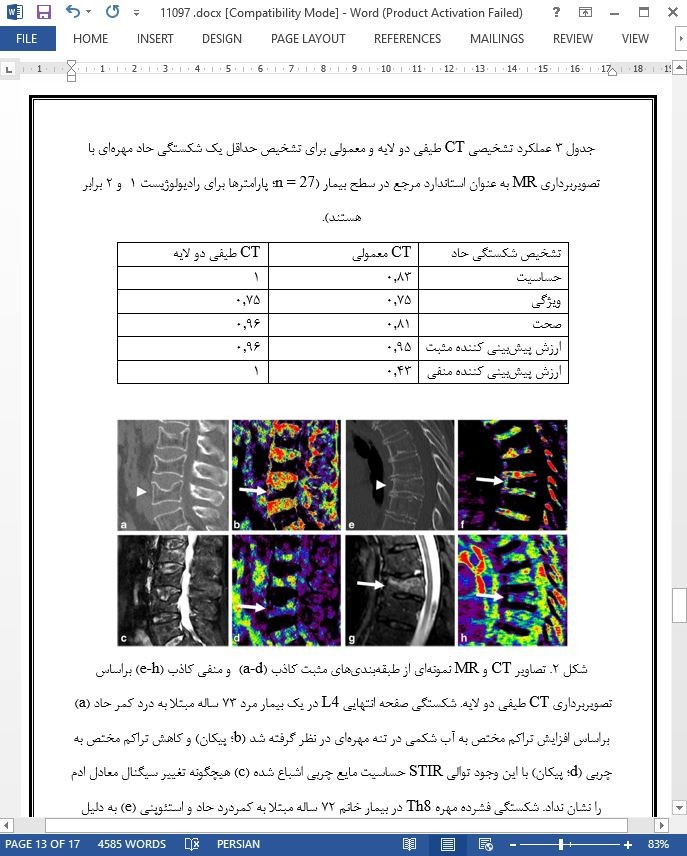
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه