سازه های بنایی محصور شده و غیرمسلح در مناطق لرزه ای
چکیده
طراحی سازه ای مدرن نیاز به در نظر گرفتن بخشهای پایداری از درک چرخه عمر و همچنین مرحله طراحی اولیه دارد که در آن اعمال ارتعاش تاثیر قابلتوجهی بر طراحی سازه دارند. در سالهای اخیر، ارزیابی لرزهای ساختمانهای بنایی با استفاده از روشهای مدلسازی آلمان بزرگ با استفاده از تکنیکهای ارزیابی مبتنی بر عملکرد با استفاده از روشهای بار جانبی غیر خطی (پوش اوور)متداول شدهاست. این مطالعه به تایید این روشها با اشاره به دو سازه ی بنایی مقیاس کامل تحت شرایط بارگذاری جانبی میپردازد. پاسخ بار جانبی سازههای بنایی مسلح نشده (URM)و سازه های بنایی محصور شده (CM) ازمایش شده با پاسخ مدلهای عددی مقایسه میشود. مدلهای عددی در نظر گرفتهشده توافق خوبی برای پیشبینی رضایتبخش پاسخ آزمایشی دارند و بنابراین میتوانند در ارزیابی مبتنی بر عملکرد مورد استفاده قرار گیرند. سپس، با اشاره به مسکن(خانه) ویژه شمال پاکستان و طراحی معمول آن با یک ساختمان بتن مسلح، مدلهای عددی معتبر برای برآورد پتانسیلهای مقاومت در برابر خطر گزینههای URM و CM برای گزینههای یک، دو و سه طبقه، به ویژه در رابطه با حداکثر ظرفیت بار جانبی مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند. پاسخ تغییر شکل - بار هر دو نوع سازه برای سه سطح طبقه ی مذکور مقایسه شد. مشاهده شد که با محصور کردن ظرفیت شکلپذیری سازه ی بنایی به طور قابلتوجهی افزایش مییابد در نتیجه، آن را برای استفاده در مناطق زلزلهخیز مناسبتر میسازد. سازههای بنایی نیز با توجه به هزینههای ساخت در مقایسه با نمونههای RC مقایسه میشوند. با توجه به خانههای مطالعه شده، رفتار بار جانبی پیشبینیشده برای سازههای بنایی نشاندهنده توانایی مقاومت کافی در برابر بارهای جانبی است. این سازه ها همچنین امکان کاهش قابلتوجه هزینهها (تا ۲۸ %)را در مقایسه با سازه های RC فراهم میکنند، از این رو به عنوان جایگزینهای چالش برانگیز ظاهر میشوند.
1. مقدمه
ساخت ساختمان تاثیر زیادی بر کل بودجه یک خانواده دارد. علاوه بر این، مردم بیشترین بخش زندگی (عمر) خود را در ساختمانها زندگی میکنند. سازههای با ارتفاع کم (سه طبقه یا کمتر)نوع رایج تری برای خانهها هستند که نیازمند توجه خاص در توسعه راهحلهای قابل کار برای ساخت آنها هستند. راهحل ساختوساز پذیرفتهشده، خود را به عنوان سرمایهگذاری اولیه ضروری برای ساختوساز خانه نشان میدهد و به عنوان تاکید(تمرکز) این مطالعه در نظر گرفته میشود.
5. نتایج
این مطالعه، مشارکت در طراحی و توسعه سازههای مقرونبهصرفه در نواحی لرزهای را پیشنهاد میکند. به همین دلیل، ابزار ارایهشده برای ارزیابی لرزهای سازههای مقاومسازی نشده (URM)و سازههای RC محصور شده به صورت آزمایشی اثبات و تایید میشوند. به طور کلی ، ابزار ارزیابی ارائه شده ، یک تخمین منطقی از منحنی ظرفیت حاصل از تحلیل بار جانبی ، بطور خاص سختی اولیه ، مقاومت نهایی و شکل پذیری ارائه می دهد ، از این رو در ارزیابی مبتنی بر عملکرد به اندازه کافی دقیق است. علاوه بر این ، نرم افزار اجازه شبیه سازی پیکربندی ساختمان های بنایی واقعی را با توجه به مورد اصلی مسکن های یک طبقه ، دو طبقه و سه طبقه می دهد. به منظور ارزیابی عملکرد مقاوم در برابر زلزله و ارزیابی هزینه ساخت سازه ی بنایی در مقایسه با سازههای RC معمولی، شبیهسازی انجام شدهاست.
Abstract
Modern structural design requires consideration of sustainability parts from a life cycle perception, but also the initial design phase in which seismic actions have a substantial influence on the design of the structure. In recent times, the seismic assessment of masonry buildings by means of macro-element modeling methodologies has become popular, by application of performance-based evaluation techniques using nonlinear lateral load procedures (Pushover). This study addresses the endorsement of these methodologies by referring to two full-scale brick masonry structures subjected to a lateral loading conditions. The lateral load response of tested unreinforced masonry (URM) and confined masonry (CM) structures is compared with the response of the numerical models. The considered numerical models have good agreement for satisfactorily predicting the response of the experimental test and hence are capable of being used in a performance-based evaluation. Then, pointing to the characteristic housing of northern Pakistan and its typical design with a reinforced concrete (RC) building, the validated numerical models are used to estimate the hazard-resistant potentials of the URM and CM options for one, two and three story options, particularly in relation with maximum lateral load capacity. The load deformation response of both the typologies was also compared for the mentioned three story levels. It was observed that by confining the masonry its ductility capacity increases considerably, hence making it more suitable to be used in earthquake prone regions. Masonry structures are also compared regarding the construction costs compared to the RC typology. With regard to the dwellings studied, the projected lateral load behavior for masonry structures indicate the ability to withstand lateral loads adequately. These structures also allow a significant reduction in costs (up to 28%) compared to RC, hence appearing as challenging alternatives.
1. Introduction
The building construction has a great effect on the total budget of a family. Furthermore, people live the maximum part of their lives in the buildings. Low rise structures (three story or less) are the common type for houses, demanding thus specific consideration in the development of workable solutions for their construction. The accepted construction solution indicates itself as an essential primary investment for house construction and is taken as the emphasis of this study.
5. Conclusions
This study proposes a contribution about the design and development of cost-effective structures in seismic areas. For this reason, the tools offered for the seismic assessment of unreinforced masonry (URM) and confined masonry (CM) structures are presented and corroborated against experimental indication. In general, the assessment tool presented, provided a reasonable estimate of the capacity curve from the lateral load analysis, specifically initial stiffness, ultimate strength and ductility, hence being precise enough to be adopted in performancebased assessment. Additionally, the software permit simulating the configurations of actual masonry buildings. Regarding a genuine case of a single-story, double-story and triple-story dwellings, simulations are performed to evaluate its earthquake-resistant performance and an assessment of the cost of construction is made for masonry solutions in comparison with the typical RC frame.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدلهای آلمان ماکرو (بزرگ) برای سازه ی بنایی
1.2. مدلهایی برای سازه های بنایی غیرمسلح (URM)
2.2.مدل هایی برای سازه ی بنایی محصور شده (CM)
3. مقایسه راه حل های مختلف سازه ای برای یک خانه ی مسکونی
1.3. مطالعه موردی
2.3. راهحل بنایی تقویت نشده
3.3. راهحل بنایی محصور شده
4.3. تحلیل های مقایسهای
4. تحلیل های هزینه
1.4. توضیحات (توصیف) ساختمان
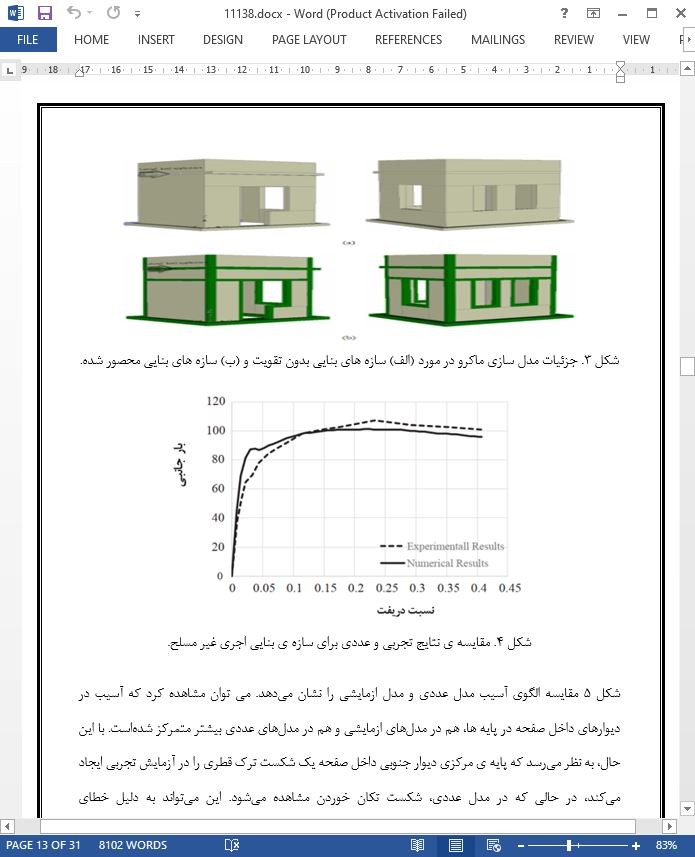
2.4. نتایج و بحثها
5. نتایج
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Macro-element models for masonry
2.1. Models for unreinforced masonry (URM)
2.2. Models for confined masonry (CM)
3. Comparison of different structural solutions for a dwelling
3.1. The case study
3.2. Unreinforced masonry solution
3.3. Confined masonry solution
3.4. Comparative analysis
4. Cost analysis
4.1. Building’s description
4.2. Results and discussions
5. Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه