عملکرد فشاری ستون های بنایی محصور شده در بتن مسلح شده با الیاف دارای شکل پذیری بالا
چکیده
این مقاله، نتایج حاصل از یک بررسی ازمایشی بر روی رفتار فشاری ستونهای آجری رسی محصور شده با بتن مسلح شده با الیاف دارای شکل پذیری بالا (HDC ) را نشان میدهد. هدف از این مطالعه اثبات اثربخشی تکنیک محصورسازی پیشنهادی و تشخیص کارایی اشکال مختلف محصورسازی HDC، از جمله HDC داخلی قرار دادهشده که به عنوان ملات اتصال در مفاصل (یعنی ملات داخلی HDC)و ژاکت(روکش) خارجی HDC مورد استفاده قرار گرفت. علاوه بر این، اثر مصالح محصورسازی نیز بررسی میشود. تحلیل های حالت (مود) شکست، منحنیهای بار محوری - جابجایی، بار پیک(اوج) و شکلپذیری نشان میدهند که ملات داخلی HDC به طور قابلتوجهی میتواند شکلپذیری ستونهای بنایی را بهبود بخشد. اگر چه روکش خارجی HDC نیز میتواند ظرفیت باربری و شکلپذیری را افزایش دهد، اما متاسفانه جداشدگی بین لایه خارجی و زیر لایه(بستر) بنایی در مرحله پس از بار پیک مشاهده میشود. سهم سیمان مبتنی بر روکش ملات در ستونهای بنایی صرفا افزایش ظرفیت باربری به جای شکلپذیری است که به دلیل مقاومت کششی نسبتا کم آن ایجاد شدهاست. علاوه بر این، براساس نظریههای مصالح آجری تقویتشده با مش(شبکه) و بتن محصور شده با لوله ی فولادی، مدلهای تحلیلی موجود در مقالات برای پیشبینی مقاومت فشاری سیستمهای HDC محصور شده ی ستونهای بنایی اتخاذ شدهاند. مدل محاسباتی تقریب بهتری را برای پیشبینی مقاومت فشاری ستونهای بنایی محصور شده ارایه میدهد اما به احتمال زیاد به دادههای ازمایشی بیشتری در آینده به غیر از آنهایی که در این مقاله برای تایید دقت و قابلیت اطمینان به کار گرفته شدهاند، نیاز داشته باشد.
1.معرفی
هنگامی که ستونهای بنایی مسلح نشده تحت بار فشاری قرار میگیرند، انبساط عرضی در مصالح بنایی رخ میدهد. به طور کلی، تغییر شکل جانبی ملات به دلیل سختی متفاوت دو مصالح و رفتار پیوند بزرگ بین آنها، بیشتر از واحدهای آجری است. از این رو، واحدهای آجری در حالتی از کشش دو جانبه همراه با فشار محوری قرار میگیرند که باعث ایجاد ترکهای عمودی شده که به سرعت گسترش مییابند. در نتیجه، تکنیکهای متعدد تقویت کردن برای ستونهای بنایی به منظور بهبود مقاومت و شکلپذیری به منظور محدود کردن انبساط عرضی آجر به کار گرفته شدهاست. برخی از رویکردها به دسته ی محصورسازی داخلی تعلق دارند، از جمله ورق های فولادی قرار داده شده به صورت درونی یا شبکههای فولادی در اتصالات ملاتی که در طول ساخت به عنوان یک سازه بنایی مرکب مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند. روشهای دیگر به دسته ی محصورسازی خارجی، مانند پیچاندن فولاد، پیچاندن سیمهای فولادی، پیچاندن پلیمر تقویتشده با الیاف (FRP)و روکش ملات سیمانی تقویتشده با الیاف (FRCM)تعلق دارند. هدف از استفاده کردن از این روشها، تقویت کردن ستونهای بنایی موجود است.
5.نتایج
این مقاله یک مطالعه ازمایشی بر روی رفتار فشاری ستونهای بنایی آجری خاک رس با بار متمرکز محصور شده با سیستمهای HDC، و به دنبال آن توسعه یک مدل محاسباتی برای پیشبینی مقاومت فشاری آجر محصور شده ارائه میدهد. براساس نتایج بهدستآمده و با در نظر گرفتن محدودیتهای متغیرهای تحلیلشده، نتایج را می توان به صورت زیر بیان کرد:
1. اگرچه ملات مبتنی بر سیمان ظرفیت باربری ستونهای بنایی را در مقایسه با ستونهای urM افزایش داد، اما شکلپذیری آن بسیار ضعیف است. شاخه نرم شدگی تند بعد از بار پیک مشاهده شد که نشان میدهد که ملات مبتنی بر سیمان به دلیل مقاومت کششی کم نمیتواند انبساط عرضی هسته بنایی را مهار کند. prisms های محصور شده هنوز یک شکست شکننده(ترد) را نشان میدهند.
Abstract
This work presents the results of an experimental investigation on the compressive behavior of clay brick masonry columns confined with highly ductile fiber reinforced concrete (HDC). The study aims to prove the effectiveness of the proposed confinement technique and detect the efficiency of different confinement forms of HDC, including internally-placed HDC which was used as binding mortar in the joints (i.e. internal HDC mortar) and external HDC jacket. Furthermore, the effect of confinement materials is examined. Analysis of the failure mode, axial load–displacement curves, peak load and ductility reveals that internal HDC mortar could considerably improve the deformability of masonry columns. Although the external HDC jacket could increase the load carrying capacity and deformability, the detachment between the external layer and masonry substrate is observed at the post-peak stage. Contribution of cement-based mortar jacket to the masonry columns is merely enhancing the load carrying capacity rather than deformability, which was caused by its quite low tensile strength. Moreover, based on the theories of mesh-reinforced brick masonry and steel tube confined concrete, analytical models available in the literatures are adopted to predict the compressive strength of HDC systems confined masonry columns. The calculation model gives a better approximation to predict the compressive strength of confined masonry columns but should need further experimental data in the future other than those adopted in this paper to verify the accuracy and reliability.
1. Introduction
When unreinforced masonry (URM) columns are subjected compressive load, transverse expansion occurs on the masonry. In general, the lateral deformation of mortar is larger than that of brick units due to the different stiffness of two materials and great bond behavior between them. Hence, the brick units are placed in a state of bilateral tension coupled with axial compression [1,2], inducing that vertical cracks appear and propagate quickly. Consequently, multiple reinforcing techniques have been adopted for masonry columns to improve the strength and deformability by confining transverse expansion of masonry. Some of approaches belong to the class of internal confinement, including internallyplaced steel plates or steel grids in the mortar joints which are used during construction as a composite masonry structure. Other techniques belong to the class of external confinement, such as steel wrapping, steel wires hooping, fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) wrapping, and fiber reinforced cementitious mortar (FRCM) jacket. The purpose of using these approaches is to strengthen existing masonry columns.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents an experimental study on the compressive behavior of concentrically-loaded clay brick masonry columns confined with HDC systems, followed by the development of a calculation model for predicting the compressive strength of confined masonry. On the basis of the results obtained and considering the limits of the analyzed variables, the conclusions can be drawn as follows:
1) Although cement-based mortar jacket increased the load carrying capacity of masonry columns compared to the URM columns, the deformability is quite weak. The steep softening branch after the peak load was observed, representing that the cement-based mortar jacket cannot restrain the transverse dilation of masonry core due to its low tensile strength. The confined prisms still showed a brittle failure.
چکیده
1.معرفی
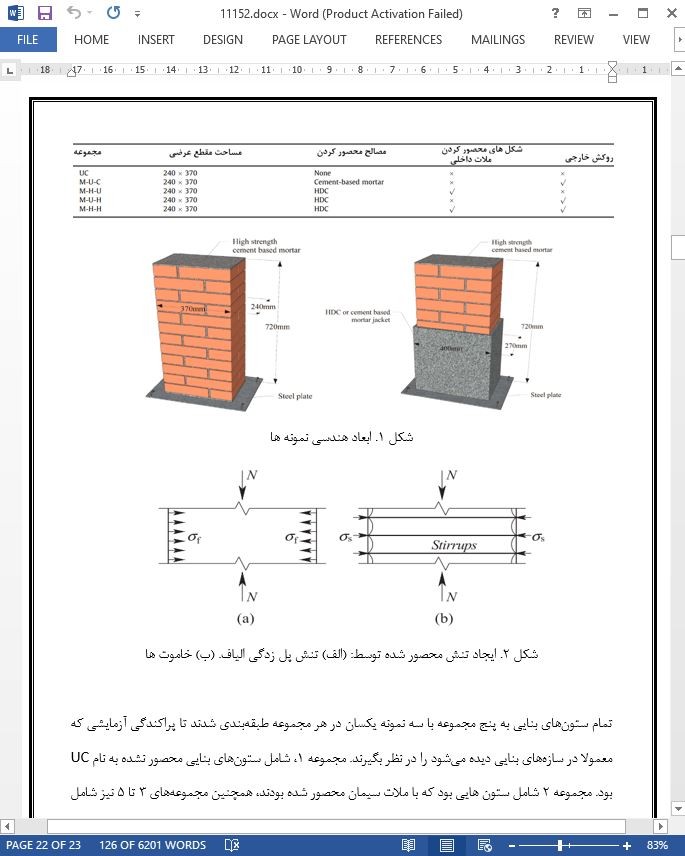
2. برنامه آزمایشی
1.2. توصیف و آمادهسازی نمونه
2.2. ویژگیهای مصالح
3.2. اماده سازی ازمایش
3. نتایج و بحثها
1.3.مودهای شکست
2.3. منحنیهای بار محوری – جابجایی
3.3. مکانیزم محصور کردن HDC
4.3.بار حداکثر
5.3.شکل پذیری
4. پیشبینی تیوریک
1.4. پیشبینی مقاومت ستونهای محصور شده با ملات داخلی HDC
2.4. پیشبینی مقاومت روکش خارجی HDC ستونهای محصور شده
3.4. مقایسه بین نتایج به دست امده از پیشبینیشده و ازمایشات
5.نتایج
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental program
2.1. Specimen description and preparation
2.2. Material properties
2.3. Test setup
3. Results and discussions
3.1. Failure modes
3.2. Axial load–displacement curves
3.3. Confinement mechanism of HDC
3.4. Peak load
3.5. Ductility
4. Theoretical prediction
4.1. Strength prediction of internal HDC mortar confined columns
4.2. Strength prediction of external HDC jacket confined columns
5. Conclusions
6. Author statement
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه