عملکرد مراکز رایانش ابری با ورودها و سرویس عمومی
چکیده
فراهم کنندگان سرویس های ابری برای تعیین مقدار درست منابع و تخصیص آنها به صورت تابعی از نیازهای مشتری و همچنین برآورده ساختن SLA (توافقنامه سطح خدمات)، بایستی سیستم هایشان را سایزبندی نموده و در همان زمان هزینه ها و مصرف انرژی را به حداقل برسانند. هنگام رسیدگی به جنبه های عملکرد QoS (کیفیت خدمات) SLA و پیش بینی بهره برداری از منابع، ابزارهای مبتنی بر نظریه صف بندی یک انتخاب طبیعی به حساب می آیند. ویژگیهای مرکز ابری منجر به یک سیستم صف بندی با سرورهای متعدد (گره ها) می گردد که تعداد بسیار بزرگی سرور وجود دارد و فرایند ورود و سرویس (خدمات) تغییرپذیری بالایی به معرض نمایش می گذارند. پیشنهاد می کنیم از مدل G/G/c گونه برای نمایش سیستم ابری و ارزیابی شاخص های عملکرد مورد انتظار استفاده شود. باتوجه به تعداد بالای سرورها در سیستم ابری، یک راه حل تقریبی کارآمد، سریع و با قابلیت پیاده سازی راحت مطرح می کنیم. دراینجا، تقریب پیشنهادی برای متریک های مختلف عملکرد QoS نظیر زمان پاسخ وظیفه و احتمال بلوکه شدگی، را مطابق شبیه سازی رویداد گسسته سنجیده و نتایج عالی بدست می آوریم. سپس از شیوه پیشنهادی برای مثالهایی در رابطه با سایزبندی سیستم استفاده نموده و مثالهای پیشنهادی اهمیت توجه به تغییرپذیری ورود وظایف را شرح داده و ریسک تامین کمتریا بیشتر از حد نیاز را به معرض نمایش می گذارند، به شرطی که بر مدلی با فرضیات پواسن تکیه شود.
1. مقدمه
سرویس های مبتنی بر ابر (ابری) به سرویسهایی فراگیر تبدیل شده و به زندگی روزمره ما نفوذ می کنند. برخلاف شیوه سنتی که شرکت ها برای رسیدگی به تقاضاهای کاربران بر منابع محاسباتی، ذخیره سازی و شبکه تکیه می کنند، رایانش ابری سرویس های طبق تقاضایی در اختیار کاربران قرار می دهد که برروی شبکه قابل دسترسی هستند ( اکثراً اینترنت) [DIK09, ARM10, XU12]. محیط های SaaS (نرم افزار به عنوان سرویس)، که نرم افزار به شکلی متمرکز در ابر میزبانی شده است، یک مورد مهم به شمار رفته و برای تعدادی از اپلیکیشن های کسب و کار و چند رسانه ای، به مدلی استاندارد تبدیل شده است. شیوه های دیگر برای رایانش ابری عبارتنداز: IaaS (زیرساخت به عنوان سرویس) و PaaS (پلتفرم به عنوان سرویس). در هر صورت، معماری ابری مزایای زیادی از جمله صرفه جویی مقیاس، استقرار سریع ویژگیهای جدید، تعیین سریع عیب و اشکال، و صرفه جویی بالقوه در هزینه از طریق مدل پرداخت به ازای هربار استفاده ، عرضه می نماید.
6. نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، در مورد اهمیت ابزارهای ارزیابی عملکرد برای سایزبندی درست سیستم ابری جهت تامین جنبه های عملکرد SLA و همچنین به حداقل رساندن مقدارمنابع مورد نیاز فراهم کننده سرویس های ابری جهت تامین سطوح QoS صحبت می کنیم. به خاطر تغییرپذیری حجم کارهای ابری، پیشنهاد می کنیم از مدل G/G/c شکل برای نمایش سیستم ابری (مبتنی بر ابر) و محاسبه شاخص های عملکرد مورد انتظار استفاده گردد. مزیت چنین مدلی آن است که توزیع عمومی حجم کارها در سیستم ابری را با توجه به الگوهای ورود و سرویس نشان می دهد.
Abstract
Cloud providers need to size their systems to determine the right amount of resources to allocate as a function of customer's needs so as to meet their SLAs (Service Level Agreement), while at the same time minimizing their costs and energy use. Queueing theory based tools are a natural choice when dealing with performance aspects of the QoS (Quality of Service) part of the SLA and forecasting resource utilization. The characteristics of a cloud center lead to a queueing system with multiple servers (nodes) in which there is potentially a very large number of servers and both the arrival and service process can exhibit high variability. We propose to use a G/G/c-like model to represent a cloud system and assess expected performance indices. Given the potentially high number of servers in a cloud system, we present an efficient, fast and easy-to-implement approximate solution. We have extensively validated our approximation against discrete-event simulation for several QoS performance metrics such as task response time and blocking probability with excellent results. We apply our approach to examples of system sizing and our examples clearly demonstrate the importance of taking into account the variability of the tasks arrivals and thus expose the risk of under- or over-provisioning if one relies on a model with Poisson assumptions.
1 INTRODUCTION
CLOUD-BASED services have become ubiquitous and permeate our every-day life. Unlike the traditional approach where companies rely on their own computing, storage and network resources to handle the user’s demands, cloud computing provides their users with ondemand services that are accessed over a network (most often Internet) [DIK09, ARM10, XU12]. SaaS (Software as a Service) environments, in which software is hosted centrally in a cloud, is a case in point, and has become a standard model for a number of business and multimedia applications. Other approaches to cloud computing include IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) and PaaS (Platform as a Service). In either case, the cloud architecture offers many advantages including economies of scale, fast deployment of new features, quick bug fixes and potential cost-saving through the “pay-as-you-go” model.
6 CONCLUSION
In this paper we argue the importance of performance evaluation tools to properly size a cloud system so as to meet performance aspects of the SLA, as well as minimize the amount resources the cloud provider needs to provision to meet the agreed upon QoS levels. Due to the variability of cloud workloads, we propose to use a G/G/c-like model to represent a cloud-based system and compute expected performance indices. The advantage of such a model is that it represents general distributions of workloads in the cloud system with respect to both the arrival and service patterns.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مرتبط
3. مدل و راه حل اش
4. صحت و عملکرد شیوه پیشنهادی
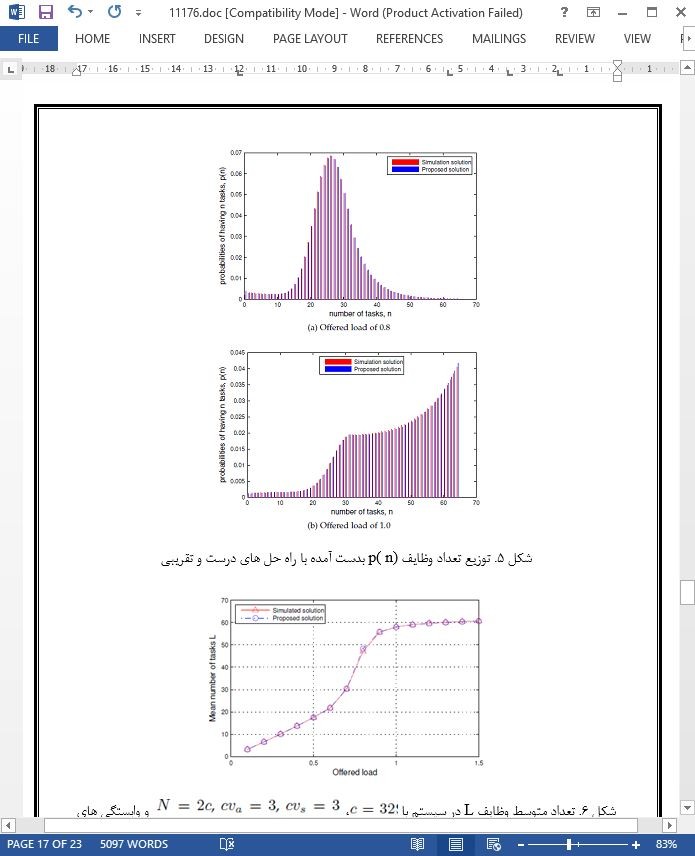
5. مثال سایزبندی سیستم
6. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1 INTRODUCTION
2 RELATED WORK
3 MODEL AND ITS SOLUTION
4 ACCURACY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROPOSED APPROACH
5 EXAMPLE OF SYSTEM SIZING
6 CONCLUSION
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه