یک شیوه مبتنی بر یادگیری برای کشینگ کنش گرا در شبکه های ارتباط بی سیم
چکیده
در شبکه های بی سیم 5G، کشینگ (کش کردن) کنشگرا به عنوان یک فناوری نویدبخش شناخته شده است. ایستگاههای پایه سلولهای کوچک (SBS) می توانند محتواهای مشهوررا کش نموده و به این طریق به ایستگاه پایه ماکرو کمک کنند، واین گونه تصور شده است که کش کردن کنشگرا با لینک های بک هال SBS مواجه می باشد. با این حال، دستیابی به محتواهای مشهور و انتخاب استراتژی کشینگ بهینه، می تواند چالش برانگیز باشد. در این مقاله، یک شیوه مبتنی بر یاداگیری جدید پیشنهاد شده است، که از فیلترینگ گروهی یا مبتنی بر همکاری (CF) مبتنی بر تجزیه مقدار تکین منظم (RSVD) برای تخمین شهرت محتوا و از یادگیری انتقالی (TL) برای بهبود صحت تخمین استفاده شده است. سپس، با در نظرگرفتن تعامل بین کاربران و SBS، الگوریتم تکراری توزیع شده برای ساخت استراتژی کشینگ با هدف به حداکثر رساندن تعداد کاربرانی که SBS همسایگی به آنها خدمت می کنند، طراحی شده است. در این راستا آزمایشاتی برای ارزیابی عملکرد الگوریتم های پیشنهادی انجام شده و نتایج شبیه سازی اثربخشی شیوه مبتنی بر یادگیری پیشنهادی برای کشینگ کنشگرایانه را تصدیق می کند.
1. مقدمه
با توسعه ارتباطات موبایل، تلفن های هوشمند موبایل و شبکه های اجتماعی، از طریق ترمینال های موبایل، تنوع وسیعی از خدمات آنلاین فراهم شده است، که این امر منجر به رشد انفجاری و سریع داده های موبایل می گردد [1]. در نتیجه، تقاضای زیاد داده ها، منابع طیف محدود انتقال های بی سیم، به ویژه لینک های بی سیم بین ایستگاههای پایه و کاربران، و لینک های بک هال بی سیم بین ایستگاههای پایه و شبکه هسته را تخلیه می کند. یکی از راه حل های نویدبخش و امیدوارکننده برای مواجه شدن با این مشکل، کش کردن محتواهای مشهور و معروف در لبه شبکه های موبایل است.
5. نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، شیوه مبتنی بر یادگیری جدیدی برای کشینگ کنشگرا پیشنهاد می کنیم. در مرحله تخمین، شیوه پیشنهادی، CF سنتی را با RSVD بهینه نموده و از TL برای بهبود صحت تخمین با انتقال اطلاعات پیشین از شبکه های اجتماعی استفاده می کند. سپس، در مرحله تصمیم گیری راجع به کشینگ (کش کردن)، با تعیین تابع مطلوبیت هر SBS، تعامل بین کاربران و SBS را مورد توجه قرار داده و برای ساخت استراتژی کشینگ براساس هدف و به حداکثررساندن تعداد مورد انتظار کاربرانی که SBS های همسایگی می توانند به آنها خدمت کنند، یک الگوریتم تکراری توزیع شده طراحی می شود. بالاخره، برای ارزیابی عملکرد الگوریتم ها، آزمایشاتی انجام شده و نتایج شبیه سازی، اثربخشی شیوه مبتنی بر یادگیری برای کشینگ یا کش کردن کنشگرا را تصدیق می نماید.
Abstract
Proactive caching is a promising technology in 5G wireless networks. Small-cell base stations (SBS) can cache popular contents to assist the macro base station, and proactive caching are considered to cope with the weak backhaul links of SBSs. However, obtaining popular contents and making the optimal caching strategy may be challenging. In this paper, a novel learning-based approach is proposed, in which regularized singular value decomposition (RSVD)-based collaborative filtering (CF) is used to estimate the content popularity and transfer learning (TL) is adopted to improve the estimation accuracy. Then considering the interaction between users and SBSs, a distributed iterative algorithm is designed to make a caching strategy with the goal to maximize the number of users who can be served by neighboring SBSs. Experiments have been conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithms and simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our learning-based approach for proactive caching.
I. INTRODUCTION
With the development of mobile communications, mobile smartphones and social networks, a wide variety of online services are provided through mobile terminals, which leads to explosive and rapid growth of mobile data [1]. As a result, the excessive demand for data is draining the limited spectrum resources of wireless transmissions, especially the wireless links between base stations and users, and the wireless backhual links between base stations and the core network. To cope with this problem, a promising solution is to cache popular contents at the edge of mobile networks.
V. CONCLUSION
In this paper, we propose a novel learning-based approach for proactive caching. In the estimating stage, the proposed approach optimize the traditional CF by RSVD and use TL to improve the estimation accuracy by ingeniously transferring the prior information from social networks. Then, in the caching decision-making stage, we consider the interaction between users and SBSs by establishing the utility function of every SBSs, and a distributed iterative algorithm is designed to make a caching strategy based on the purpose to maximize the expected number of users who can be served by neighboring SBSs. Finally, experiments are conducted to evaluate the performance of the algorithms, and simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our learning-based approach for proactive caching.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
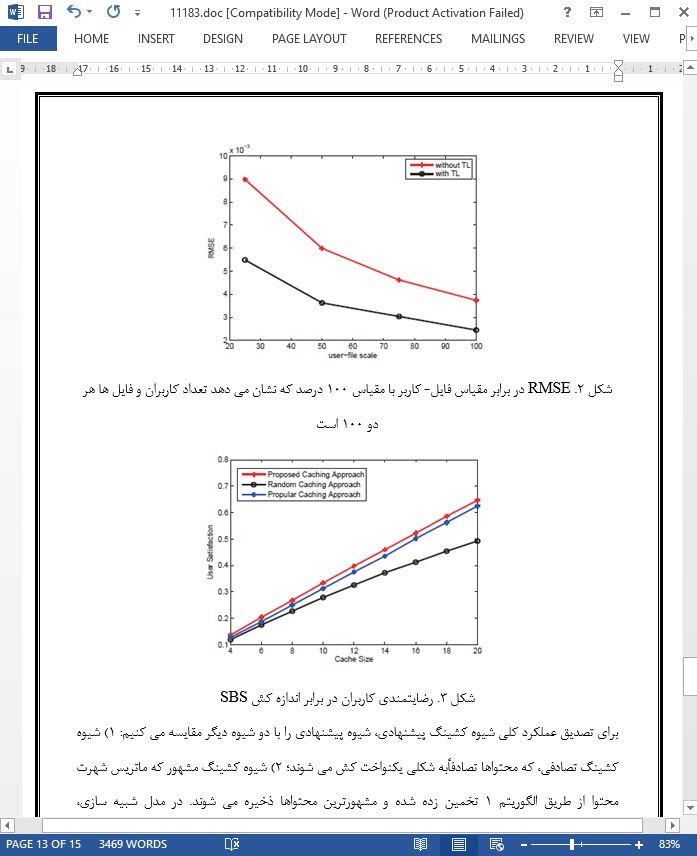
2. مدل سیستم و صورت مسئله
A. مدل سیستم
B. صورت مسئله
3. تخمین ماتریس شهرت و ساخت استراتژی کشینگ
A. تخمین ماتریس شهرت
B. ساخت استراتژی کشینگ
4. آزمایشات و تحلیل نتایج
5. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
I. INTRODUCTION
II. SYSTEM MODEL AND PROBLEM STATEMENT
A. System Model
B. Problem Statement
III. ESTIMATING THE POPULARITY MATRIX AND MAKING CACHING STRATEGY
A. Estimating the Popularity Matrix
B. Making Caching Strategy
IV. EXPERIMENTS AND RESULTS ANALYSIS
V. CONCLUSION
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه