تجزیه و تحلیل جریان برق با مدل بندی کنترل گر پخش بار لایه ای
چکیده
این مقاله یک مدل بندی آسان کنترل گر جریان برق داخلی (IPFC) را در روش جریان بار نیوتن-رافسون اصلاح شده، بیان می کند. در این مدل، کنترل گر جریان برق داخلی (IPFC) به صورت امپدانس های سری (متوالی) با مقاومت های موازی جریان تزریقی، که در باس ها (گذرگاه ) های پایانه آن قرار گرفته اند، ارائه شده است. برای کنترل کردن جریان برق فعال و واکنشی می توان این جریان ها را به عنوان تابعی از جریان برق موردنیاز و ولتاژ باس ها در پایانه های IPFC، محاسبه کرد. در صورتی که فقط قصد کنترل کردن جریان برق فعال را داشته باشیم، این جریان ها با همان روش محاسبه می شوند. اما جریان برق واکنشی از طریق خود سیستم محاسبه و شناسایی می شود. جریان های اصلی آپدیت شده و به داخل بردار عدم تطابق جریان اصلی که متعلق به الگوریتم جریان بار است، تزریق می شوند. با استفاده از این مدل، تقارن ماتریس های ادمیتانس (وارون امپدانس) و ژاکوبین حفظ خواهد شد و بدون نیاز به تغییر دادن مبنای برنامه محاسباتی جریان بار اولیه، می توان مدل IPFC را اجرا کرد. در نتیجه، پیچیدگی های مربوط به کدنویسی در کامپیوتر هم کاهش پیدا خواهد کرد. نتایج عددی بر اساس سیستم های 5-bus، IEEE 57-bus، و IEEE 118-bus برای تعیین میزان دقت و کارایی مدل IPFC پیشنهادی، مورد استفاده قرار گرفته اند.
1. مقدمه
کنترل گرهای سیستم انعطاف پذیر انتقال AC (کنترل گرهای FACTS)، نقش مهمی را در کنترل کارای جریان برق داخلی و بهبود مقادیر ولتاژ شبکه سیستم برق بر عهده دارند. می توان از این کنترل گرهای FACTS برای افزایش قابلیت اعتماد و کارایی سیستم های انتقال و توزیع استفاده کرد. [1-7]
به صورت کلی، دو نسل از این دستگاه های کنترل توسعه یافته موجود می باشد. نسل اول براساس خازن های تریستور مرسوم و واکنش دهنده ها (راکتورها)، و مبدل های قابل تغییر عمل می کنند، درحالی که، نسل دوم از مبدل های تریستور GTO به عنوان مبدل های منبع ولتاژ (VSCs) استفاده می کند.
6. نتیجه گیری
این مقاله یک راه آسان برای مدل بندی IPFC در درون تجزیه و تحلیل جریان بار تزریق شدت جریان نیوتن رافسون اصلاح شده را ارائه کرده است. این مدل براساس شدت جریان های تزریقی شنت در محل های پایانی IPFC عمل می کند. این شدت جریان های تزریق شده، در حین فرایند تکرار با توجه به مقدار جریان برق موردنیاز، اصلاح ولتاژ باس ها و جریان برق واکنشی سیستم بین دومین باس کمکی و باس دریافتی آپدیت می شوند. با استفاده از این مدل، ساختار اصلی و تقارن ماتریس ادمتانس هنوز حفظ خواهند شد. دخالت IPFC در جریان بار، در زمان تغییر الگوریتم محاسباتی مبنا آسان تر می شود. در نتیجه، پیچیدگی های مربوط به کدهای برنامه کامپیوتری کاهش پیدا می کنند. پارامترهای IPFC را می توان بررسی کرد و در فرآیند مکرر می توان فهمید که مقادیر این پارامترها در بین حدود مورد نظر هستند یا نه. همچنین این مدل پیشرفته بر مشکلی که در زمان استفاده از لینک های IPFC در بین دو زیر شبکه وجود داشت، غلبه می کند. برنامه جدید جریان برق تزریق شدت جریان نیوتن رافسون با این مدل IPFC یک ابزار مفید برای برنامه ریزی سیستم برق و کنترل فرایند در سیستم برق های بزرگ مقیاس می باشد. مدل پیشرفته IPFC بر روی سیستم های 5-bus، IEEE 57-bus و 118-bus بررسی و تعیین اعتبار شده است و دارای خصوصیات عملکردی عالی است.
Abstract
This paper proposes an easy modelling of interline power flow controller (IPFC) into Revised Newton Raphson current injection load flow method. In this model, the IPFC is represented as series impedances with shunt injected currents at its terminal buses. The target of control for active and reactive power flow can be achieved by calculating these currents as a function of the desired power flow and the buses voltage at the terminals of IPFC. In case of controlling the active power flow only, these currents are calculated with the same method. But the reactive power flow is released and calculated according to the system. The injected currents are updated and added into the original current mismatches vector of load flow algorithm. By using this model, the symmetry of the admittance and Jacobian matrices can still be kept and incorporating of IPFC becomes easy without changing the basic load flow computational program. Consequently, the complexities of the computer program codes are reduced. Numerical results based on the literature 5-bus, IEEE 57-bus and IEEE 118-bus systems are used to demonstrate the effectiveness and performance of the proposed IPFC model.
1. Introduction
Flexible AC transmission system controllers are playing a leading role in efficiently controlling the line power flow and improving voltage profiles of the power system network. These FACTS controllers can be used to increase the reliability and efficiency of transmission and distribution systems [1–7].
In general, there are two generations of these developed control devices; the first generation is based on the conventional thyristor switched capacitors and reactors, and tap changing transformers, while, the second generation uses the GTO thyristor switched converters as voltage source converters (VSCs).
6. Conclusions
This paper has presented an easy modelling of IPFC into Revised Newton Raphson current injection load flow analysis. The model is based on shunt injected currents at the ends of IPFC. These injected currents are updated during the iterative process according to the desired power flow, correction of buses voltage and system reactive power flow between the second auxiliary and received buses. By using this model, the original structure and symmetry of admittance matrix can still be kept. The incorporating of IPFC in load flow becomes easy without changing in the basic computational algorithm. Consequently, the complexities of the computer program codes are reduced. The IPFC parameters can be checked and if their values are within the limits or not during the iterative process. Also the developed model overcomes the problem which exists when only the IPFC links between two sub-networks. The Revised Newton current injection power flow program with this IPFC model is useful tool for power system planning and operation control of large scale power system. The developed IPFC model has been validated on the literature 5-bus, IEEE 57-bus and 118-bus systems with excellent performance characteristics
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. روش جریان بار شدت جریان تزریقی نیوتن-رافسون
3. مدل پیشرفته شدت جریان تزریقی در کنترل گر IPFC
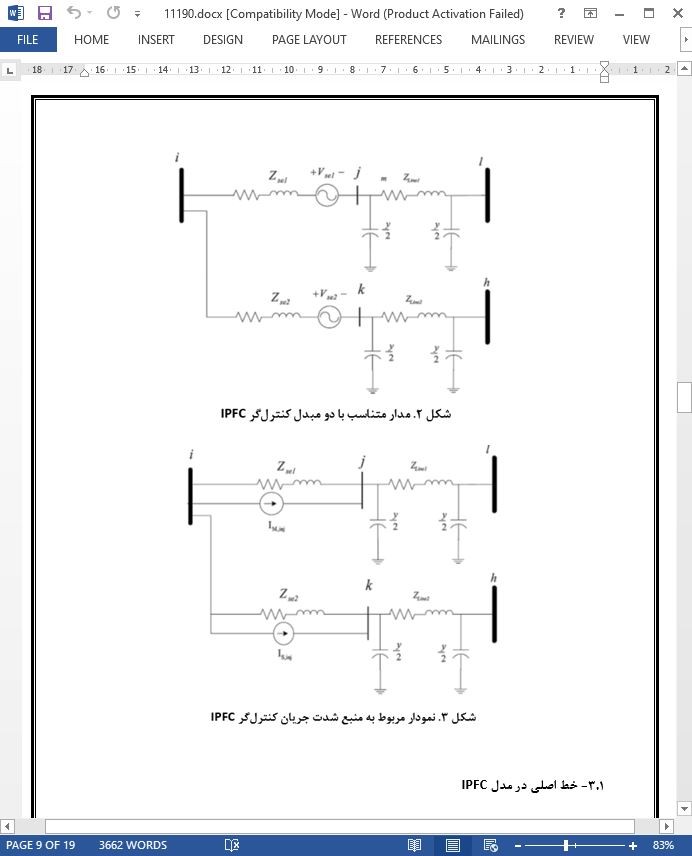
3.1- خط اصلی در مدل IPFC
3.2- خط فرعی در مدل IPFC
4. دخالت مدل IPFC در برنامه جریان بار شدت جریان تزریقی اصلاح شده NR
5. نتایج
5.1- سیستم آزمایش 5-bus
5.2- سیستم آزمایش IEEE 57-bus
5.3- سیستم آزمایش IEEE 118-bus
6. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Newton Raphson current injections load flow method
3. Developed current injection model of IPFC controller
3.1. Master line in IPFC model
3.2. Slave line in IPFC model
4. Incorporating of IPFC model in revised NR current injection load flow program
5. Results
5.1. 5-Bus test system
5.2. IEEE 57-bus test system
5.3. IEEE 118 bus test system
6. Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه