مهار بیان تیروزیناز و دوپاکروم توتومراز در سلولهای ملانومای مورین B16
روغن آرگان (Argania spinosa L) از قرن ها پیش در در مراکش به عنوان روغن زینتی برای حفظ تعادل چهره و درمان اسکارهای پوستول ابله مرغان استفاده می شده است. اگرچه این روغن بسیار پر طرافدار است اما هنوز پایه های علمی در مورد اثرات آن بر پوست اثبات نشده است. در اینجا اثر تنظیمی روغن آرگان بر ملانوژنز در سلولهای ملانومای مورینB16 ارزیابی می شود. ارزیابی نتایج ملانین با استفاده از سلولهای B16 تیمار شده با غلظت های مختلف روغن آرگان نشان دهنده ی کاهش وابسته به دوز در محتوای ملانین بود. نتایج وسترن بلات نشان دادکه سطوح بیان تیروزیناز (TYR)، پروتیین وابسته به تیروزیناز-1(TRP1) و پروتیین دوپوکرام توتومراز(DCT) کاهش می یابد. علاوه بر این افزایش در فعال شدن MITF و ERK1/2 نیز مشاهده شد. نتایج Real-time PCR نشان دهنده ی تنظیم کاهشی در بیان mRNA ژن های TYR، Trp1،DCT و Mitf بود. تیمار با روغن آرگان باعث فسفریلاسیون MITF و در نتیجه مهار رونویسی آنزیم های ملانوژنیک –TYR و DCT میشود. اثر بازدارندگی روغن آرگان بر بیوسنتز ملانین می تواند به توکوفرول و اثرات سینرژیک آن مربوط باشد. نتایج این مطالعه پایه های علمی برای فواید سنتی روغن آرگان را فراهم آورد و توانایی بالقوه ی آن برای درمان بیماری های هیپرپیگمانتاسیون را آشکار کرد.
1. مقدمه
استفاده از روغن آرگان برای مرطوب کردن پوست و حفظ تعادل چهره در میان زنان مراکشی ثابت شده است. Argania spinosa (Skeel) یک گونه ی درختی بومی در مراکش بوده و دارای ارزش اقتصادی-اجتماعی فراوان در این ناحیه است. میوه ی A. spinosa دارای یک دانه ی روغن زاست که از آن روغن آرگان بدست می آید که در طب بومی و لوازم آرایشی بویژه در مناطق جنوب غربی استفاده میشود. از قدیم ، روغن آرگان آرایشی برای درمان انواعی از جوش های پوستی مانند جوش جوانی و اسکارهای پوستول های ابله مرغان استفاده می شد. همچنین گفته میشود که این روغن باعث کاهش مسائل خشکی پوست شده و ظهور چین چروک را کند می کند. این روغن همچنین برای درمان پسوریازیس، اگزما، دردهای مفصلی، التهاب پوست و جرب ، برای بهبود سوختگی و زخم ، برای بهبود شکنندگی ناخن و نیز جلوگیری از ریزش مو و خشکی مو استفاده میشود. روغن آرگان استفاده شده در لوازم آرایشی روغن استخراج شده با فشار سرما از دانه های میوه ی آرگان است که اکنون در جهان شناخته شده است. این روغن به عنوان گرانترین سبزیجات و روغن آرایشی شناخته میشود و منبع درآمد زنان مراکشی است که عضو تعاونی زنان هستند. در نواحی جنوبی مراکش تعاونی ها روغن آرگان را برای مصارف غذایی و آرایشی تولید می کنند. استخراج روغن آرگان برای مصارف خوراکی و ارایشی اکنون با روش های سنتی انجام می شود. روغن آرگان غنی از توکوفرول ها ، اسیدهای چرب متوسط زنجیر ، کارتنوئیدها ،اسکوالن ها و اولئیک اسید است.
5. نتیجه گیری
اکنون یک رغبت دوباره نسبت به گیاهان به عنوان ترکیبات دارویی در دنیای غرب وجود دارد و این رغبت به دلیل کشف مولکلوهای زیستی جدید و پذیرش عمومی گیاهان برای خود درمانی در افکار عمومی است. طب سنتی افریقای شمالی ، در حفظ سلامت تمام بخش های دنیا و ارائه درمان های جدید سهم مهمی داشته است. اگرچه برخی از افراد ممکن است استخراج نرکیبات و استفاده از آنها به عنوان ترکیبات شییمیایی واخد را گزینه ی بهتر بدانند اما اکنون دیدگاهی وجود دارد مبنی بر اینکه استفاده از عصاره به جای استخراج یک ترکیب واحد دارای مزیت های بیشتر ی است. گزارش های منتشر شده در باره ی فواید دارویی مصرف خوراکی روغن آرگان توسط 52 خلاصه شده است، اما اثرات آن بر سلولهای رنگدانه ای هنوز گزارش نشده است. در اینجا ما روغن آرگان را به عنوان یک مهارکننده ی موثر بیوسنتز ملانین معرفی میکنیم که اثرات ان میتواند به اجزاء واحد آن یا عملکرد سینرژیک تمام اجزاء نسبت داده شود. اگرچه اثر اجزاء روغن آرگال (توکوفورل ها ، اسیدهای چرب و غیره ) بر بیوسنتز ملانین گزارش شده است اما این گزارش درباه ی اولین گزارش در خصوص اثر مهارکنندگی روغن آرگان بر ملانوژنز در سلولهای B16 است که پایه های علمی لازم برای یک دانش سنتی مبنی بر اثرات مفید روغن آرگال بر پوست را فراهم میکند.
Argan (Argania spinosa L.) oil has been used for centuries in Morocco as cosmetic oil to maintain a fair complexion and to cure skin pimples and chicken pox pustules scars. Although it is popular, the scientific basis for its effect on the skin has not yet been established. Here, the melanogenesis regulatory effect of argan oil was evaluated using B16 murine melanoma cells. Results of melanin assay using B16 cells treated with different concentrations of argan oil showed a dose-dependent decrease in melanin content. Western blot results showed that the expression levels of tyrosinase (TYR), tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TRP1), and dopachrome tautomerase (DCT) proteins were decreased. In addition, there was an increase in the activation of MITF and ERK1/2. Real-time PCR results revealed a downregulation of Tyr, Trp1, Dct, and Mitf mRNA expressions. Argan oil treatment causes MITF phosphorylation which subsequently inhibited the transcription of melanogenic enzymes, TYR and DCT. The inhibitory effect of argan oil on melanin biosynthesis may be attributed to tocopherols as well as the synergistic effect of its components. The results of this study provide the scientific basis for the traditionally established benefits of argan oil and present its therapeutic potential against hyperpigmentation disorders.
1. Introduction
The use of argan oil to moisturize the skin and to maintain a fair complexion has been an established tradition among Moroccan women. Argania spinosa (L.) Skeels (Sapotaceae) is a tree species endemic to Morocco and has a great ecological and socioeconomic value in this area. The fruit of A. spinosa has an oleaginous kernel from which a well-known oil, “argan oil,” is used in folk medicine and in cosmetics [1], especially in the southwestern region [2]. Traditionally, cosmetic argan oil was used to cure all kinds of skin pimples as well as juvenile acne and chicken pox pustules scars. It is also recommended to reduce dry skin matters and slow down the appearance of wrinkles. This oil is also used to treat psoriasis, eczema, joint pain, skin inflammation, and scabies, to heal burns and wounds, to cure brittle fingernails, to prevent hair loss and dry hair [3]. Argan oil for cosmetic use is cold-pressed oil extracted from unroasted kernels of argan fruit, which at present has gained worldwide recognition. It has been referred to as the “most expensive vegetable and cosmetic oil” [4] and as such has been a source of income for many Moroccan women who are members of cooperatives run by women. In the southern part of Morocco, cooperatives produce argan oil for food or for cosmetic use. The extraction of argan oil for food and cosmetic use is still being done using the traditional method. Argan oil is rich in tocopherols, medium chain fatty acids, carotenoids [5–7], squalene, and oleic acid [8].
5. Conclusion
There is a renewed interest in plants as pharmaceuticals in the Western world and this is on the discovery of new biologically active molecules and into the adoption of crude extracts of plants for self-medication by the general public [47]. North African traditional medicine, therefore, has an important contribution in the maintenance of health in all parts of the world and in the introduction of new treatments. And although some may view the isolation of compounds and their use as single chemical entities as a better option and has resulted to the replacement of plant extracts use, nowadays, a view that there may be some advantages to the medical use of extracts as opposed to isolated single compounds, is gaining popularity [50, 51]. Published reports on the therapeutic benefits of consumption of argan oil have been summarized by [52], but its effect on pigment cells has not yet been reported. Here, we present argan oil as an effective melanin biosynthesis inhibitor, the effect of which may be contributed by the individual components or their synergistic effect. Although the effect of argan oil components (tocopherols, fatty acids, etc.) on melanin biosynthesis has been reported, this is the first report on the inhibitory effect of argan oil on melanogenesis in B16 cells, providing the scientific basis for the centuries-long knowledge of its beneficial effect on the skin.
1. مقدمه
2. مواد و روش
2.1. منشاء نمونه¬ی روغن آرگان و انالیز ترکیبات اجزاء سازنده.
2.2 فعالیت آنتی اکسیدانی روغن آرگان
2.3 کشت سلول
2.4 کمی سازی ملانین
2.5. وسترن بلات
2.6 انالیز REAL-TIME PCR کمی
2.7 انالیزهای آماری
3 نتایج
3.1. انالیزهای شیمیایی
3.2. فعالیت انتی اکسیدانتی و پتانسیل احیایی روغن آرگان
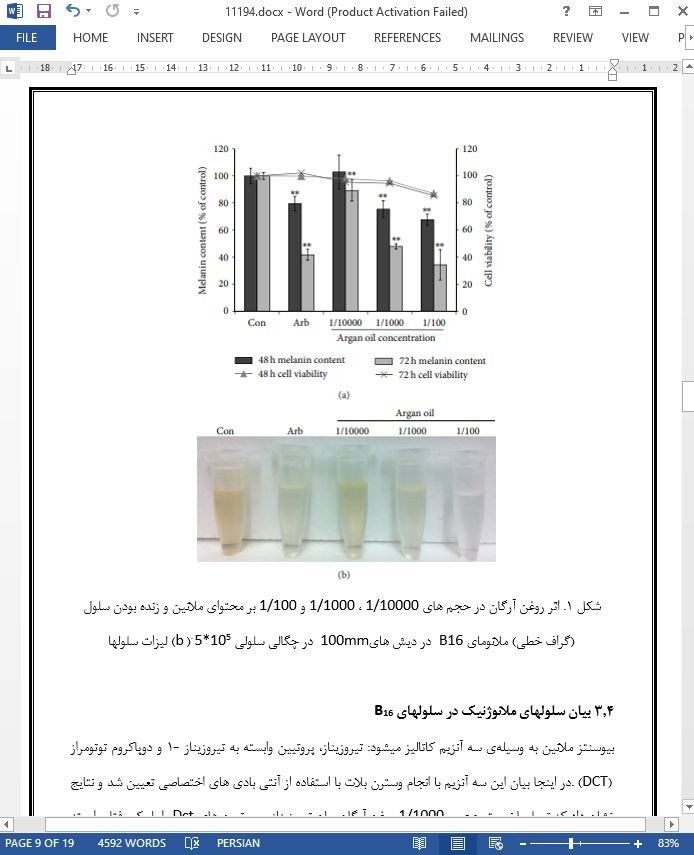
3.3 تاثیر بر محتوای ملانین سلول¬های B16
3.4 بیان سلولهای ملانوژنیک در سلولهای B16
3.5 مکانیسم مولکولی مربوط به اثر دپیگمنتاسیون
4 بحث
5. نتیجه گیری
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin of Argan Oil Sample and Oil Components Composition Analysis
2.2. Antioxidant Activity of Argan Oil
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Melanin Quantification
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Analyses
3.2. Antioxidant Activity and Reductive Potential of Argan Oil
3.3. Effect on the Melanin Content in B16 Cells
3.4. Melanogenic Enzymes Expressions in B16 Cells
3.5. Molecular Mechanism Underlying the Depigmenting Effect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه