ارزیابی مشخصه های V-t ناشی از برخورد صاعقه در مناطق مختلف در خطوط انتقال
چکیده
برخورد صاعقه در خطوط انتقال، منجر به تزریق یک جریان در محل اتصال می شود. درک عملکرد صاعقه بدون استفاده از یک برنامه شبیه ساز می تواند دشوار باشد. جهت توسعه داده های مناسب که برای بررسی این پدیده مورد نیاز است، یک نرم افزار قدرتمند PSCAD انتخاب شد.
در این مقاله ، دو نقطه در امتداد خطوط انتقال، جهت مطالعه مشخصه ولتاژ- زمان (V-t) انتخاب شدند که هر کدام از این نقطه ها به طور جداگانه در معرض صاعقه قرار می گیرند. نقطه مفروض اول، جاییکه جریان صاعقه در نوک برج انتقال، وارد سیم محافظ می شود انتخاب شده است، در حالیکه نقطه مفروض دوم جایی انتخاب شده است که جریان خیز در نقطه ای بین دو برج که ماکزیمم میزان خمیدگی را دارد وارد سیم محافظ می شود. خمیدگی خطوط انتقال اخیرا با استفاده از PSCAP توسعه داده شده و شبیه سازی شده است.
هم خطوط انتقال دارای خمیدگی و هم تزریق جریان ناشی از صاعقه به خوبی مدل سازی شده اند. گذر سریع جرقه و همچنین وقوع جرقه برگشت بررسی شد. نتایج نشان داد که خمیدگی خطوط انتقال تاثیر قابل توجهی روی جرقه و ولتاژ القایی در مقره های خط و همچنین خطوط فاز دارد. اثر اتصال برقگیر در ایستگاه های فرعی مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. جهت مینیمم کردن وقوع اورولتاژ ناشی از جرقه و متعاقبا جرقه برگشت در مقره ها ، یک برقگیر خط انتقال (TLA) مناسب طراحی شد.
1. مقدمه
یکی از منابع طبیعی اورولتاژ گذرا در سیستم قدرت برخورد صاعقه است. برخورد صاعقه یک تغییر ناگهانی گذرا است که دارای قطبیت تک جهته ( مثبت یا منفی) می باشد. خط انتقال هوایی مهمترین بخش در معرض پدیده صاعقه است . خطوط انتقال با استفاده از سیم های محافظ از برخورد مستقیم صاعقه محافظت شده اند. تزریق جریان ناشی از صاعقه به درون سیم های محافظ یا بدنه برج ها باعث القای ولتاژ در مقره ها و خطوط فاز می شود.
در کارهای اخیر، محققان زیادی چندین پارامتر که عملکرد صاعقه بر سیستم انتقال را تحت تاثیر قرار می دهد، مطالعه کرده اند. پارامترهای رایج صاعقه عبارت اند از: زمان جبهه، زمان دنباله، پیک جریان صاعقه، هندسه برج، مقاومت پی، تاج، جرقه و غیره.
4. نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، اثر جریان صاعقه تزریق شده در نوک برج انتقال و همچنین در ناحیه ای با بیشترین میزان خمیدگی در سیستم انتقال 500 kV، در دو حالت باحضور برقگیر و بدون حضور برقگیر شبیه سازی شد. نتایج حاصل نشان می دهد که خمیدگی خط انتقال اثر آشکاری روی مشخصه های V-t حاصل از برخورد صاعقه و متعاقبا حفاظت اورولتاژ گذرا ، دارد.
Abstract
Lightning stroke causes a current injection into transmission lines at the point of contact. The lightning performance can be difficult to understand without using simulation programs. PSCAD a powerful software was selected to develop the appropriate data required to investigate this phenomena.
In this paper, two points along transmission line are selected for studying voltage–time (V–t) characteristics when any of those points is subjected to lightning strokes separately. The first assumed point is taken when lightning current is injected to the shielding wire at the top of the transmission tower, while, the other assumed point is taken when surge current is injected to the shielding wire at maximum sag location in the mid-span between two towers. The sag of transmission line has been newly developed and simulated using PSCAD.
Both transmission line containing sag as well as lightning injection current are modeled. Fast transient of flashover as well as back flashover occurrence is investigated. The results revealed that the sag of transmission line has considerable influence on flashover and induced voltages across line insulators and phase lines as well. The influence of connecting surge arrester in substations is investigated. A proper transmission line arrester (TLA) is designed in order to minimize the occurrences of overvoltages due to flashover and consequently back flashover across insulators.
1. Introduction
One of the natural sources of transient overvoltage in the power system is lightning strokes. Lightning stroke is an impulsive transient variation which is unidirectional in polarity (positive or negative). Overhead transmission line is the most part subjected to the lightning phenomena. Transmission lines are protected from the direct lightning by shield wires. The lightning current injection to shield wires or tower body will cause induced voltage across insulators and phase lines (Bollen et al., 2005).
In previous works, most researchers had studied several parameters that affect the lightning performance on transmission system. The common parameters of lightning are: front time, tail time, peak lightning current, tower geometry, footing resistance, corona, flashover, etc (Chowdhuri, 2001; Talib et al., 2012; Yadee and Prem, 2007).
4. Conclusion
In this paper, the effect of lightning current injected at the top of transmission tower as well as at maximum sag location of 500 kV transmission system is simulated with and without using surge arresters. The obtained results report that the sag of transmission line has an obvious effect on V–t characteristics caused by lightning surges and consequently transient overvoltage protection.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مدل سازی سیستم انتقال 500 kV
1.2 ماژول برج
2.2 مقاومت پی
3.2 ماژول مقره
4.2 ماژول جرقه برگشت
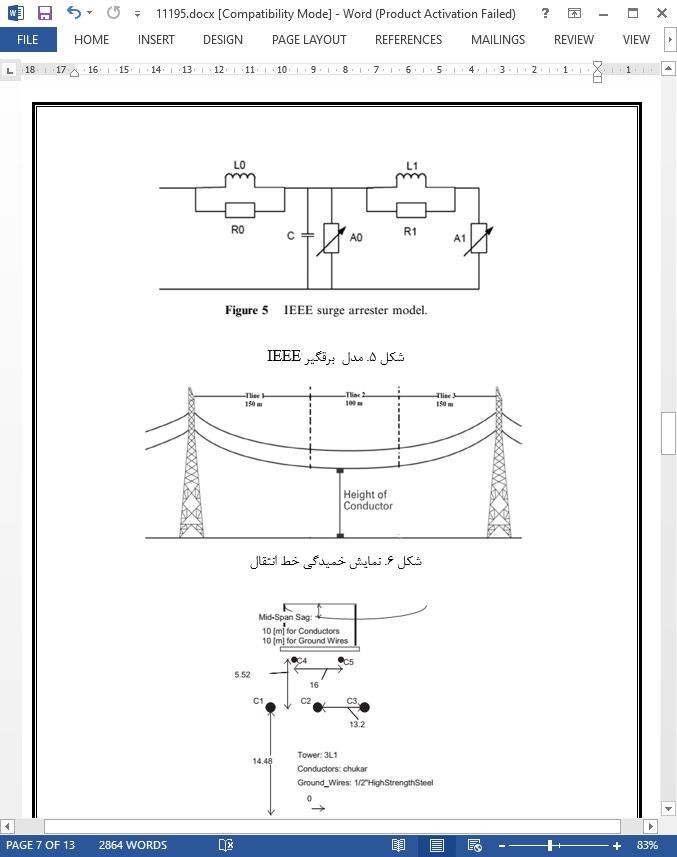
5.2 ماژول برقگیر
6.2 ماژول خمیدگی خط
7.2 ماژول سیستم انتقال 500 kV
8.2 برقگیرهای خطوط انتقال
9.2 مدل برخورد صاعقه
3. نتایج و بحث
1.3 برخورد بدون برقگیر در ایستگاه های فرعی و بدون جرقه
2.3 برخورد بدون برقگیر در ایستگاه های فرعی و با جرقه
3.3 برخورد با برقگیر در ایستگاه فرعی و با جرقه
4.3 برخورد با حضور TLA
4. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling of 500 kV transmission system
2.1. Tower module
2.2. Footing resistance
2.3. Insulator module
2.4. Back flashover module
2.5. Surge arrester module
2.6. Transmission line sag module
2.7. 500 kV transmission system module
2.8. Transmission line arresters
2.9. Lightning stroke module
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Striking without substation arresters and without flashover
3.2. Striking without substation arrester and with flashover
3.3. Striking with substation arrester and with flashover
3.4. Striking with the presence of TLA
4. Conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه