خوشه بندی براساس مکان مجازی ماشین ها در محاسبات ابری توزیع شده
چکیده
مجازی سازی منبع یکی از مهم ترین ویژگی های محاسبات ابری می باشد. مکان ماشین های مجازی (VMها) درماشین های فیزیکی بازده مصرف منابع و کیفیت سرویس را مشخص می نماید. مخصوصا در محاسبات ابری توزیع شده، که مراکز داده (DCها) محدوده جغرافیایی وسیعی را پوشش می دهند و تمام DCها توسط اینترنت سرعت بالا به هم متصل اند، مکان VMهای یک فعالیت بزرگ یا سازمانی بر کاهش فاصله و پهنای باند DCها تمرکز دارد. این امر موجب حداقل شدن تاخیر ارتباط و بهبود دسترسی می گردد. یک خوشه مرکز داده در ابتدا باید خودش را با درخواست VMها تطبیق دهد. هدف کاهش بیشترین فاصله داخلی DCها است. در مقابل روش های موجود که تنها فاصله بین مراکز داده را در نظر می گیرند، یک الگوریتم خوشه بندی کارآمد که توسط استفاده کامل از توپولوژی و ویژگی تراکم شبکه ابری گسترش داده شده است، ارائه می شود. شبیه سازی نشان می دهد که الگوریتم ارائه شده برای مسائل مقیاس بزرگ بسیار مناسب است. سپس، VMهای درخواستی باید به خوشه های DC تفکیک شوند، تا در پهنای باند داخلی DC صرفه جویی شود و دسترسی نیز بهبود داده شود. با معرفی مدل نیم ارتباطی، الگوریتمی جدید که مصرف پهنای باند را کاهش می دهد برای تفکیک VMها ارائه می گردد. پیچیدگی زمان این الگوریتم با ضریب O(logn) به O(n2) کاهش داده می شود و نسبت به روش های موجود 3 برابر سریع تر اجرا می شود.
1.مقدمه
محاسبات ابری در سال های اخیر به منظور مصرف درست منابع و دسترسی آسان خدمات رواج زیادی یافته است [1، 2]. این قدرت های رقابتی به معرفی فن آوری مجازی و شبکه توزیع ابری کمک می کنند. براساس استانداردهای صنعتی مجازی سازی، هسته ماشین های فیزیکی (PMها) را می توان به CPUهای مجازی بیشتری تبدیل نمود (vCPUها) [3]. ماشین های مجازی می توانند در مرکز vCPUها قرار گیرند و در نتیجه مصرف منابع کارآمدتری داشته باشند. این امر موجب تحریک VMها شده که برای گسترش آن ها توسط شبکه توزیع در کاربران انتهایی مکانی متفاوت مفید می باشد. ابرهای توزیع از تعداد زیادی مرکز داده تشکیل می شود که بوسیله اینترنت پر سرعت به هم متصل می باشند [4]. در مقابل این ابرهای متمرکز، DCهای توزیع شده قرار دارند که قابلیت های نسبتا کمی دارند، چراکه براساس ترافیک پایین محیط پراکنده ایی که در آن قرار دارند طراحی شده اند.
6.نتیجه و کارهای آینده
توسط مفهوم روش های خوشه بندی، این مقاله الگوریتم CBMinDia را برای مساله انتخاب DC معرفی کرد که دارای بازده بهتری است. CBMinDia مشخصه 2-تقریبی را حفظ می کند و برای DCها یا درخواست های VM مقیاس بزرگ مناسب تر است. چراکه از اطلاعات تراکم و ظرفیت DCهای شبکه استفاده کاملی می کند و راه حل هایی که نسبتا بهینه هستند را در مقایسه با راه حل های امکان پذیر کنار می گذارد. محاسبات بشدت کم می شوند و شبیه سازی بیشترین بازده را برای خوشه بندی توزیع DC نشان می دهد.
برای مساله تفکیک VM، با معرفی مفهوم HCM یک الگوریتم نسبتا بهتر بررسی می شود. این الگوریتم یک زوج AOT و AIT مناسب برای هر انتخاب VM مشخص می کند. مقدار AOT و AIT امکان ماکزیمم نمودن ترافیک میان DC و مینیمم نمودن ترافیک درون DC را فراهم می کند. مهمتر اینکه، این مفهوم می تواند انتخاب VMها را توسط اضافه نمودن یک بردار ساده ساده تر کند و محاسبات ماتریس ترافیک را کاهش دهد. از این رو پیچیدگی زمان با ضریب O(logn) به O(n2) کاهش می یابد و بازده 3 برابر بهتر می شود.
Abstract
Resource virtualization is one of the most prominent characteristics of cloud computing. The placement of virtual machines (VMs) in the physical machines determines the resource utilization efficiency and service quality. Especially for distributed cloud computing, where the data centers (DCs) span a large number of geographical areas and all DCs are connected by high speed internet, the placement of VMs of one big task or of one organization focuses on minimizing the distances and bandwidths between DCs. This minimizes communication latency and improves availability. A data center cluster should be found firstly to accommodate the requested VMs. The purpose is to minimize the maximum inter-DC distance. In contrast to existing method that only considers the distances between data centers, a more efficient clustering based 2-approximation algorithm is developed by taking full use of the topology and the density property of cloud network. The simulation shows the proposed algorithm is especially appropriate for very large scale problems. Then, the requested VMs should be partitioned to the DC cluster, so that the expensive inter-DC bandwidth is saved and the availability is improved. With the introduction of a half communication model, a novel heuristic algorithm which further cuts down the used bandwidths is presented to partition VMs. Its time complexity is reduced to O(n2) by a factor of O(logn) and it runs 3 times faster than the existing method.
1. Introduction
Cloud computing has gained great popularity in recent years for the efficient resource usage and convenient service access [1, 2]. These competitive powers are attributable to the introduction of virtual technology and distributed networking of cloud. Based on the actual standard of virtualization industry, the cores of physical machines (PMs) can be virtualized into more virtual CPUs (vCPUs) [3]. Virtual machines (VMs) can be placed on the granularity of vCPUs and thus gain a more efficient resource utilization. It is also hoped VMs can be deployed closer to the end users in different geographical locations by distributed networking. Distributed cloud consists of a lot of data centers (DCs) and all DCs are connected by high speed internet [4]. Contrary to the counterparts of centralized cloud, distributed DCs have relatively small capability because they are planned according to the less traffic of the dispersed area they locate.
6. Conclusions and future work
By means of the notions of clustering methods, this paper presents a more efficient algorithm, CBMinDia, for the DC selection problem. CBMinDia keeps the 2-approximation property and is more appropriate for large scale DCs or requested VMs. Because the algorithm takes full use of the density and DC capacity information of the network, it cuts off the sub-optimum DCs compared to a rather good feasible solution. The computing effort is greatly decreased and the simulation reveals that it is the most efficient for clustering DC distribution.
For VM partition problem, a slightly more effective algorithm is investigated with the introduction of HCM concept. This algorithm determines an appropriate pair of AOT and AIT for each selection of a VM. The value of AOT and AIT permits maximizing the intra-DC traffic and minimizing the inter-DC traffic. More importantly, the concept can facilitate the convenient selection of VMs by means of simple vector addition and subtraction calculation of the traffic matrix. Hence the time complexity is reduced to O(n 2 ) by a factor of O(log n) and the efficiency is improved about 3 times.
چکیده
1.مقدمه
2.کارهای مرتبط
2.1.قرار دادن VM و استاندارد مجازی سازی اخیر
2.2.خوشه بندی براساس تراکم
3.انتخاب مرکز داده براساس خوشه بندی
3.1.انگیزه
3.2.انتخاب مرکز داده
4.تفکیک ماشین های مجازی برای انتخاب مراکز داده
4.1.مدل نیم ارتباطی (HCM) VMها
4.2.تفکیک ماشین های مجازی
5.آزمایش
5.1.انتخاب مرکز داده براساس خوشه بندی
5.2.تفکیک ماشین های مجازی
6.نتیجه و کارهای آینده
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related work
2.1. VM placement and current virtualization standard
2.2. Density-based clustering
3. Clustering based data center selection
3.1. Motivation
3.2. Data center selection
3.3. Complexity analysis and effectiveness proof
4. Virtual machines partition to selected data centers
4.1. Half communication model (HCM) of VMs
4.2. Virtual machines partition
5. Experiments
5.1. Clustering based data centers selection
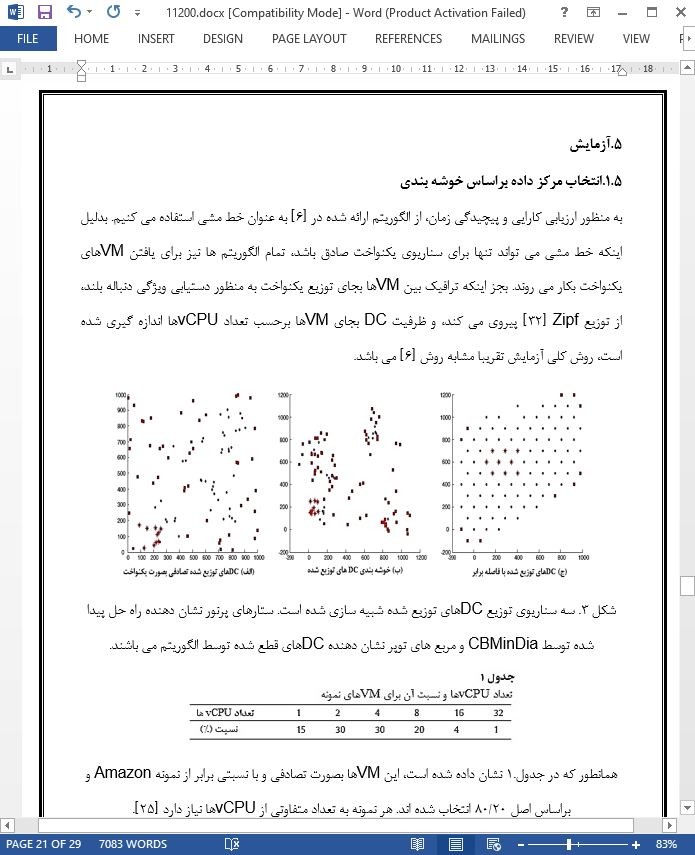
5.2. Virtual machines partition
6. Conclusions and future work
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه