تنش های پسماند در مقاطع H شکل فولادی پر مقاومت بریده شده با شعله و جوشکاری شده
چکیده
حضور تنش پسماند در اعضا بهطور قابلتوجهی میتواند مقدار سختی و طول عمر خستگی اعضا سازهای فلزی را در شک و تردید قرار دهد. تحقیقات در این زمینه برای اعضا سازهای با فولاد کمکربن، بهخوبی مستندسازی شده است. بااینوجود، به علت اختلاف در روابط تنش-کرنش و ویژگیهای مواد تحت دماهای محصور و بالا، توزیع تنش پسماند در عضو فولادی پر مقاومت، بهطور فیزیکی، متفاوت است با اعضایی که از فولاد کمکربن ساختهشدهاند. مطالعه توزیع تنش پسماند برای اعضا سازهای ساختهشده از فولاد پر مقاومت، ضروری است. در این مقاله، تنشهای پسماند سه عدد ستون با مقطع H شکل بریدهشده با شعله و جوشکاری شده با مقاومت تسلیم اسمی 460 مگا پاسکال اما با ابعاد مقطع عرضی متفاوت، موردبررسی قرارگرفته است. هردوی روشهای مقطع زنی و حفره زنی، برای اندازهگیری استفادهشده و تنشهای پسماند بهدستآمده، بین دو روش مقایسه شده است. مقادیر و توزیعهای تنشهای پسماند اندازهگیری شده، با آنهایی که از فولاد کربنی هستند یکسان است، اما در نسبتهای تنش پسماند نسبتاً کوچکتر. نهایتاً، بر اساس اندازهگیریها یک توزیع تنش پسماند سادهسازی شده برای اعضا فولادی پر مقاومت 460 مگا پاسکال با مقطع H شکل بریدهشده با شعله و جوشکاری شده، پیشنهادشده است.
معرفی
اعضا سازهای جوشکاری شده، نورد گرم، بریدهشده با شعله و یا صافشده با شعله معمولاً در ابتدا بدون تنش نمیباشند. تنشهای پسماندی در این اعضا فلزی سازهای وجود دارد که بهوسیلهی توزیعهای حرارت غیریکنواخت در طول فرآیندهای ساخت، تولید یا بهسازی ایجادشدهاند. به علت شکلپذیری بالا و کافی مواد فولادی، تنشهای پسماند اغلب برای مقاومت پلاستیک مقاطع عرضی مشکلی ایجاد نمیکند، ولی حضور تنش پسماند ممکن است بهطور قابلتوجهی سختی اعضا فشاری را تغییر دهد و طول عمر خستگی اعضا فولادی را تحت بار متناوب و یا بار دینامیکی کاهش دهد. برای بررسی اثر تنشهای پسماند، مقادیر و توزیعهای تنشهای پسماند در مقاطع فولادی کمکربن جوشی، بهطور گسترده موردبررسی قرارگرفته است[1,2]. به علت اینکه منحنیهای تنش-کرنش و ویژگیهای مادهای[3] مربوط به دمای بالای فولاد پر مقاومت (HSS، مقاومت تسلیم برابر یا بیشتر از 460 مگا پاسکال) متفاوت است با فولاد با مقاومت معمولی، انتظار میرود که تنشهای پسماند در مقاطع پر مقاومت با مقاطع فولادی کمکربن متفاوت باشد.
نتیجهگیری
توزیعهای تنش پسماند برای سه مقطع H شکل متفاوت، ساختهشده از ورقهای فولادی پر مقاومت Q460 با شعله بریدهشده ارائه گردید. توزیعهای تنش پسماند سادهسازی شده پیشنهاد شد. تنشهای پسماند فشاری میانگین σ_rc در بالها با توجه به نسبتهای عرض به ضخامت بالهای بیرون زده 7.1 ، 5 و 3.4 به ترتیب برابر با -19.5%، -27.1% و -40.8% مقاومت تسلیم بود. میانگین تنشهای پسماند کششی محاسبهشده σ_rt در هر مقطع 73.1% ، 90% و 103.9% مقاومت تسلیم به ترتیب برای نمونههای R-H-7 ، R-H5 و R-H-3 بود. نتایج بهدستآمده از دو روش مقطع زنی و حفره زنی باهم مقایسه شد. مشاهده شد که میانگین مقادیر تنش پسماند فشاری بهدستآمده از هردو روش مشابه است اما توزیعهای تنش پسماند بهدستآمده از روش مقطع زنی برای استفاده در تحلیلهای عددی مناسبتر است. با مقایسه نمونههای اندازهگیری شده، به دست میآید که افزایش نسبتهای عرض به ضخامت بال بیرون زده، به کاهش تنشهای پسماند فشاری در بالها و افزایش تنشهای پسماند کششی در نوکهای بال منجر خواهد شد. مقایسه نتایج آزمایش با نتایج آزمایشهای نمونههای کمکربن نشان میدهد که نسبتهای تنش پسماند مقاطع H شکل جوشی بریدهشده با شعله فولادی پر مقاومت نسبت به مقاطع H شکل فولادی معمولی، کمضرر تر برای مقاومت ستون به نظر میآید.
Abstract
The presence of residual stress in members can significantly compromise the stiffness and fatigue life of steel structural components. Researches in this area are well documented for structural members of mild carbon steels. Nevertheless, due to the difference of stress–strain relations and material properties under ambient and high temperatures, the residual stress distribution in a high strength steel member is physically different from those fabricated from mild carbon steel. It is imperative to study the residual stress distribution for structural members fabricated from high strength steel. In this paper, the residual stresses of three welded flame-cut H-section columns with a nominal yield strength of 460 MPa but different cross-section dimensions were investigated. Both sectioning and hole-drilling methods were used in the measurement and the obtained residual stresses were compared between the two methods. The magnitudes and distributions of the measured residual stresses are identical with those of carbon steel, however in relatively smaller residual stress ratios. Finally, based on the measurements, a simplified residual stress distribution for 460 MPa high strength steel members with welded flame-cut H-section is proposed.
1. Introduction
Welded, hot-rolled, flame-cut or flame-straightened structural components are usually not initially stress free. Residual stresses exist in these structural steel members induced by the non-uniform temperature distributions during the manufacture, fabrication or refinement processes. Owing to the sufficiently high ductility of steel material, residual stresses are often not detrimental to the plastic strength of cross sections, but the presence of residual stress may significantly impair the stiffness of compression members and shorten the fatigue life of steel members under periodical load or dynamic load. In order to investigate the effect of residual stresses, the magnitudes and distributions of residual stresses in welded mild carbon steel sections have been extensively investigated [1,2]. Since the stress–strain curves and high-temperature material properties [3] of high strength steel (HSS, yield strength≥460 MPa) are different from the regular strength steel, it is expected that the residual stresses in HSS sections are different from those in mild carbon steel sections.
6. Conclusion
The residual stress distributions of three different H-sections fabricated from flame-cut Q460 high strength steel plates were presented. The simplified residual stress distributions were proposed. The average compressive residual stresses σrc in flanges were −19.5%, −27.1% and −40.8% of yield strength according to the width to thickness ratios of outstanding flanges, which were 7.1, 5.0 and 3.4 respectively. The average calculated tensile residual stresses σrt in each section were 73.1%, 90.0% and 103.9% of yield strength for specimens R-H-7, R-H-5 and R-H-3, respectively. The test results obtained by both sectioning and hole-drilling methods were compared. It is observed that the average values of compressive residual stress obtained by the two methods are similar, but the residual stress distributions obtained by sectioning method is more convenient to be employed in the numerical analysis. By comparing the measured specimens, it is found that the increase in width to thickness ratios of an outstanding flange will result in decreasing of compressive residual stresses within flanges and increasing of tensile residual stresses at flange tips. The comparison of the test result with those of mild carbon steel shows that the residual stress ratios of HSS flame-cut welded H-sections tend to be less detrimental to the column strength than the ordinary steel H-sections.
چکیده
معرفی
تحقیقات تنش پسماند قبلی در مورد مقاطع H شکل با فولاد پر مقاومت
تکنیکهای اندازهگیری تنش پسماند
برنامه آزمایشی
ویژگیهای مصالح
ساخت و آمادهسازی نمونهها
روش حفره زنی
روش مقطع زنی
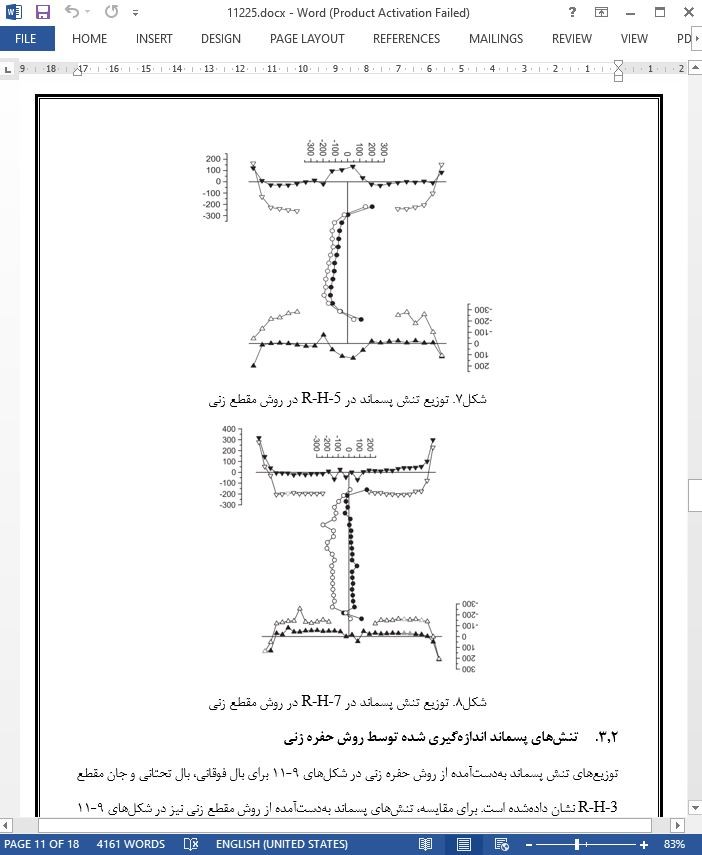
نتایج آزمایش
تنش پسماند اندازهگیری شده توسط روش مقطع زنی
تنشهای پسماند اندازهگیری شده توسط روش حفره زنی
الگوی تنش پسماند سادهسازی شده
بحث
تنشهای پسماند را با تغییر d⁄t_f را مقایسه کنید
تنشهای پسماند فولادهای مختلف را مقایسه کنید
تنشهای پسماند اندازهگیری شده را با فرضیات قبلی مقایسه کنید
نتیجهگیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Previous residual stress researches in HSS H-sections
1.2. Residual stress measurement techniques
2. Experimental program
2.1. Material properties
2.2. Fabrication and preparation of specimens
2.3. Hole-drilling method
2.4. Sectioning method
3. Experimental results
3.1. Residual stress measured by sectioning method
3.2. Residual stresses measured by hole-drilling method
4. Simplified residual stress pattern
5. Discussion
5.1. Compare residual stresses with varying d/tf
5.2. Compare residual stresses of different steels
5.3. Compare measured residual stresses with previous assumptions
6. Conclusion
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه