استفاده از رسوبات دریایی به عنوان ماده پایه سنگ فرش
چکیده
مدیریت رسوبات دریایی پس از لاروبی به طور فزاینده ای پیچیده شده است. در زمینه توسعه پایدار، راه های سنتی مانند غوطه وری به طور فزاینده تعدیل خواهندشد. با کمبود مصالح از معادن، ماده لایروبی شده بیش از همیشه، یک منبع جدید از مواد را تشکیل می دهد.
در این مطالعه پتانسیل استفاده از رسوبات دریابی در ساخت جاده، هدف اول تعیین ویژگی های فیزیکی و مکانیکی رسوبات ریز لایروبی شده از بندرگاه در شمال فرانسه می باشد. اثرات این مواد بر محیط نیز بررسی شده است. در مرحله دوم، ویژگی های رسوب ریز برای استفاده به عنوان ماده راه ارتقاء می یابد. در این مرحله، درمان مورد استفاده با محدودیت های صنعتی سازگار می باشد. برای کاهش محتوای آب رسوبات ریز، جداکنندگی (Decantation : دکانتور) طبیعی بکار رفته است؛ علاوه برآن، شن لاروبی شده به منظور ارتقاء توزیع دانه ای و استحکام اسکلت گرانول افزوده می شوند. سرانجام، ویژگی های مخلوط با ترکیب چسبنده ها (سیمان و/یا آهک) ارتقاء می یابند. ویژگی های مکانیکی اندازه گیری شده در مخلوط ها، با استفاده از آن ها به عنوان ماده لایه پایه سازگار می باشد. علاوه برآن، نتایج بدست آمده اثرگذاری آهک در مخلوط ها را نشان می دهد. به لحاظ تاثیرات محیطی، برپایه آزمون های آبشویی و برطبق مقادیر آستانه در دسترس برای استفاده از خاکستر زیر حاصل از سوزاندن ضایعات جامد شهری (MSWI) در ساخت جاده، توسعه یافته است؛ مخلوط های لاروبی طراحی شده در مقادیر آستانه توصیه شده صدق می کنند.
1. مقدمه
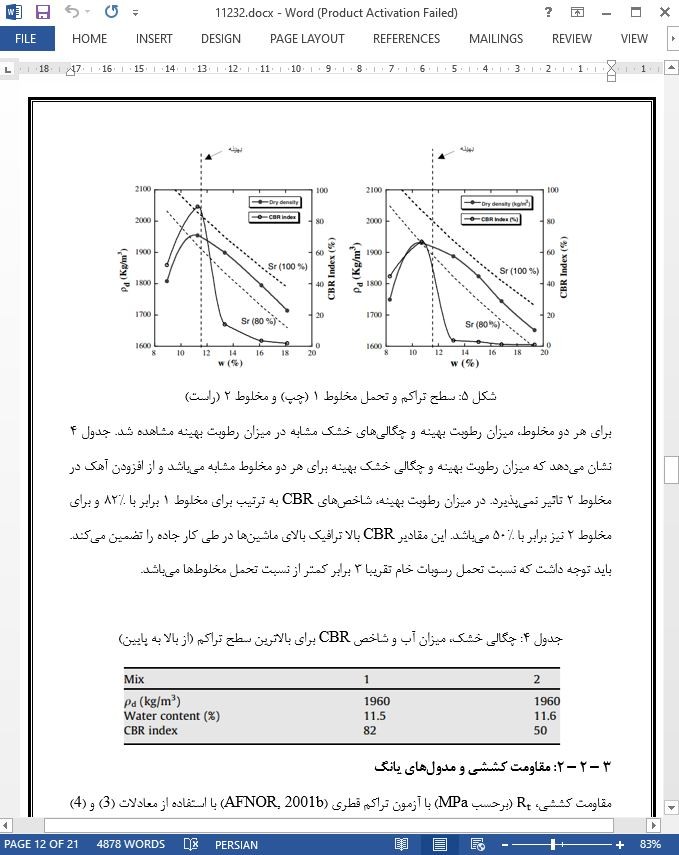
عملیات لاروبی به منظور حفظ جهت یابی در مسیرهای آبی و دسترسی به بنادر ضروری می باشد. هر سال، چند صد میلیون تن مصالح در سراسر دنیا لاروبی می شود (Boutin, 1999). این مصالح، که از تخته سنگ ها تا خاک رس می باشند، دارای مقدار متغیری از ماده آلی، انواع و سطوح مختلف از آلاینده ها می باشند.
مدیریت رسوبات لاروبی شده یک مسئله بسیار گسترده است. پس از لاروبی، راه حل های سنتی مانند روبرداری رسوبات در دریا، به وسیله مقررات ملی و بین المللی محدود شده اند. راه حل های جایگزین، مانند دفع زمینی، نیز هزینه بر هستند و نیازمند نواحی بزرگ می باشند (LIFE, 2002; Grégoire, 2004). بنابراین توسعه راهبردهای استفاده سودمند برای رسوبات لاروبی شده بسیار ضروری می باشد.
5. نتیجه گیری
برای مدیران بندرگاه، مدیریت بهتر رسوبات لاروبی شده یک الزام کلیدی در حفظ جهت یابی و تطبیق توسعه پایدار را ایجاد می کند. در این مقاله، راه حل جایگزین برای استفاده مجدد از رسوبات لاروبی شده (رسوبات لاروبی ریز و شن لاروبی شده) در ساخت راه پیشنهاد شده است.
روش پیاده سازی شده در این مطالعه به منظور توسعه مخلوط های طراحی شده شامل آبکشی رسوبات ریز به وسیله جداکنندگی (دکانتور) و بهبود توزیع گرانولار با افزودن شن لاروبی شده می باشد. فرایند جداکنندگی اولیه به منظور کاهش نمک های محلول در آب روزنه ضروری می باشد. بهبود توزیع گرانولار (ذره ای) ظرفیت تحمل رسوبات لاروبی شده را بهبود می بخشد و میزان چسبنده های موردنیاز برای برآورده کردن عملکرد توصیه شده جهت استفاده هدفمند را کاهش می دهد. این نتایج مخلوط های لاروبی شده را از لحاظ اقتصادی با دوام تر می سازد.
Abstract
The management of marine sediments after dredging has become increasingly complex. In the context of sustainable development, traditional solutions such as immersion will be increasingly regulated. More than ever, with the shortage of aggregates from quarries, dredged material could constitute a new source of materials.
In this study of the potential of using dredged marine sediments in road construction, the first objective is to determine the physical and mechanical characteristics of fine sediments dredged from a harbour in the north of France. The impacts of these materials on the environment are also explored. In the second stage, the characteristics of the fine sediment are enhanced for use as a road material. At this stage, the treatment used is compatible with industrial constraints. To decrease the water content of the fine sediments, natural decantation is employed; in addition, dredged sand is added to enhance the granular distribution and to reinforce the granular skeleton. Finally, the characteristics of the mix are enhanced by incorporating binders (cement and/or lime). The mechanical characteristics measured on the mixes are compatible with their use as a base course material. Moreover, the obtained results demonstrate the effectiveness of lime in the mixes. In terms of environmental impacts, on the basis of leaching tests and according to available thresholds developed for the use of municipal solid waste incineration (MSWI) bottom ash in road construction, the designed dredged mixes satisfy the prescribed thresholds.
1. Introduction
Dredging operations are necessary to maintain navigation in waterways and access to harbours. Each year, several 100 millions of tons of materials are dredged around the world (Boutin, 1999). These materials, ranging from rocks to clays, can contain a variable amount of organic matter and different types and levels of contaminants.
Management of dredged sediments is a worldwide problem. After dredging, traditional solutions such as dumping the sediments at sea are constrained by national and international regulations. Alternative solutions, such as terrestrial disposal, are costly and require large areas (LIFE, 2002; Grégoire, 2004). The development of beneficial use strategies for dredged sediments is therefore necessary.
5. Conclusions
For harbour managers, better management of dredged materials constitutes a key requirement to maintain navigation and to accommodate sustainable development. In this paper, an alternative solution for re-use of dredged sediments (fine dredged sediments and dredged sand) in road construction is proposed.
The methodology implemented in this study to develop the designed mixes consists of dewatering the fine sediments by decantation and improving the granular distribution by adding dredged sand. The initial decantation process is necessary to reduce dissolved salts in the pore water. The enhancement of the granular distribution improves the bearing capacity of the dredged sediments and reduces the amount of binders needed to meet the performance prescribed for the targeted use. In this study, the amount of binders added to the proposed mixes is comparable to the amount used in standard materials. These results make the designed mixes economically viable
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. مواد و روش ها
2 – 1: توصیف مکان
2 – 2: خصوصیات رسوبات لاروبی شده
2 – 3: روش برای استفاده مجدد
3. نتایج
3 – 1: طراحی ماده
3 – 2: مطالعه رفتار مکانیکی مواد
3 – 3: اثر محیطی ماده طراحی شده
4. بحث وبررسی
5. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Site description
2.2. Characterization of dredged sediments
2.3. Methodology for re-use
3. Results
3.1. Design of the material
3.2. Study of the mechanical behaviour of the materials
3.3. Environmental impact of designed material
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه