جریان متلاطم و افزایش انتقال حرارت در یک مبدل حرارتی لوله ای با شیارهای گسسته شیب دار
چکیده
در مطالعه حاضر از یک لوله با شیارهای شیب دار برای انتقال حرارت و مینیمم کردن مصرف انرژی برق از طریق تولید جریان های چرخشی طولی با گرداب های متعدد در یک لوله شیاردار، استفاده شد. برای ارزیابی ساختار جریان متلاطم و اثرات پارامترهای هندسی روی عملکرد حرارتی از یک روش عددی استفاده شده است. بر اساس نتایج ما، جریان های طولی چرخشی با گرداب های چند گانه در لوله شیب دار ایجاد می شود، و تعداد گرداب های القایی متناسب با تعداد شیارها است. انتقال حرارت و ضریب اصطکاک در یک لوله صاف به ترتیب 23/1-17/2 و 02/1 تا 75/3 افزایش می یابد. به منظور درک بیشتر مکانیسم فیزیکی لوله شیاردار افزایشی و ارزیابی پارامترهای فیزیکی، بررسی های تولید آنتروپی انجام شد. نتایج نشان داد نسبت مقدار تولید انتروپی با افزایش شیار ها و با کاهش نسبت شیب شیار و تعداد شیار گاهش می یابد و نسبت شیب شیار برابر 3 برای لوله پیشنهاد می شود. به علاوه مقایسه هایی که با کارهای قبلی انجام شده نشان می دهد که لوله شیاردار عملکرد حرارتی بسیار چشمگیری نسبت به لوله شیار دار تراگذار، لوله با شیارهای داخلی راه راه و لوله با شیار پیوسته دارد اما عملکرد حرارتی آن نسبت به لوله با شیارهای گسست در عدد رینولوز پایین کمتر است. این امر نشان می دهد که این لوله شیاردار در کاربردهای عملی برای افزایش انتقال حرارت بسیار مناسب است.
1- مقدمه
مبدل های حرارتی، که موجب انتقال حرارت از یک محیط به محیط دیگر می شود کاربردهای بسیار وسیعی از جمله کاربردهای نفتی، شیمیایی ، صنایع تولید انرژی و کاربرد های خانگی دارد. افزایش عملکرد کلی مبدل حرارتی موجب کاهش سایز مبدل و مواد سازنده و صرفه جویی در انرژی مربوط به فرایند تبادل حرارت می گردد[1]. در کاربرد های عملی، معمولا توسعه لوله های افزایش انتقال حرارت برای افزایش بازدهی مبدل حرارتی به این علت که عملکرد کلی مبدل توسط انتقال حرارت در لوله ها که واحد های پایه انتقال حرارت مبدل هستند اندازه گیری می شود، ضروری به نظر می رسد. نصب نوارهای پیچیده و سیم های کویلی یا عناصر زبری مصنوعی مثل شیارها و موج ها روی سطح به طور معمول برای تکنیک های افزایش انتقال حرارت در لوله به کار برده می شود. از میان این تکنیک ها لوله های با شیار مصنوعی بهاین علت که در افزایش انتقال حرارت بسیار موثر است عملکرد حرارتی بهتری نشان داده و به طور وسیعی مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است انتقال حرارت در لوله به کاربرده می شود. از میان این تکنیک ها لوله های با شیار مصنوعی به این علت که در افزایش انتقال حرارت بسیار موثر است، عملکرد حرارتی بهتری نشان داده و به طور وسیعی ومورد استفاده قرار گرفته است[2].
5- نتیجه گیری
جریان متلاطم و انتقال حرارت در یک لوله دوار با شیار گسسته به صورت عددی مورد بررسی قرار گرفت. جزئیات جریان متلاطم و انتقال حرارت و اثرات پارامترهای هندسی بر انتقال حرارت ارائه و آنالیز شد. بررسی های تولید آنتروپی بریا درک بیشتر مکانیسم فیزیکی لوله افزایشی انجام شد. مقایسه ای نیز بین لوله افزایشی پیشنهادی با لوله افزایشی قبلی انجام شد. بر اساس بررسی عددی نتایج زیر استنتاج شد:
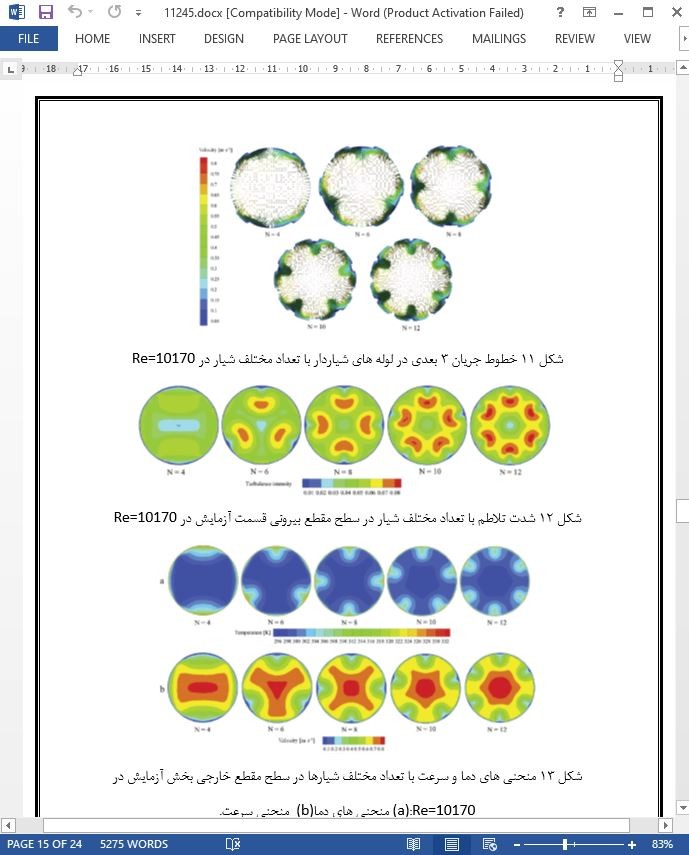
1) جریان های چرخشی طولی با گرداب های متعدد در لوله شیاردار القا می شود. الگوی جریان لوله منجر به مسیر طولانی جریان و اختلاط شدید جریان بین مناطق دیواره و مرکزی جریان می شود. به علت اختلاط مناسب توسط جریان های طولی چرخشی، دما به خوبی توزیع می شود.
Abstract
In the present work, we propose a novel enhanced tube with discrete inclined grooves, aiming to enhance heat transfer with minimum consumption of pump power by generating longitudinal swirl flows with multiple vortices in the proposed grooved tube. A numerical study has been conducted to investigate the turbulent flow structures and the effects of geometric parameters on the thermal performance. According to the results, longitudinal swirl flows with multiple vortices are generated in the grooved tube, and the number of induced vortices is proportional to the number of circumferential grooves. The heat transfer and friction factor are enhanced by a factor of approximately 1.23–2.17 and 1.02 to 3.75 over the smooth tube, respectively. To further understand the physical mechanism of the enhanced grooved tube and to assess the effects of geometric parameters, entropy generation analyses have also been performed. The results show that the entropy generation number ratios decrease with increasing the number of circumferential grooves and with the reduced groove pitch ratio, and a number of circumferential grooves of 12 and a groove pitch ratio of 3 are recommended for the proposed grooved tube. In addition, comparisons with previous work show that the proposed grooved tube provides considerably higher overall thermal performance than the transversally grooved tube, internally helical grooved tube and continuous corrugated tube, but lower thermal performance than the discrete corrugated tube at lower Reynolds numbers, indicating that the proposed grooved tube is very promising for heat transfer enhancement in practical applications.
1. Introduction
Heat exchangers, which ensure heat transfer from one medium to another, have wide applications ranging from petroleum, chemical, power generation industries and domestic uses. Enhancement in a heat exchanger's overall performance contributes to reducing the size of heat exchangers and make material and energy savings related to the heat exchange processes [1]. In practical applications, it is usually necessary to develop efficient enhanced heat transfer tubes to improve the efficiency of a heat exchanger, due to the fact that a heat exchanger's overall performance is determined by the heat transfer in the tubes which are the basic heat transfer units for a heat exchanger. Tube inserts like twisted tapes and coiled wires or artificial roughness elements such as ribs, grooves and corrugations on the surface are commonly used heat transfer enhancement techniques for tubes. Among these techniques available, artificial grooved tubes show better overall thermal performance and are widely used in modern heat exchangers, because they are very effective in heat transfer augmentation [2].
5. Conclusions
Turbulent flow and heat transfer in a circular tube with discrete inclined grooves were numerically investigated. Turbulent flow and heat transfer details, and effects of geometric parameters on the heat transfer performance were presented and analyzed. Entropy generation analyses were performed to further understand the physical mechanism of the enhanced grooved tube. Comparison between the proposed grooved tube and previous enhanced tubes was also conducted. Based on the numerical investigation, following conclusions can be drawn:
(1) Longitudinal swirl flows with multiple vortices are induced in the grooved tube. The flow pattern results in a long flow path and relatively intense flow mixing between the wall and the core flow regions. The temperature is more evenly distributed due to better flow mixing induced by the longitudinal swirl flows.
چکیده
1- مقدمه
2- توضیح مدل
3- شبیه سازی عددی
3.1 انتخاب مدل تلاطم
2-3 معادلات حاکم و شرایط مرزی
3-3 ایجاد شبکه و تست مستقل
4- بحث و نتیجه گیری
1-4 تایید اعتبار کد
2-4 ساختار جریان و توزیع دما
3-4 اثرات پارامترهای هندسی بر عملکرد حرارتی- هیدرولیکی
4-4 آنالیزهای تولید آنتروپی
5-4 مقایسه با کارهای قبلی
5- نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Model description
3. Numerical simulations
3.1. Selection of turbulence model
3.2. Governing equations and boundary conditions
3.3. Grid generation and independence test
3.4. Parameter definition
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Code validation
4.2. Flow structure and temperature distributions
4.3. Effects of geometric parameters on the thermal-hydraulic performance
4.4. Entropy generation analysis
4.5. Comparison with previous work
5. Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه