تاثیر بکارگیری کارت امتیازی بر اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری
چکیده
بدیهی است که اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری (AIS) در سازمان های بخش دولتی (PSO) نقش مهمی در حصول به عملکرد پایدار (SP) ایفا می کند. البته، به دلیل تغییرات سریع در اقتصادی جهانی، اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری نمی تواند به تنهایی به عملکرد پایدار منجر شود. بر این اساس، تقاضای روز افزونی در چارچوب ارزیابی وجود دارد که به نظر می رسد با ویژگی های سازمان های بخش دولتی به منظور موضع گیری، مدیریت و ارزیابی عملکردهای سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری در راستای حصول به عملکرد پایدار متناسب باشد. بنابراین، هدف از این مطالعه بررسی رابطه میان تاثیر اجرای کارت امتیازی بخش دولتی (PSS) و اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری بر عملکرد پایدار بر اساس شواهد جمع آوری شده از 883 حسابدار بخش دولتی در منطقه مکونگ دلتا است. داده های بدست آمده از مدل سازی معادلات ساختاری (SEM) نشان می دهند که پیاده سازی PSS تأثیر قابل توجهی در اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری دارد. همچنین، شواهد حاکی از یک مبنای معتبر برای ارتباط میان اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری و عملکرد پایدار می باشد. اگرچه این موضوع تحقیق همچنان در آغاز مسیر خود است، ولیکن پیش بینی می شود که یافته های این مقاله به دلیل مزایایی که در عملکرد سازمان های بخش دولتی از خود نشان داده است، بتواند به عنوان راهکاری برای محققان، ذینفعان و سیاستگذاران عمل کند.
1. مقدمه
سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری (AIS) ابزاری مؤثر برای مقابله با تغییرات بیرونی و داخلی است (شاگری ، عبدالله ، و سعات ، 2017) که بواسطه پردازش داده ها و مبادلات، اطلاعات مفیدی را برای برنامه ریزی، کنترل و اجرای فعالیت های سازمانی تولید کرده (رامنی ، اشتاینبرت ، و کوشینگ ، 1997) و همچنین سبب تسهیل سازی و کسب عملکرد سازمانی مطلوب می گردد (ساگانوان ، اسماعیل و احمد ، 2013). این مسئله توجه محققان را به اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری معطوف كرده است، زیرا اینگونه اطلاعات مفید حسابداری به بهبود بهره وری سازمان و دستیابی به پاسخگویی بهینه كمك شایانی خواهد كرد (مللمویك ، مونسن ، و اولسون ، 1988).
7.1. نتیجه گیری
بر اساس یک دیدگاه نظری و با شواهد جمع آوری شده از سازمان های دولتی در منطقه مکونگ دلتا، هدف از مطالعه حاضر بررسی این امر است که آیا پیاده سازی کارت امتیازی در بخش دولتی سبب اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری بر عملکرد پایدار می شود یا خیر. نتایج این تحقیق، یک مبنای قابل اعتماد را برای ارتباط میان پیاده سازی PSS و اثربخشی سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری در سازمان های دولتی فراهم می کند. بر این اساس، هر یک از مؤلفه های سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری نقش مهمی در ارتقای عملکرد اجتماعی، عملکرد محیطی و عملکرد اقتصادی ایفا می کند، به طوری که منجر به یک افزایش کلی در عملکرد پایداری سازمانی می شود. در این راستا، تجربیات محققان حاکی از مفاهیم و پیامدهایی است که باید مورد توجه بیشتر قرار گیرد.
Abstract
The effectiveness of accounting information system (AIS) in public sector organization (PSO) is well recognized to play an important part in obtaining sustainable performance (SP). Nevertheless, the effectiveness of AIS cannot achieve the SP on its own due to the rapid changing in the global economic world. Accordingly, there is an increasing demand on a framework of evaluation which is considered to be appropriate with the characteristics of PSO to orientate, manage, and assess operations of AIS toward attaining SP. Thus, this study is undertaken with the aim at exploring the relationship between the impact of public sector scorecard (PSS) implementations and effectiveness of AIS toward SP enhancement with evidence gathered from 883 PSOs’ accountants in Mekong Delta region. Data analyzed by the Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) highlight that PSS adoption has a significant impact on the effectiveness of AIS. It also provides a reliable basis for the association between the effectiveness of AIS and SP. Although the topic of research is still immature, these findings are predicted to serve as a catalyst for scholars, practitioners, and policymakers to inquire and adopt because of its potential benefits in PSOs’ operations.
1. Introduction
Accounting information system (AIS) is acknowledged as an effective tool to deal with the exterior and interior changes (Shagari, Abdullah, & Saat, 2017) through processing data and transaction to generating useful information for planning, controlling, and operating the organizational activities (Romney, Steinbart, & Cushing, 1997) as well as facilitating and gaining organizational performance (Saganuwan, Ismail, & Ahmad, 2013). This issue has directed the scholars’ attention on AIS effectiveness since such useful accounting information will contribute to the organizational efficiency improvement and accountability accomplishment (Mellemvik, Monsen, & Olson, 1988).
7.1. Conclusion
Based a theoretical point of view, the current research aims to explore whether PSS implementations are associated with the effectiveness of AIS in enhancement SP with evidence gathered from PSOs in Mekong Delta region. The results of the study provide a reliable basis for the link between PSS implementation and the effectiveness of AIS in PSOs. Accordingly, each of AISs’ components plays a vital role in promoting environment performance, social performance, and economic performance to ensure the enhancement in overall organizational SP. In this regard, the researchers’ experiences propose some implications that need to be further taken into consideration.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. بکارگیری کارت امتیازی بخش دولتی، سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری و عملکرد پایدار در بخش دولتی
2.1. کارت امتیازی بخش دولتی (PSS)
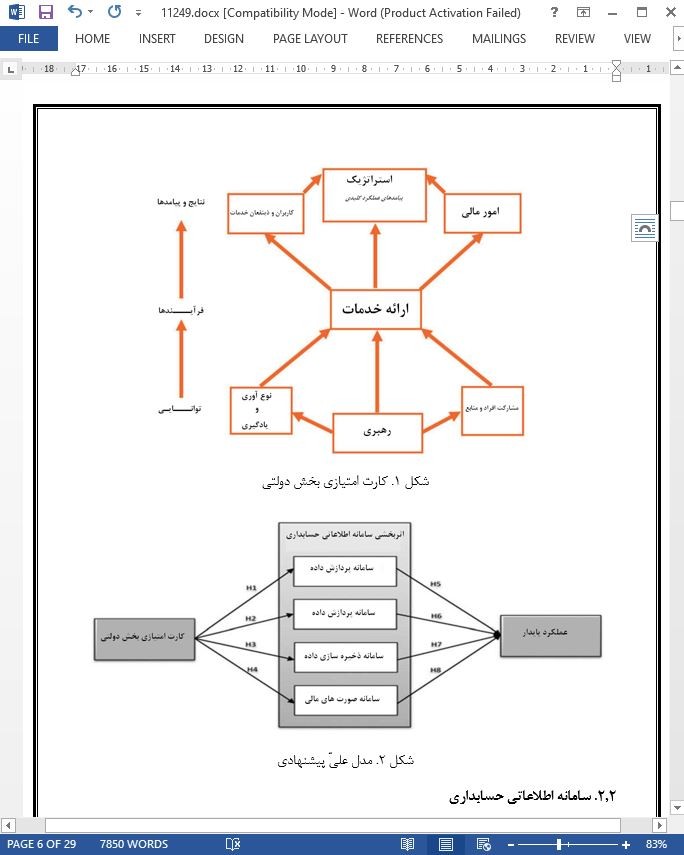
2.2. سامانه اطلاعاتی حسابداری
2.3. عملکرد پایدار
3. چارچوب نظری
3.1. نظریه هدف گذاری
4. مروری بر مقالات پیشین و فرضیه سازی
4.1. مروری بر مقالات پیشین
4.2. فرضیه سازی
5. روش تحقیق
5.1. طراحی، جمعیت و نمونه تحقیق
5.2. معیارها و پرسشنامه
6. نتایج و مباحث تجربی
6.1. ویژگی آماری جمعیت نمونه
6.2. مرحله تأییدی: مطالعه مقیاس بزرگ
6.3. نتایج حاصل از مدل سازی معادلات ساختاری
7. رئوس مطالب و نتیجه گیری
7.1. نتیجه گیری
7.2. پیامدها
7.3. محدودیت ها و فرصت های موجود برای تحقیقات آتی
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PSS adoption, AIS, and SP in public sector
2.1. Public sector scorecard
2.2. Accounting information system
2.3. Sustainable performance
3. Theoretical framework
3.1. Goal-setting theory
4. Empirical literature review and hypotheses development
4.1. Empirical literature review
4.2. Hypotheses development
5. Research design
5.1. Design, population, and sample
5.2. Measures and the questionnaire
6. Empirical results and discussion
6.1. Demographic profile of the sample
6.2. Confirmatory phase: large-scale study
6.3. Result of the SEM
7. Summary and conclusion
7.1. Conclusion
7.2. Implication
7.3. Limitations and extensions for further research
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه