استراتژی های خاموش / روشن کردن ایستگاه های دینامیک برای شبکه های سلولی سبز
چکیده
در این مقاله، به بررسی ایستگاه کلیدزنی پایه دینامیک (BS) به منظور کاهش انرژی مصرفی در شبکه های سلولی بی سیم می پردازیم. به طور خاص ، ما یک مساله حداقل سازی انرژی کلی مربوط به کلیدزنی BS را فرموله می کنیم که به عنوان یک مساله دشوار با محاسبات پیچیده و بار سیگنالی بالا شناخته می شود. ما یک الگوریتم به صرفه انرژی براساس کلیدزنی روشن / خاموش (SWES) پیشنهاد می کنیم که قابلیت پیاده سازی در روش پراکنده با پیچیدگی محاسبات پایین را دارد. قانون کلیدی طراحی الگوریتم پیشنهادی خاموش کردن BS ها یکی پس از دیگری می باشد که با معرفی شبکه جدیدی تاثیرات بر شبکه را به حدقل می رساند ، که بارهای اضافی BS های مجاور را نیز محاسبه می کند. به منظور کاهش بیشتر علامت دهی و بکارگیری سربار روی هوا و داده های متمرکز ، سه نسخه ی دیگر SWES را ارائه می دهیم که از مقادیر تقریبی به عنوان معیار تصمیم گیری بهره می برند. توضیح می دهیم که چگونه از الگوریتم ارائه شده می توان در عمل در سطح پروتکل و همچنین برای محاسبه میزان صرفه جویی انرژی از طریق تجزیه و تحلیل مرتبه اول در یک محیط ساده استفاده کرد. شبیه سازی گسترده نشان می دهد که الگوریتم SWES به طور قابل توجهی می تواند به کاهش مصرف انرژی کلی منجر شود ، بعنوان مثال برآورد ما 50-80٪ صرفه جویی بالقوه بر اساس مشخصات ترافیک واقعی در یک منطقه شهری است.
1 . معرفی
الف . انگیزه
به تازگی انقلابی در داده های موبایل [2] رخ داده است که توسط گوشی های هوشمندی که به اینترنت دسترسی داشته و برنامه های چند رسانه ایی متنوعی دارند هدایت می شود. با این حال این مطلب مصرف انرژی را افزایش داده و ردپای کربن را به صنعت ارتباطات باز می کند. بطور خاص تمام تکنولوژی اطلاعات و ارتباطات (ICT) سهمی به اندازه 2٪ از انتشار CO2 در حال حاضر و سهمی به اندازه 5/1٪ (CO2e)1 در سال 2007 داشتند [3],[4] . یک مطالعه کمی در [5] شکلی که در ادامه می آید نرخ انتشار CO2 را برای شبکه های سلولی به ترتیب در سال 2007 و 2020 به میزان 4/0 و 2/0 تخمین می زند. توجه داشته باشید ، درحالیکه اثر کلی ICT بین سال های 2007 و 2020 دوبرابر است ، اثر شبکه های سلولی تقریبا سه برابر در همان دوره زمانی پیش بینی شده است.
6 . نتیجه گیری
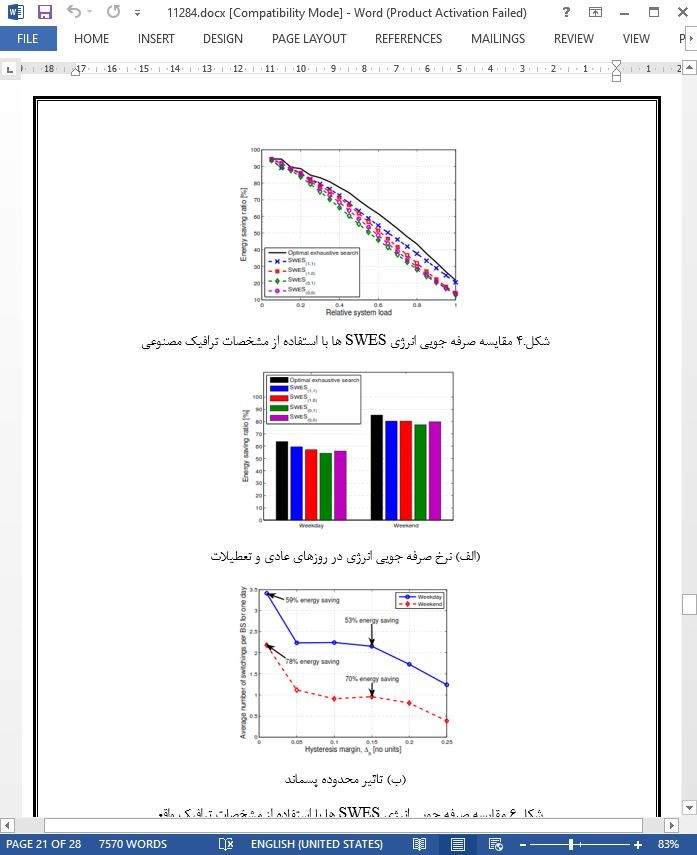
در این مقاله، ما بر روی مشکل کلیدزنی BS برای صرفه جویی در انرژی در شبکه های سلولی بی سیم متمرکز شدیم. بطور خاص یک اصل طراحی براساس مفهوم تازه ی تاثیر شبکه را پیشنهاد نمودیم. با توجه به مشکل پیاده سازی، پیچیدگی محاسباتی و میزان مشکلات اطلاعات بازخورد، ما چندین الگوریتم SWES ارائه دادیم. بعلاوه الگوریتم پیشنهادی ما برای الگوریتم توزیع برخط طراحی شده است که می تواند بدون کنترلر مرکزی کار کند. در نهایت، با استفاده از تجزیه و تحلیل مرتبه اول نشان دادیم که میزان انرژی صرفه جویی شده به نسبت ترافیک ، میانگین ، واریانس و استقرار BS وابسته می باشد. ما به صورت تجربی نشان دادیم که الگوریتم های ساده پیشنهادی نه تنها می توانند عملکردی نزدیک به الگوریتم جامع بهینه داشته باشند بلکه می توانند به صرفه جویی قابل توجهی تا 80٪ دست یابند.
Abstract
In this paper, we investigate dynamic base station (BS) switching to reduce energy consumption in wireless cellular networks. Specifically, we formulate a general energy minimization problem pertaining to BS switching that is known to be a difficult combinatorial problem and requires high computational complexity as well as large signaling overhead. We propose a practically implementable switching-on/off based energy saving (SWES) algorithm that can be operated in a distributed manner with low computational complexity. A key design principle of the proposed algorithm is to turn off a BS one by one that will minimally affect the network by using a newly introduced notion of network-impact, which takes into account the additional load increments brought to its neighboring BSs. In order to further reduce the signaling and implementation overhead over the air and backhaul, we propose three other heuristic versions of SWES that use the approximate values of network-impact as their decision metrics. We describe how the proposed algorithms can be implemented in practice at the protocol-level and also estimate the amount of energy savings through a first-order analysis in a simple setting. Extensive simulations demonstrate that the SWES algorithms can significantly reduce the total energy consumption, e.g., we estimate up to 50-80% potential savings based on a real traffic profile from a metropolitan urban area.
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Motivation
Recently, there has been an explosion in mobile data [2], which is mainly driven by smart-phones that offer ubiquitous Internet access and diverse multimedia applications. However, this also brings ever-increasing energy consumptions and carbon footprint to the mobile communications industry. In particular, the whole information and communication technology (ICT) sector has been estimated to contribute to about 2 percent of global CO2 emissions, and about 1.5 percent of global CO2 equivalent (CO2e1) emissions in 2007 [3], [4]. A quantitative study in [5] estimated the corresponding figure for cellular networks to be 0.2 and 0.4 percent of the global CO2e emissions in 2007 and 2020, respectively. Note that while the overall ICT footprint will less than double between 2007 and 2020, the footprint of cellular networks is predicted to almost triple within the same period.
VI. CONCLUSION
In this paper, we focused on the problem of BS switching for energy savings in wireless cellular networks. In particular, we suggested a design principle based on the newly introduced concept of network-impact. Taking into account the implementation difficulty, the computational complexity and the amount of feedback information problems, we proposed several SWES algorithms. Furthermore, our proposed algorithms are designed to be online distributed algorithms that could be operated without any centralized controller. Finally, from the first-order analysis we showed the amount of energy saving is dependent upon the traffic ratio of mean and variance and the BS deployment. We empirically showed that the proposed simple algorithms can not only perform close to the optimal exhaustive algorithm but also can achieve significant energy savings up to 80%.
چکیده
1 . معرفی
الف . انگیزه
ب . سهم اصلی
ج . کارهای قبلی
2 . مشخصات سیستم و فرمولبندی مساله
الف . مشخصات سیستم
ب . فرمولبندی کلی مساله
3 . الگوریتم پیشنهادی SWES
الف . طرح منطقی : نماد تاثیر سیستم
ب . جزئیات الگوریتم
ج . ابتکارات با توجه به پیاده سازی عملی
د . دیگر مسائل پیاده سازی
4 . آنالیز مرتبه اول
5 . آنالیز عددی
الف . صرفه جویی انرژی توسط الگوریتم SWES
ب . مشخصات الگوریتم SWES
6 . نتیجه گیری
7. کارهای آینده
Abstract
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Motivation
B. Main Contribution
C. Prior Work
II. SYSTEM DESCRIPTION AND PROBLEM FORMULATION
A. System Description
B. General Problem Formulation
III. THE PROPOSED SWES ALGORITHM
A. Design Rationale: A Notion of Network-impact
B. Algorithm Description
C. Heuristics Considering Practical Implementation
D. Other Implementation Issues
IV. FIRST-ORDER ANALYSIS
V. NUMERICAL ANALYSIS
A. Energy Saving by the SWES Algorithm
B. Characteristics of the SWES Algorithm
VI. CONCLUSION
VII. FUTURE WORK
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه