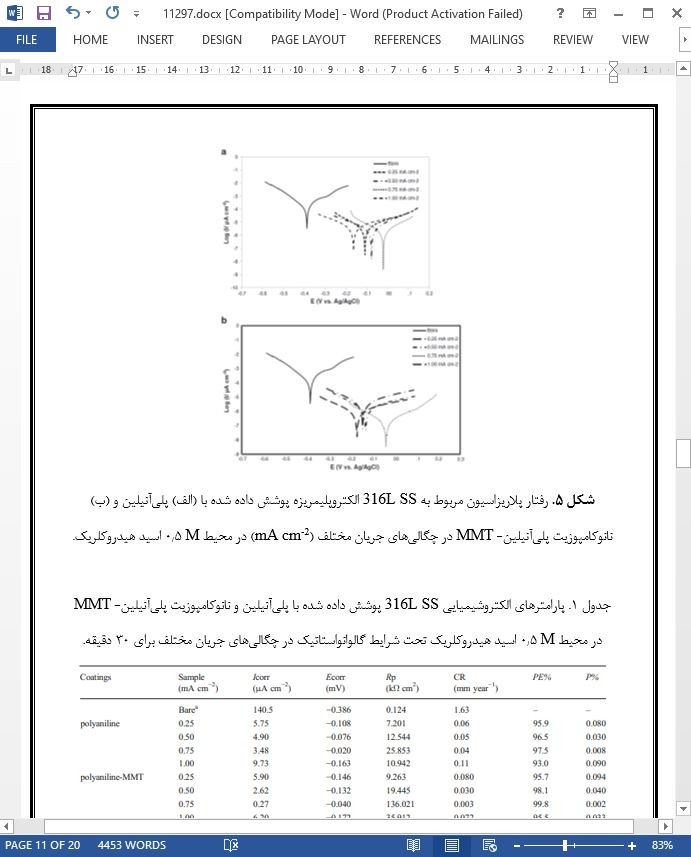
رسوب دهی الکتریکی پوشش های نانوکامپوزیتی پلیآنیلین- مونت موریلونیت بر فولاد ضدزنگ 316L
چکیده
سنتز پوششهای نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- مونتموریلونیت (MMT) بر سطح فولاد ضدزنگ 316L (316L SS) با استفاده از روش گالوانواستاتیک مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. پوششهای سنتز شده به وسیله اسپکتروسکوپی مادون قرمز تبدیل فوریه (FT-IR)، اسپکتروسکوپی جذبی UV-vis و میکروسکوپ الکترونی پویشی (SEM) مشخصهیابی شدهاند. عملکرد ضدخوردگی پوششهای نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT در محیط اسید هیدروکلریک M 5/0 از روش پلاریزاسیون پتانسیودینامیک و اسپکتروسکوپی آمپدانس الکتروشیمیایی (EIS) مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. نرخ خوردگی 316L SS پوشش داده شده با نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT، تقریباً 540 برابر کمتر از 316L بدون پوشش بوده و خوردگی بالقوه از V 386/0- در مقابل Ag/AgCl برای 316L SS بدون پوشش تا V 040/0- در مقابل Ag/AgCl برای الکترودهای 316L SS پوشش داده شده با نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT افزایش یافته است. اندازهگیریهای الکتروشیمیایی حاکی از آن میباشند که 316L SS پوشش داده شده با نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT داری خواص بازدارندگی خوبی با بازدهی متوسط تقریباً %8/99 در چگالی جریان mA cm-2 75/0 اعمالی بر 316L SS خورده شده در محیط اسیدی میباشد. نتایج این تحقیق به روشنی ثابت میکند که نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT دارای پتانسیل بالقوهای جهت حفاظت از 316L SS در مقابل خوردگی در محیط اسیدی میباشد.
مقدمه
آهن و آلیاژهای آن در بسیاری از کاربردها به صورت گسترده مورد استفاده بوده و تنوع این کاربردها موجب افزایش تعداد تحقیقهای مربوط به افزایش مقاومت خوردگی فلزات مبتنی بر آهن در محیطهای خنثی و تهاجمی شده است [1- 7]. فولاد ضدزنگ از گونه 316L (316L SS) به دستهای از فلزات و آلیاژها تعلق دارد که به وسیله لایه غیرفعالی که بر روی آن ایجاد شده است، محافظت میگردد. با این وجود این آلیاژها در مقابل خطرات موضعی، آسیبپذیر میباشند؛ حتی فولادهای بسیار آلیاژی نیز در محلولهای قوی کلرید خورده میشوند. خوردگی موضعی 316L SS، یکی از جدیترین مشکلات فراروی بکارگیری این آلیاژها است [8]. این حملات موضعی یکی از محدودیتهای حائز اهمیت مواد برای کاربردهای زیستپزشکی است [9، 10]. رهایش یونهای فلزی همچون آهن، کروم و نیکل در محیط بیولوژیک اطراف آلیاژ باعث کاهش زیستسازگاری آن میشود. روشهای مختلفی جهت ایجاد سطوحمشترک با قابلیت حفاظت بیشتر بر فولادهای ضدزنگ وجود دارند که از جمیه این روشها میتوان به پلیمرهای هادی اشاره نمود [11- 13].
نتیجهگیری
پوششهای پلیآنیلین و نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT با موفقیت از سنتز الکتریکی مستقیم بر زیرلایههای 316L SS از محلول آبی حاوی H2SO4 و مونومرهای آنیلین با نانوذرات MMT پخش شده برای ایجاد نانوکامپوزیت ایجاد شدهاند. پوششهای یکنواخت، متراکم و چسبنده را میتوان تحت شرایط گالوانواستاتیک بدست آورد. برای ایجاد پوششهای پلیآنیلین و نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT بر روی 316L SS از چگالی جریانهای مختلف 25/0، 5/0، 75/0 و mA cm-2 00/1 استفاده شده است. نتایج نشان میدهند که mA cm-2 75/0 برای مرحله پلیمریزاسیون، بهترین شرایط موجود برای سنتز پوششهای پلیآنیلین و نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT متراکمتر و چسبندهتر بر روی 316L SS به شمار میآیند. پوششهای پلیآنیلین و نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT به وسیله FT-IR، UV-vis و SEM مشخصهیابی شده و ویژگیهای مقاومت در برابر خوردگی آنها با استفاده از پلاریزاسیون تافل و اسپکتروسکوپی آمپدانس الکتروشیمیایی در محیط M 5/0 اسید هیدروکلریک مورد ارزیابی قرار گرفتهاند. تخلخل پوشش با استفاده از اندازهگیریهای پلاریزاسیون پتانسیودینامیک ارزیابی شده و دریافته شده است که مقادیر تخلخل برای پوششهای نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT در مقایسه با پوششهای پلیآنیلین به میزان چشمگیری پایینتر است.
Abstract
The synthesis of polyaniline- montmorrilonite (MMT) nanocomposite coatings on 316L stainless steel (316L SS) surface has been investigated by using the galvanostatic method. The synthesized coatings were characterized by Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR), UV-visible absorption spectrometry and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The anticorrosion performances of polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coatings were investigated in 0.5 M HCl medium by the potentiodynamic polarization technique and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS). The corrosion rate of polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coated 316L SS was found ∼540 times lower than bare 316L SS and potential corrosion increased from −0.386 V versus Ag/AgCl for uncoated 316L SS to −0.040 V versus Ag/AgCl for polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coated 316L SS electrodes. Electrochemical measurements indicate that polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coated have good inhibiting properties with mean efficiency of ~99.8 % at 0.75 mA cm−2 current density applied on 316L SS corrosion in acid media. The results of this study clearly ascertain that the polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite has an outstanding potential to protect 316L SS against corrosion in an acidic environment.
Introduction
Iron and its alloys are widely used in many applications and diversity of these applications were intensified the researches relating to enhancement of corrosion resistance of iron based metals in various neutral or aggressive environments [1–7] Type 316L stainless steel (316L SS) belong to a class of metals and alloys that are protected by a passive film formed on their surface. However, these alloys are susceptible to localised attack; even high alloyed steels may corrode in strong chloride solutions. The localised corrosion of 316L SS is one of the most serious problems facing the use of these alloys [8]. This localized attack is an especially important limitation of the material for biomedical applications [9, 10]. The release of metal ions such as iron, chromium and nickel in the biological environment surrounding the alloy results in a decreased biocompatibility. Several strategies have been used to generate more protective interfaces on stainless steels, including the use of conducting polymers [11–13].
Conclusions
The polyaniline and polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coatings were successfully direct electrosynthesized on 316L SS substrates from aqueous solution containing H2SO4 and aniline monomers with dispersed MMT nanoparticles for nanocomposite. Uniform compact and adherent coatings can be obtained under galvanostatic condition. Four various current densities of 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1.00 mA cm−2 were applied for the formation of polyaniline and polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coatings on 316L SS. The results showed that the current density of 0.75 mA cm−2 for the polymerization stage is the best condition for the synthesis of more compact and strongly adherent polyaniline and polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coatings on 316L SS. The polyaniline and polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coatings were characterized by FT-IR, UV–vis and SEM and the corrosion resistant properties of the electropolymerized coatings were evaluated using Tafel polarization and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in 0.5 M HCl medium. The coating porosity was estimated by using the potentiodynamic polarization measurements and it was found that the porosity values are significantly lower for the polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite coatings as compared to the polyaniline.
چکیده
مقدمه
مواد و روشها
نتایج و بحث
الکتروپلیمریزاسیون
مشخصهیابی فیلمهای نانوکامپوزیت پلیآنیلین- MMT
عملکرد حفاظت خوردگی پوشش سنتز شده با روش الکتریکی
مشخصهیابی SEM
نتیجهگیری
Abstract
Introduction
Material and methods
Results and discussion
Electropolymerization
Characterization of polyaniline-MMT nanocomposite films
Corrosion protection performances of the electrosynthesized
SEM characterization
Conclusions
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه