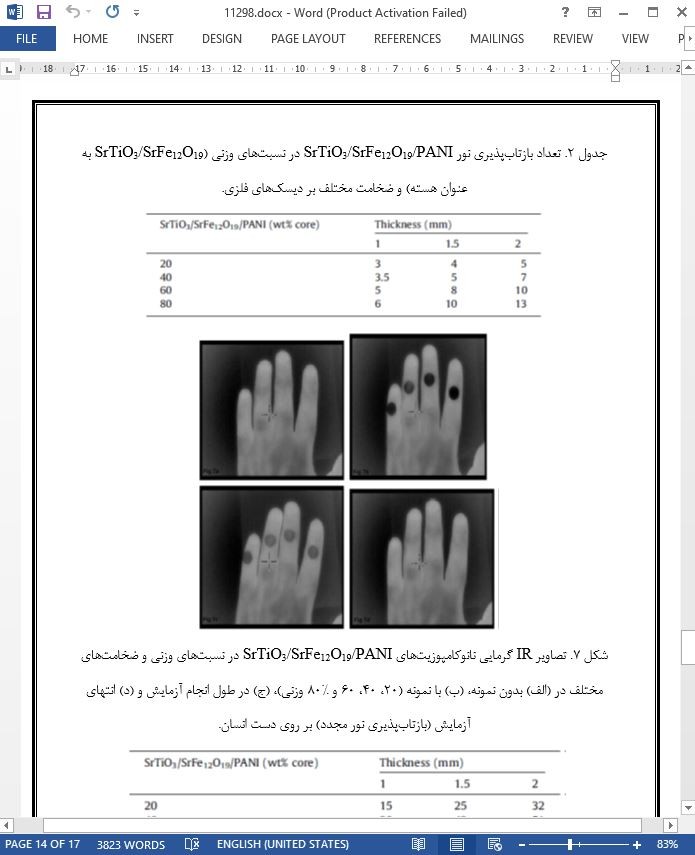
خواص جذبی مادون قرمز و میکروویو حرارتی نانوکامپوزیت های SrTiO3/ SrFe12O19/ پلیآنیلین
چکیده
پلیآنیلین (PANI)، پلیمر منحصر به فردی است که دارای خاصیت جذب الکترومغناطیسی بوده و به عنوان زیرلایه مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد. در این تحقیق، SrTiO3 به عنوان جاذب نور مادون قرمز و هسته و سپس با روش همرسوبی، SrFe12O19 به عنوان جاذب مایکروویو به عنوان پوسته ماده نخست بر روی آن SrTiO3 سنتز میشود. در گام بعدی، PANI از طریق پلیمریزاسیون در جا با ساختارهای هسته- پوسته چندگانه بر نانوذرات SrTiO3/ SrFe12O19 پوشش داده میشود. اندازه نانومتری و ساختار این نمونهها با استفاده از TEM، XRD و FTIR مورد بررسی قرار میگیرند. مورفولوژی نانوکامپوزیت توسط تصاویر SEM نشان داده شده است. خواص مغناطیسی و الکتریکی نیز با روشهای VSM و چهار پروبه انجام شده است. جذب مادون قرمز (IR) گرمایی و اتلاف بازتاب مایکروویو در μm 40 -10 و GHz 12 -8 به ترتیب مربوط به بسامدهای مادون قرمز و مایکروویو مورد بررسی قرار گرفتهاند. نتایج نشان دادهاند که نانوکامپوزیتهای SrTiO3/ SrFe12O19/PANI دارای خواص الکتریکی و مغناطیسی بسیار سازگاری بوده و بنابراین جذبپذیری مایکروویو، خواص پهنباند بسیار عریضی را نشان میدهد. آزمون تصویر گرمایی مادون قرمز، تابع تصویربرداری گرمایی مادون قرمز را نشان داده است که با افزایش SrTiO3/ SrFe12O19 به عنوان هسته بهینهسازی شده و وابسته به افزایش PANI به عنوان پوسته نهایی میباشد.
1. مقدمه
تابش مادون قرمز گرمایی به عنوان متداولترین منبع گرمای تابشی شناخته شده است. ناحیه مادون قرمز گرمایی، محدوده طولموج طیف الکترومغناطیسی است که از مشخصههای تابش گرمایی یا حرارتی از سطح و جو زمین میباشد. در تعادل گرمایی، قانون پلانک بر گسیل تابش در محدوده مادون قرمز حاکم میباشد که توزیع طیفی انرژی منتشر شده از اجسام ”سیاه“ (یعنی اجسامی که در تمامی طولموجها دارای تابندگی یا گسیلپذیری واحد میباشند) به صورت تابعی از دما را توصیف مینماید. هم سطح و هم اتمسفر زمین در محدوده مادون قرمز ”گرمایی“ از خود تابش منتشر مینمایند که دارای توزیعهای طیفی هستند که به وسیله تابع پلانک متناظر با دمای موضعی (یعنی دمای سطح زمین و دما به صورت تابعی از ارتفاع از سطح زمین) توصیف میشوند.
4. نتیجهگیری
نانوکامپوزیتهای SrTiO3/SrFe12O19/PANI دارای شکل و اندازه تعریف شده بسیار خوبی بوده و هدایت الکتریکی خوبی را از خود نشان میدهند. تعداد دفعات بازتابش نور نمونههای روی بدن انسان از دیسکهای فلزی بالاتر میباشد. بنابراین این نانوکامپوزیتها برای جذب تابش مادون قرمز گرمایی بسیار مناسب میباشند. با افزایش نسبت وزنی و ضخامت، تعداد دفعات بازتابپذیری نور افزایش یافته است. با افزایش نسبت وزنی هسته، دمای بدن انسان را نمیتوان به نمونهها انتقال داد. بنابراین نسبت وزنی (SrTiO3/SrFe12O19 به عنوان هسته) بالاتر از %40 و قطر mm ، بهترین نتیجه بدست آمده برای مواد جاذب مادون قرمز حرارتی میباشد. افزایش جذب نور مادون قرمز پهنباند در محدوده طولموج μm 40 -10 مشاهده شدهاند. کمترین مقدار RL برابر با dB 15- در GHz 2/9 برای نانوکامپوزیتی با ضخامت mm 1 مشاهده شده است. بکارگیری این نمونهها میتواند کارایی آشکارسازی ترموگرافی IR، کاتالیزورها، سنسورها، ذخیرهسازی مغناطیسی دادهها، جذب امواج تشدید الکترومغناطیسی، بلورهای فوتونیک و ابزارهای میکروالکترونیک و جنبههای نظامی را بهبود بخشیده و آنها را افزایش دهد.
Abstract
Polyaniline (PANI) as a unique polymer that also has electromagnetic absorption used as the substrate. In this research, SrTiO3 was synthesized as IR absorbent and core and then SrFe12O19 as microwave absorbent was prepared on SrTiO3 via co-precipitation method as the first shell. As the next step, PANI was coated on SrTiO3/SrFe12O19 nanoparticles via in situ polymerization by multi core–shell structures (SrTiO3/SrFe12O19/PANI). Nanometer size and structures of samples were measured by TEM, XRD and FTIR. Morphology of nanocomposite was showed by SEM images. The magnetic and electric properties were also performed by VSM and four probe techniques. Thermal infrared (IR) absorption and microwave reflection loss of nanocomposites were investigated at 10–40 μm and 8–12 GHz, IR and microwave frequencies, respectively. The results showed that the SrTiO3/SrFe12O19/PANI nanocomposites have good compatible electric and magnetic properties and hence the microwave absorbency shows wide bandwidth properties. The infrared thermal image testing showed that the function of infrared thermal imaging was optimized by increasing SrTiO3/SrFe12O19 as core and independent to increasing PANI as the final shell.
1. Introduction
Thermal infrared radiation is much commonly known as kind of radiative heat. The thermal infrared region is the wavelength range of the electromagnetic spectrum which is also a characteristic of the thermal or heat radiation from the Earth’s surface and from the atmosphere. In thermal equilibrium, the emission of radiation in the infrared is governed by Planck’s law, which describes the spectral distribution of the energy emitted by ‘‘black’’ bodies (i.e. having unit emissivity at all wavelengths) as a function of temperature. Both the Earth’s surface and the atmosphere emit in the so-called ‘‘thermal’’ infrared, having spectral distributions described by the Planck function corresponding to the local temperature, (i.e. the surface temperature of the Earth and the temperature as function of altitude.)
4. Conclusion
The SrTiO3/SrFe12O19/PANI nanocomposites were well defined in size and shape and exhibited good electrical conductivity. The light reflectivity times of samples on human body are higher than metallic disks. So, they are suitable for thermal IR absorbers. The light reflectivity times of samples were increased by increasing weight ratio and thickness. Human temperature could not transmit to samples by increasing weight ratio of core. Therefore weight ratio (SrTiO3/SrFe12O19 as core) above 40% and 1 mm diameter are the best result as thermal IR absorber. The SrTiO3/SrFe12O19/PANI enhanced broad band infrared light absorption was observed in the wavelength range of 10–40 lm. A minimum RL of 15 dB was observed at 9.2 GHz for a 1 mm thickness nanocomposite. The application of these samples may improve the IR thermographic detection, catalysis, sensors, magnetic data storage, electromagnetic resonance wave absorption, photonic crystals, and microelectronic devices and military aspects.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. بخش تجربی
2. 1. مواد
2. 2. آماده سازی پلیمتیل متاکریلات (PMMA)
2. 3. آمادهسازی نانوذرات SrTiO3
2. 4. سنتز نانوذرات SrTiO3/SrFe12O19 (با درصد وزنی %50/50)
2. 5. سنتز نانوکامپوزیتهای SrTiO3/SrFe12O19/PANI
2. 6. مشخصهیابی
3. نتایج و بحث
3. 1. دادههای XRD
3. 2. اسپکتروسکوپی FTIR
3. 3. آنالیز TEM
3. 4. تصاویر SEM
3. 5. مغناطیسسنج نمونه مرتعش (VSM)
3. 6. رسانایی
3. 7. بررسی جذب مادون قرمز گرمایی
3. 8. مطالعه جذب مایکروویو
4. نتیجهگیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA)
2.3. Preparation of SrTiO3 nanoparticles
2.4. Synthesis of SrTiO3/SrFe12O19 nanoparticles (50/50% w/w)
2.5. Synthesis of SrTiO3/SrFe12O19/PANI nanocomposites
2.6. Characterization
3. Results and discussion
3.1. XRD data
3.2. FTIR spectroscopy
3.3. TEM analysis
3.4. SEM images
3.5. Vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM)
3.6. Conductivity
3.7. Thermal infrared absorption study
3.8. Microwave absorbing study
4. Conclusion
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه