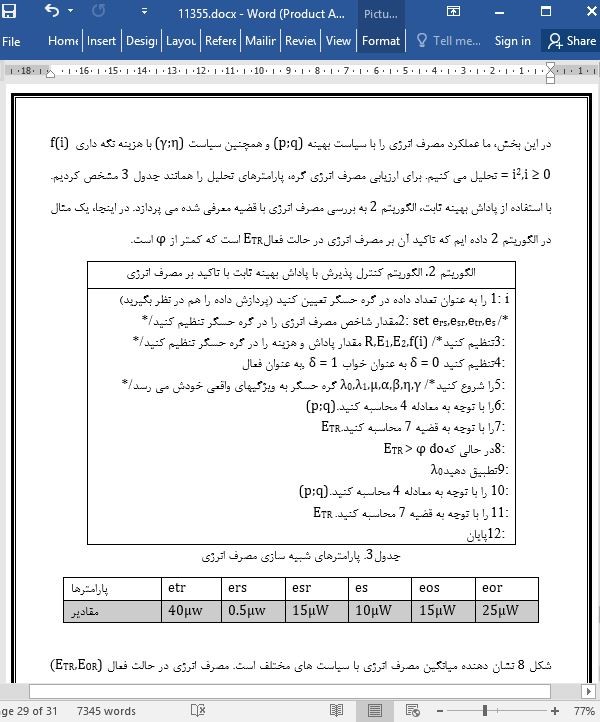
حداکثر بازده در شرایط کنترل پذیرش با طول صف نامشخص در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم
چکیده
در یک گره شبکه حسگر بی سیم (WSN)، با افزایش ترافیک ورودی، بازده می تواند ابتدا افزایش داشته باشد و سپس کاهش پیدا کند و این مطلب دلالت بر تراکم در حائل دارد. این عامل بیانگر نیاز به مکانیزم کنترل پذیرش برای حفظ بازده بالا با افزایش ترافیک ورودی می باشد. با در نظر گرفتن ماهیت تصادفی شبکه حسگر بی سیم) (WSN، اطلاعات طول صف بسته های داده های ورودی جدید می تواند در یک گره نا مشخص باشد. این مقاله یک مدل کنترل پذیرش احتمالی با حداکثر بازده برای گره معرفی کرده است. در مدل معرفی شده، پاداش وقتی که بسته داده به حسگر می رسد پذیرفته می شود (رد نمی شود) و در نظر گرفته می شود، اما حفظ هزینه در هر واحد زمان برای تاخیر در بسته های پذیرفته شده در حسگر نیز تحمیل می شود. در گره حسگر، با ساخت یک فرآیند تصمیم گیری مناسب مارکوف (MDP)، یک الگوریتم احتمالی کنترل پذیرش در مورد چگونگی پذیرش بسته های داده ها در فازهای خواب و فعال برای رسیدن به حداکثر بازده معرفی شده است. به علاوه، برای مدل شناسایی شده(p;q)، مصرف انرژی در گره در فازهای خواب و فعال و همچنین تغییر مصرف انرژی از حالت فعال به خواب در هر واحد زمان و برعکس بررسی شده است. یک شبیه سازی گسترده استفاده شده است. نتایج عددی نشان می دهد که این مسئله از طریق یک طرح بهینه با کارایی بالای انرژی حل می شود. نتایج این مقاله می توانند در طراحی گره های حسگر بهینه در شبکه حسگر بی سیم) WSN (استفاده شوند.
1. مقدمه
شبکه های حسگر بی سیم به صورت گسترده در حوزه های متعددی چون کنترل محیط، هشدار بلایای طبیعی و هوش صنعتی استفاده می شوند که دلیل آن گسترش ساده و هزینه پایین است. در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم
(WSN)، گره ها متغیرها را از محیط دریافت می کنند و داده های گردآوری شده را از طریق بسته های داده ها با سایر گره ها تبادل می کنند. بازده یکی از شاخص های شبکه حسگر بی سیم) WSN (است. با افزایش بازده، بار گره نیز افزایش می یابد. سیاست های کنترل پذیرش برای حفظ بازده بالا برای یک شبکه یکی از موضوعات تحقیقاتی در دوره زمانی بلند مدت بوده است (1). در مدلهای کنترل پذیرش، هزینه نگه داری برای تاخیر در بسته های داده ها در یک حسگر وجود دارد. هزینه نگه داری با افزایش بسته های داده ها در بافر حسگر افزایش می یابد (2),(3),(4). توسعه یک سیاست کنترل پذیرش بهینه در فرآیند گردآوری داده در شبکه حسگر بی سیم (WSN) معنا دار است.
VII. نتیجه گیری
در این مقاله، ما سیاست (p;q) را برای مسئله حداکثر بازده در فرآیند پذیرش داده در گره های حسگر مطرح کردیم. فرآیند فعال در گره حسگر می تواند به صورت یک سیستم صف چند فازی مدلسازی شود که در آن مرحله اول برای مدیریت پذیرش داده های ورودی استفاده می شود و مرحله دوم برای برای مدیریت داده ها مورد استفاده قرار می گیرد. در مرحله اول، گره اطلاعات مربوط به طول صف ورودی یا بسته های اطلاعاتی تازه ارسال شده جدید را نمی داند. بنابراین، یک مدل (p;q) معرفی شده است که در آن یک حسگر، بسته های اطلاعاتی با احتمال p را در حالت خواب و احتمال q در حالت فعال تولید می کند. در این مدل، در طول فرآیند پذیرش داده، پاداش برای پذیرش بسته های داده و هزینه نگه داری در هر واحد زمانی برای تاخیر بسته های داده ها در حسگر در نظر گرفته شده است. ما مشاهده کردیم که، با توجه به فرضیه خاص، یک سیاست بهینه (p;q) برای رسیدن به حداکثر بازده در طول فرآیند پذیرش داده وجود دارد. مقدار بهینه p وq برای سیاست (p;q) مورد بررسی قرار گرفته است. عملکرد مصرف انرژی در مدل معرفی شده مطالعه شده است. به علاوه، بازده، میزان پاداش ثابت و عملکرد انرژی مدل از طریق تحلیل عددی انجام شده است. نتایج این مقاله می توانند در طراحی گره های حسگر بهینه در شبکه های حسگر بی سیم(WSN) مورد استفاده قرار بگیرند.
Abstract
In a Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) node, as the input traffic increases, the throughput can be assumed to first increase and then start to decrease, indicating congestion in the buffer. This suggests the need for an admission control mechanism to maintain high throughput as the arrival traffic increases. Considering the stochastic nature of WSNs, the information of the queue-length of arrival or newly sensed data packets can be unknown to a sensor node. This paper proposes a probabilistic admission control model with the maximum throughput for the node. In the proposed model, a reward when a data packet arriving to a sensor is accepted (not rejected) for transmission is considered, but a holding cost per unit time for the delay of accepted data packets in the sensor is also incurred. For the sensor node, by constructing a suitable Markov decision process (MDP), a probabilistic admission control algorithm on how to accept data packets on sleep and active phases to achieve a maximum throughput is proposed. Furthermore, for the identified (p;q) model, the energy consumption of the node in active and sleep phases, as well as the energy consumption switching from active to sleep per unit time and vice versa is investigated. An extensive simulation is implemented. The numerical results show that the problem is effectively solved by an optimal scheme with high energy efficiency. The results of this paper can be applied in designing optimal sensor nodes in WSNs.
I. INTRODUCTION
WIRELESS Sensor Networks are widely used in many areas, such as environmental monitoring, disaster warning and industrial intelligence, due to the simple deployment and low cost. In WSNs, nodes sense variables from the environment and exchange collected data with other nodes through data packets. Throughput is a metric in WSNs. As the throughput increases, the load of the node increases.
Admission control policies for maintaining high throughput for a network have been an ongoing research topic for a long period of time [1]. In admission control models, there exists a holding cost for the delay of data packets in a sensor. The holding cost increases as the increase of data packets in the sensor’s buffer [2], [3], [4]. Developing an optimal admission control policy in data gathering process is meaningful in WSNs.
VII. CONCLUSION
In this article, we have proposed a (p; q) policy for the problem of the maximum throughput under data admission process in sensor nodes. A sensor node’s working process can be modeled as a multi-phase queuing system in which the fist stage is used to manage the admission of arrivals and the second stage is used to manage the service. In the fist stage, the node can not know the information of the queue-length of arrival or newly sensed data packets. Thus, a (p; q) model has been proposed in which a sensor generates data packets with probability p on sleep status and with probability q on active status. In the model, during data admission process, some reward for accepting data packets and a holding cost per unit time for data packets’ delay in the sensor have been considered. We have observed that, under certain assumptions, there exists an optimal (p; q) policy to obtain the maximum throughput during data admission process. The optimal value of p and q for the (p; q) policy has been investigated. The performance on energy consumption of the proposed model has been studied. In addition, the throughput, expected discounted reward and energy performance of the model through numerical analysis have been performed. The results of this paper can be applied in designing optimal sensor nodes in wireless sensor networks.
چکیده
I. مقدمه
II. تحقیقات مرتبط
III. مدل پایه حداکثر بازده
A. فرضیه ها
B. مسئله حداکثر بازده تحت کنترل پذیرش داده
IV. مدل مطرح شده برای حداکثر بازده
A. بازده در طول فرآیند پذیرش داده
B. چارچوب روش زمان پیوسته فرآیند تصمیم گیری مارکوف CTMDP)) برای رفتار گره های حسگر
C. سیاست کنترل بهینه
D. سیاست بهینه (p;q)
V. تحلیل مصرف انرژی
VI. نتایج شبیه سازی و تحلیل
A. عملکرد پاداش های ثابت
B. عملکرد مصرف انرژی
VII. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
I. INTRODUCTION
II. RELATED WORK
III. MAXIMUM THROUGHPUT BASE MODEL
A. Assumptions
B. The maximum throughput problem under data admission control
IV. PROPOSED MODEL FOR MAXIMUM THROUGHPUT
A. Throughput during data admission process
B. CTMDP framework for sensor nodes’ behavior
C. Optimal control policy
V. ENERGY CONSUMPTION ANALYSIS
VI. SIMULATION RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
A. Discounted rewards performance
B. Energy consumption performance
VII. CONCLUSION
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه