وابستگی معیشت روستایی به منابع جنگلی دره چپروت
خلاصه
برداشت بیش از حد منابع جنگلی ممتد به تهدیدی جدی برای محیط زیست در دره چپروت در شمال پاکستان است. بنابراین، این تحقیق به بررسی عوامل اصلی وابستگی خانوار ها به منابع جنگلی برای امرار معاش در دره چپروت می پردازد. ما داده ها را به روش تصادفی از 193 نفر از طریق پرسشنامه نیمه ساختار یافته جمع آوری کردیم. سهم درآمد جنگل در مجموع درآمد خانوار 32 درصد بود در حالیکه درآمد غیرکشاورزی، درآمد کشاورزی و درآمد دام به ترتیب 44 درصد، 13 درصد و 9 درصد بود. در میان تمام محصولات جنگلی، هیزم با 47 درصد سهم، بیشترین مشارکت در درآمد جنگل را داشت. علاوه بر این، این مطالعه نشان داد که افزایش در تحصیلات سرپرست خانوار، درآمد دام، درآمد کشاورزی، درآمد غیرکشاورزی و درآمد حاصل از مالکیت زمین باعث کاهش وابستگی جنگل خواهد شد. این مطالعه نتیجه گیری می کند که منابع جایگزین انرژی، روش های کشاورزی مدرن، دسترسی به تحصیلات عالی و آگاهی عمومی در مورد تنوع زیستی برای ایجاد تعادل بین وابستگی به جنگل و حفاظت از تنوع زیستی ضروری هستند.
مقدمه
معیشت روستایی به شدت به منابع محیطی در کشور های در حال توسعه وابسته است. مهمتر از همه، منابع اکولوژیکی مانند الوار، هیزم، غذا دارو نقش حیاتی در معیشت مردم روستایی ایفا می کنند (Angelsen et al., 2014;Babulo et al., 2009;Fikir et al., 2016). خانوارهای مناطق روستایی نه تنها از منابع جنگلی برای برآورده کردن نیازهای معیشتی خود استفاده می کنند بلکه درآمد نقدی قابل توجهی را با محصولات جنگلی مبادله می کنند (Mamo et al., 2007). طبق یک تخمین، 20 درصد از جمعیت جهان به منابع جنگلی برای برآورده کردن نیاز های زندگی ضروری خود وابسته هستند (Cheng et al., 2019). این پیوند بین وابستگی به جنگل و حفاظت از تنوع زیستی نگرانی قابل توجهی را برای محققان به منظور درک عوامل وابستگی خانوار به منابع جنگلی در جهت پایداری مدیریت جنگل و حفاظت از تنوع زیستی ابراز می کند.
4- نتیجه گیری و کابردهای سیاستی
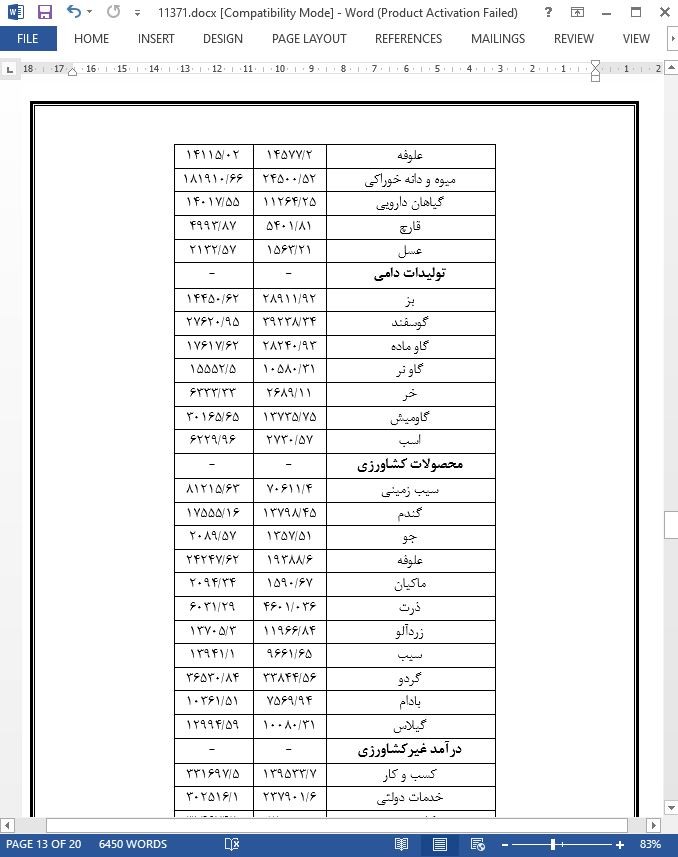
منابع جنگلی نقش مهمی در زندگی روستایی بازی می کنند، اما برداشت بی رویه این منابع باعث ایجاد مشکلات زیست محیطی برای حفاظت از تنوع زیستی و اکو سیستم می شود. هدف از این مطالعه بررسی عوامل موثر بر وابستگی به جنگل در دره چپروت در شمال پاکستان است. منابع اصلی درآمد در دره چاپروت شامل درآمد جنگل، درآمد دام، درآمد کشاورزی و درآمد غیرکشاورزی می باشد. نتایج این تحقیق نشان داد که درآمد جنگل دارای سهم قابلتوجه ۳۲ درصدی از کل درآمد خانوار است در حالی که درآمد غیر کشاورزی، درآمد کشاورزی و درآمد دام به ترتیب ۴۴ درصد، ۱۳ درصد و ۹ درصد است. درآمد جنگل دومین منبع بزرگ درآمد در میان سایر منابع درآمد است. هیزم با سهم 47 درصدی دارای سهم مهمی در درآمد حاصل از جنگل است. گذشته از این، ارتباط منفی تحصیلات سرپرست خانوار، درآمد کشاورزی، درآمد غیر کشاورزی و مالکیت زمین، نگرش مفیدی را برای محققان و سیاست گذاران ارائه می دهد. از این رو ، نتایج مطالعه ما تأیید می کند که افزایش درآمد غیرکشاورزی و درآمد کشاورزی منتج به کاهش وابستگی به جنگل در دره چاپروت می گردد.
Abstract
Overexploitation of forest resources continues to pose a severe threat to the environment in Chaprote Valley, Northern Pakistan. Therefore, this study investigates the main determinants of household dependency on forest resources for livelihoods in Chaprote Valley. We collected data randomly from 193 household heads through semi-structured questionnaires. To investigate the dependence of rural households on forest resources, we employed a Logistic regression model. The findings reveal that household’s education level, household size, livestock income and agriculture income significantly affect the dependency of households on forest resources, while other variables seem to be insignificant. The share of forest income to the total household income was 32%, while off-farm income, agriculture income and livestock income were 44%, 13% and 9% respectively. Among all forest products, firewood contributes more to forest income with a share of 47%. Moreover, the study found that an increase in household head’s education, livestock income, agriculture income, off-farm income and own landholding will result in reducing forest dependency. The study concludes that alternate sources of energy, modern agricultural methods, access to higher education, and public awareness about biodiversity are essential for creating a balance between forest dependency and biodiversity conservation.
1. Introduction
Rural livelihoods are highly dependent on environmental sources in developing countries. Most notably, the ecological resources such as timber, firewood, food, and medicines play a vital role in the livelihood of rural people (Angelsen et al., 2014; Babulo et al., 2009; Fikir et al., 2016). The households of rural areas not only utilize forest resources to fulfill their subsistence needs but also generate a significant cash income by trading forest products (Mamo et al., 2007). According to an estimation, 20% of the global population is dependent on forest resources to meet their essential livelihood needs (Cheng et al., 2019). This nexus between forest dependency and biodiversity conservation demonstrates a considerable concern for researchers and academicians to understand the factors of household dependence on forest resources for the sustainability of forest resource management and biodiversity conservation.
4. Conclusion and policy implications
Forest resources play a significant role in rural livelihood, but over-extraction of these resources causes environmental issues for biodiversity conservation and ecosystem. The study aimed to investigate the determinants affecting forest dependency in Chaprote Valley, Northern Pakistan. The primary sources of income in Chaprote Valley include forest income, livestock income, agriculture income, and off-farm income. The results of the study reveal that forest income contributes a significant share of 32% to the total annual household income while off-farm income, agriculture income and livestock income contributes 44%, 13% and 9% respectively. Forest income is the second-largest source of income among all others. Firewood makes a most substantial contribution in forest income with a share of 47%. Furthermore, the negative association of household head’s education, agriculture income, off-farm income and own landholding offers helpful insight for researchers and policymakers. Hence, the results of our study endorse that an increase of off-farm income and agriculture income will result in a lessening of forest dependency in Chaprote Valley.
خلاصه
1- مقدمه
2 - روش مطالعه
1-2- منطقه مورد مطالعه و نمونه گیری
2-2- جمع آوری داده ها
3-2- محاسبه درآمد
4-2- تصریح مدل
5-2- منطق انتخاب متغیر ها
3- نتایج و بحث
1-3- وضعیت خانوار
2-3- منابع عمده درآمد خانوار ها
3-3- سهم محصولات جنگلی در درآمد کل جنگل
4-3- عوامل تعیین کننده وابستگی به جنگل
4- نتیجه گیری و کابردهای سیاستی
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Study area and sampling
2.2. Data collection
2.3. Income computation
2.4. Model specification
2.5. The rationale for selecting variables
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Household profile
3.2. Primary income sources of households
3.3. Share of forest products to total forest income
3.4. Determinants of forest dependency
4. Conclusion and policy implications
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه