تخصیص منابع تطبیقی در پروتکل های موافق مبتنی بر رایانش ابری
چکیده
در سال های اخیر یک توجه ویژه به استفاده از سیستم های توزیع شده در هر حوزه ای، به خصوص سیستم های ابری وجود داشته است. مدیریت منابع به منظور تضمین کیفیت سرویس ها برای هر نوع برنامه کاربردی مشارکت می-کند، به خصوص وقتی یک سیستم عناصر ناهمگونی را دربر می گیرد که با محدوده متنوعی از منابع که ممکن-است با سیستم عامل های مخصوص یا محیط ها ترکیب شود یا نشود، مشخص می شود. یک مسئله بسیار نزدیک به صنعت، توانایی اختصاص منابع به طریق مؤثر و برآورد هزینه ها، به خصوص هنگام سوئیچینگ از یک ارائه دهنده به دیگری می باشد. در این فصل ما یک تحقیق تعمیم یافته از اختصاص منابع مبتنی بر توافق، با هدف ایجاد یک سیستم توزیعی با تلورانس (تحمل) خطای انطباقی ارائه می دهیم. برای پروتکل قراردادی، ما ساختار 3 لایه منابه (دستگاه های مجازی و هاست ها) را توصیف و تحلیل کردیم. سپس یک مکانیزم انطباقی برای ایجاد توافق توصیف می شود. روش تخصیص توزیع حجم کار، ناهمگونی منابع، شفافیت، قابلیت تطبیق و همچنین تعمیم آسان آن با ترکیب دیگر الگوریتم های برنامه ریزی را درنظر می گیرد.
1. مقدمه
(رایانش) ابری بسیاری از برنامه های کاربردی مانند ایمیل ها، جریان سازی ویدیو، محیط های کاری آنلاین، اشتراک فایل (به خصوص تصاویر و ویدیوها)، سرویس های دولتی یا اجتماعی آنلاین را پشتیبانی می کنند. حتی بیشتر، کاربران آن از کودکانی که با گوشی والدین خود عکس می گیرند و به طور لحظه ای بر روی برنامه های اجتماعی (رایانش ابری اجتماعی) پست می کنند، تا مهندسانی که از نرم افزارها به منظور کمک در طراحی های خود استفاده می کنند، دربر می گیرد. این امر نیازمند انطباق با تقاضای بسیار گسترده و کار با داده های بزرگ است. به همین دلیل است که داده های پردازش شده در سیستم های ابری چنین اهمیتی را بدست آورده اند. بنابراین، هر کاری را می توان انجام داد و در ابر نگهداری کرد.روش های تخصیص منابع مورد استفاده به منظور پشتیبانی از زمان بندی وظایف برای تضمین توافق نامه سطح خدمات (SLA) حیاتی می باشند. یک الگوریتم تطبیقی با الهام از SLA چندین مزیت در تخصیص و مدیریت منابع دارد، به خصوص وقتی معماری پایه به شدت ناهمگن باشد، مزیت های آن بیشتر نیز خواهدبود.
5. نتیجه گیری
ما یک الگوریتم مبتنی بر توافق را برای ارتقاء فرایند برنامه ریزی وظیفه ارائه کردیم و این فرایند را بسیار انعطاف پذیرتر، شفاف تر و قابل تعمیم ساختیم. الگوریتم تطبیقی، تلورانس (قابلیت تحمل) خطا، با توزیع حجم کار و قابلیت های تعمیم بسیار زیاد می باشد. ما الگوریتم پیشنهادی را با استفاده از CloudSim با تعداد مختلف از گره-ها در هر لایه بررسی کردیم. شواهد نشان می دهد که داشتن گره بیشتر در لایه آخر به جای لایه دوم بهتر می-باشد، و نسبت 6:1 بهترین نتایج را بدست می دهد. برای تحقیق آینده ما چنین پیشنهاد دادیم: تعریف سیاست-های آگاهی هزینه برای توافق و گسترش مذاکرات پروتکل مبتنی بر آن؛ ترکیب گره های لایه 1 با الگوریتم تکاملی به منظور تخصصی سازی گره های لایه 1 بر روی انواع مختلفی از وظایف، تخصصی سازی که هم در گره هایی که توافق را ایجاد می کنند و هم در الگوریتم هایی که از تخصصی سازی برای برنامه ریزی وظیفه پس از آن استفاده می-کنند، مشاهده خواهدشد. همچنین، موافقت ها در سطوح بالاتر استفاده می شوند؛ SLA ها برای چندین مدت وجود داشته اند و مبتنی بر مذاکره می باشند، درحالی که موافقت های کسب وکار برای زمان های به مراتب بیشتری وجود داشته اند.
Abstract
In the last years there has been considerable interest in using distributed systems, especially Cloud Systems, in any domains. Resource management contributes to ensure quality of services for any type of application, especially when a system involves elements of heterogeneity characterized by a variety of resources that may or may not be coupled with specific platforms or environments. A problem very close to the industry is the capability to allocate resources in an efficient way and estimate costs, especially when switching from one provider to another. In this chapter we present an extended work oriented on agreement–based resource allocation and a scheduling algorithm, aimed to bring an adaptive fault tolerant distributed system. For the agreement protocol we describe and analyze a 3-Tier structure of resources (hosts and virtual machines). Then an adaptive mechanism for agreement establishment is described. The allocation method considers workload distribution, resources heterogeneity, transparency, adaptability and also the ease to extend by combining with other scheduling algorithms.
1 Introduction
Cloud supports many type of applications like emails, video–streaming, online working environments, file sharing (especially photos and videos), government services or socializing online. Even more, its users vary from children taking pictures with their parents’ phone and posting them instantly on social apps (Social Cloud) to engineers using software to aid in their designs. This means having to comply with very broad needs and working with big data. That is why data processing in Cloud systems has gained such an importance. So, everything can be done and kept in the Cloud. Resource allocation techniques used to support tasks scheduling become critical for Service Level Agreement (SLA) assurance. An adaptive algorithm inspired from SLA would bring several benefits to resource allocation and management, more so when the underlying architecture is highly heterogeneous.
5 Conclusion
We proposed an agreement based algorithm to enhance the task scheduling process and make it more flexible, transparent and extendible. The algorithm is adaptive, fault tolerant, with workload distribution and large extension capabilities. We tested the proposed algorithm using CloudSim with different numbers of nodes on each Tier. Evidence showed that it is better to have more nodes on the last Tier than on the second, with the 6:1 ratio giving the best results. For future work we propose: defining cost awareness policies for the agreement and extending the (re)negotiation protocol based on that; combining Tier1 nodes with a evolutionary algorithm in order to specialize Tier1 nodes on different types of tasks, specialization that would be seen both in the nodes they establish agreement with and in the algorithm they use to schedule task afterward. Also, agreements are used at higher levels; SLAs have been around for a while now and they are based on negotiation, whereas business agreements have been around for even more time.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. کارهای مرتبط
3. پروتکل های موافق برای تخصیص منابع تطبیقی
3 – 1: مدل سازی و فرمولاسیون
3 – 2: الزامات
3 – 3: طراحی معماری
3 – 4: توافق و پیش نیازها
3 – 5: پروتکل های موافق
3 – 6: تخصیص منابع تطبیقی
3 – 7: تلورانس (تحمل) خطا
4. نتایج تجربی
4 – 1: روش شناسی و سناریو شبیه سازی
4 – 2: سناریوهای تجربی
4 – 3: تحلیل مقایسه ای نتایج تجربی
5. نتیجه گیری
Abstract
1 Introduction
2 Related Work
3 Agreement Protocols for Adaptive Resource Allocation
3.1 Modeling and Formulation
3.2 Requirements
3.3 Architecture Design
3.4 Agreement and Prerequisites
3.5 Agreement Protocols
3.6 Adaptive Resource Allocation
3.7 Fault Tolerance
4 Experimental Results
4.1 Methodology and Simulation Scenario
4.2 Experimental Scenarios
4.3 Comparative Analysis of Experimental Results
5 Conclusion
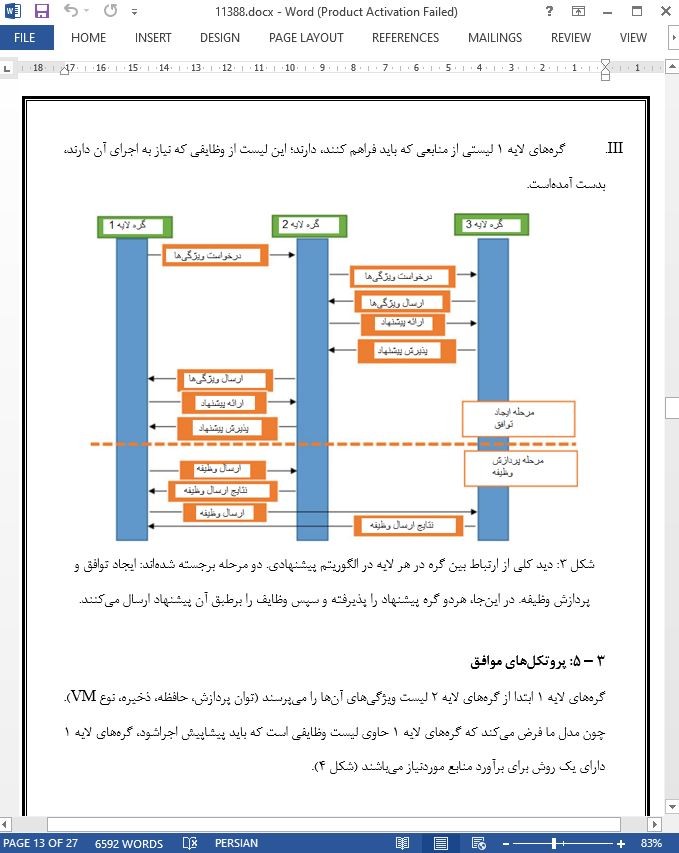
- اصل مقاله انگلیسی با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه