مدلسازی پیرولیز قرص های چوبی راش تحت تابش متمرکز نور خورشید
چکیده
مدل ذره منفرد دوبعدی و ناپایدار CFD (دینامیک سیالات محاسباتی) ارائه و برای شبیهسازی فرایند پیرولیز قرصهای چوبی راش (با قطر 10 میلیمتر و ارتفاع 5 میلیمتر) مورد استفاده قرار گرفته است. ضرایب شبهاستوکیومتری در مورد کسر جرمی تار اولیه که توسط برهمکنشی به گاز و تار ثانویه تبدیل شدهاند برای نخستین بار در دماها و نرخهای گرمایش مختلف تعیین شدهاند. پیشبینیهای مدل دوبعدی با موفقیت با آزمونهای انجام شده در دماهای °C 600 تا دمای نهایی °C 2000 با نرخهای گرمایش 10 و °C/s 50 تایید شدهاند. تکامل محصولات نهایی و اتلاف جرمی زیستتوده پیرولیز شده با دما و نرخ گرمایش، افزایش یافتهاند. بهعلاوه هرچه دما و نرخ گرمایش بالاتر باشند، بازدهی گاز بالاتر خواهد بود. این موضوع بر برهمکنش ثانویه درونذرهای تار به گاز برای پیرولیز نمونهای با اندازه بزرگ تحت دما و نرخ گرمایش بالا تاکید دارد.
1. مقدمه
تولید پایدار گرما و توان از منابع انرژی تجدیدپذیر همچون زیستتوده و جذب انرژی خورشیدی به دلیل کاهش مستمر سوختهای فسیلی و تشدید مسائل زیستمحیطی، توجه بسیاری را به خود معطوف داشته است. انتظار میرود بین سالهای 2010 و 2040، پیشرفت قابل ملاحظهای در تولید انرژی تجدیدپذیر از زیستتوده (از 4/45217 تا PJ 2/136950) و از خورشید (از 2/184 تا PJ 2/55768) حاصل گردد [1].
5. نتیجهگیری
ویژگیهای پیرولیز خورشیدی چوب راش تحت دماها و نرخهای گرمایش مختلف به صورت نظری به وسیله مدلسازی CFD مورد بررسی قرار گرفته و نتایج شبیهسازی با دادههای تجربی بدست آمده با یک کوره خورشیدی عمودی kW 2 مقایسه شدهاند. پیشبینیهای مدل عددی ناپایدار دوبعدی با نتایج تجربی در توافق خوبی میباشند. تغییر شکل (تکامل) محصولات نهایی و تلفات جرمی زیستتوده پیرولیز شده با افزایش دما و نرخ گرمایش، افزایش مییابند. بهعلاوه هرچه دما و نرخ گرمایش بالاتر باشند، بازدهی گاز بالاتر خواهد بود. این موضوع بر واکنش ثانویه درونذرهای تار درون گاز برای پیرولیز نمونه با اندازه بزرگ تحت دما و نرخ گرمایش بالا تاکید دارد. ضرایب شبهاستوکیومتری موجود درباره کسر جرمی تار اولیه تبدیل شده به وسیله واکنش به گاز و تار ثانویه در دماها و نرخهای گرمایش مختلف برای نخستین بار تعیین شدهاند.
Abstract
A two-dimensional, unsteady CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) single particle model was developed and used to simulate the solar pyrolysis process of beech wood pellets (10 mm in diameter and 5 mm in height). Pseudo-stoichiometric coefficients about the mass fraction of primary tar converted by the reaction into gas and secondary tar were determined at different temperatures and heating rates for the first time. The 2D model predictions were successfully validated with tests performed at 600 °C to 2000 °C final temperature, with 10 and 50 °C/s heating rates. The evolution of the final products and mass losses of pyrolyzed biomass are enhanced with temperature and heating rate. Moreover, the higher the temperature and heating rate, the higher the gas yield. This emphasizes the intra-particle tar secondary reaction into gas for pyrolysis of large size sample under high temperature and heating rate.
1. Introduction
Sustainable heat and power generation from renewable energy sources such as biomass and solar attract more and more attention owing to the continuous diminution of fossil fuels and the intensifying environmental problems. Between 2010 and 2040 significant developments in renewable energy production are expected in biomass energy (from 45217.4 to 136950.2 PJ) and solar energy (from 184.2 to 55768.2 PJ) [1].
5. Conclusions
Solar pyrolysis characteristics of beech wood under different temperatures and heating rates were investigated theoretically by CFD modeling, and simulation results were compared with experimental data obtained with a 2 kW vertical solar furnace. The 2D unsteady numerical model predictions are in good agreement with the experimental results. The evolution of the final products and mass losses of pyrolyzed biomass are enhanced with temperature and heating rate. Moreover, the higher the temperature and heating rate, the higher the gas yield. This emphasizes the intra-particle tar secondary reaction into gas for pyrolysis of large size sample under high temperature and heating rate. Pseudo-stoichiometric coefficients about the mass fraction of primary tar converted by the reaction to gas and secondary tar were determined at different temperatures and heating rates for the first time.
چکیده
1. مقدمه
2. بخش تجربی
3. مدل عددی
3. 1. الگوی سینتیک پیشنهادی
3. 2. فرضیات اصلی
3. 3. معادلات حاکم
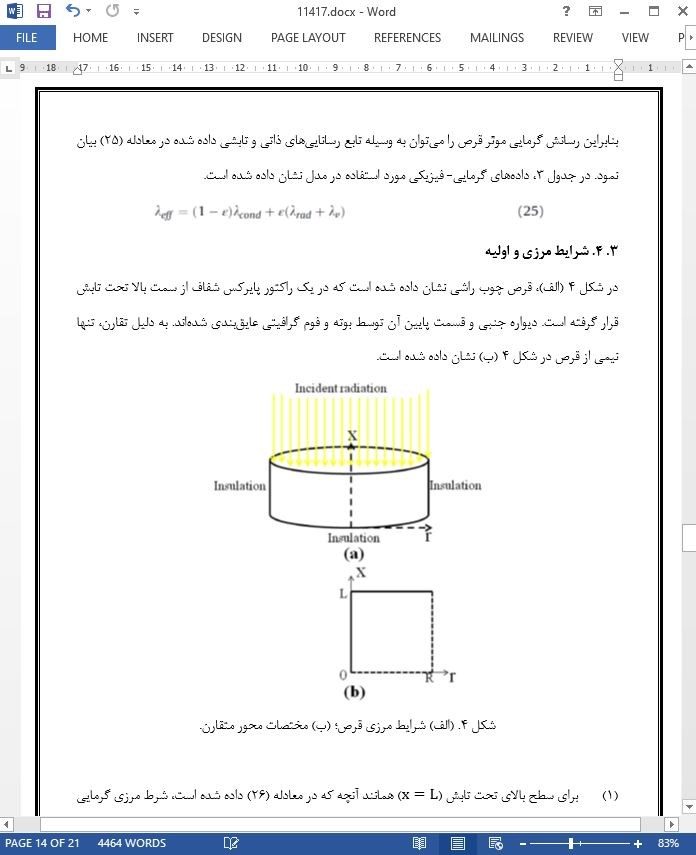
3. 4. شرایط مرزی و اولیه
3. 5. راهحل عددی
4. نتایج و بحث
4. 1. تاثیر دما و نرخ گرمایش بر توزیع محصول
4. 2. تاثیر دما و نرخ گرمایش بر تاریخچه اتلاف وزن
4. 3. تاثیر دما و نرخ گرمایش بر تغییرشکل گازها
5. نتیجهگیری
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
3. Numerical model
3.1. Proposed kinetic scheme
3.2. Main assumptions
3.3. Governing equations
3.4. Boundary and initial conditions
3.5. Numerical solution
4. Results and discussion
4.1. Influence of temperature and heating rate on the product distribution
4.2. Influence of temperature and heating rate on the weight loss history
4.3. Influence of temperature and heating rate on gases evolution
5. Conclusions
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت ورد (word) با قابلیت ویرایش، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه
- ترجمه فارسی مقاله با فرمت pdf، بدون آرم سایت ای ترجمه